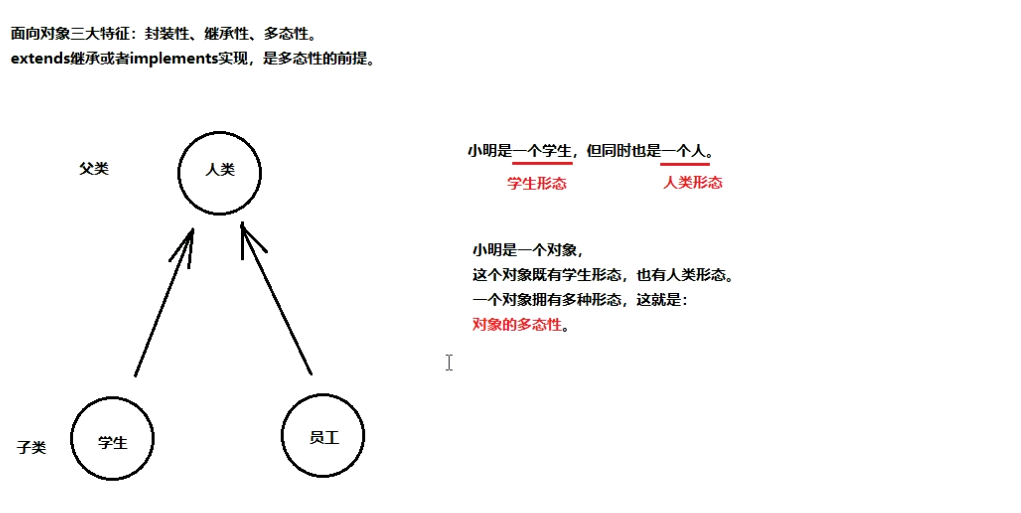
多态图解
代码中体现多态性
父类名称 对象名 = new 子类名称();
or
接口名称 对象名 = new 实现类名称();
// 父类 public class Father { public void method(){ System.out.println("parent class method call"); } public void methodFather(){ System.out.println("parent class specific method"); // 父类特有方法 } } // 子类 public class Son extends Father{ @Override public void method(){ System.out.println("sub class method call"); } } public class DemoMulti{ public static void main(String[] args){ // 使用多态写法,左侧父类的引用,指向了右侧子类的对象(类似于一只狗被当做了一只动物) Father son = new Son(); son.method(); // sub class method call son.methodFather(); // parent class specific method } }
访问成员变量的两种方式:
-
直接通过对象名称访问成员变量:看等号左边是谁,优先用谁,没有则向上找
-
间接通过成员方法访问成员变量:看该方法属于谁,优先用谁,没有则向上找
指的是 Father f = new Son(); 中的等号
口诀:编译看右边,运行还看右边 (成员变量的话, 运行是看左边?)
// 父类 public class Father { String name = "Father"; public String showName() { return this.name; } } // 子类 public class Son extends Father{ String name = "Son"; int age = 20; @Override public String showName() { return this.name; } } public class DemoMulti{ public static void main(String[] args){ // 使用多态写法,左侧父类的引用,指向了右侧子类的对象(类似于一只狗被当做了一只动物) Father f = new Son(); System.out.println(f.name); // Father // System.out.println(son.age); // 错误写法 // 子类没有覆盖重写,就是父:Father // 子类有覆盖重写,就是子:Son System.out.println(f.showName()); // Son } }
看 new 的是谁,就优先用谁,没有则向上找
口诀:编译看左边,运行看右边
// 父类 public class Father { public void method(){ System.out.println("parent class method call"); } public void methodFather(){ System.out.println("parent class specific method"); // 父类特有方法 } } // 子类 public class Son extends Father{ @Override public void method(){ System.out.println("sub class method call"); } public void methodSon(){ System.out.println("son class specific method"); // 子类特有方法 } } public class DemoMulti{ public static void main(String[] args){ Father f = new Son(); // 多态 f.method(); // 父子都有,优先用子 f.emthodFather(); // 子类没有,父类有,向上找到父类 // f.methodSon(); // 错误写法 } }
对象转型图解
public abstract class Animal { public abstract void eat(); } public class Cat extends Animal{ @Override public void eat(){ System.out.println("cat eat fish"); } } public class DemoTransition { public static void main(String[] args) { // 向上转型,就是父类引用 指向 子类对象 Animal cat = new Cat(); cat.eat(); // cat eat fish } }
向上转型有一个弊端:对象一旦向上转型为父类,那么就无法调用子类原本特有的内容
public abstract class Animal { public abstract void eat(); } public class Cat extends Animal{ @Override public void eat(){ System.out.println("cat eat fish"); } public void catchMouse(){ System.out.println("cat catches mouse"); } } public class DemoTransition { public static void main(String[] args) { // 对象的向上转型,就是父类引用 指向 子类对象 Animal cat = new Cat(); cat.eat(); // cat eat fish // cat.catchMouse(); // 错误写法 // 向下转型,进行还原 Cat transitionCat = (Cat) cat; transitionCat.catchMouse(); // cat catches mouse } }
用 instanceof 关键字进行类型判断(为了避免向下转型异常:ClassCastException)
if (cat instanceof Cat){ Cat transitionCat = (Cat) cat; }
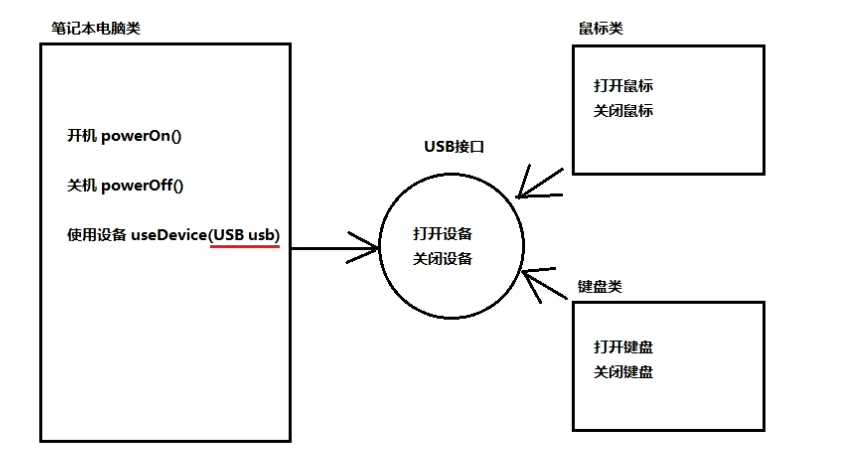
// 定义 USB 接口
public interface USB { void enable(); void disable(); }
// 鼠标实现类
// 鼠标是一种 USB 设备 public class Mouse implements USB { String name = "mouse"; @Override public void enable() { System.out.println("enable " + this.name); } @Override public void disable() { System.out.println("disable " + this.name); } public void click(){ System.out.println("click on the event"); } }
// 键盘实现类
// 键盘也是一种 USB 设备 public class KeyBoard implements USB { String name = "key board"; @Override public void enable() { System.out.println("enable " + this.name); } @Override public void disable() { System.out.println("disable " + this.name); } public void tap(){ System.out.println("tap on a event"); } }
// 电脑类
public class MacBookPro { public void powerOn() { System.out.println("powerOn"); } public void powerOff() { System.out.println("powerOff"); } // 使用 USB 设备的方法,使用接口作为方法的参数 public void useDevice(USB usb) { usb.enable(); if (usb instanceof Mouse){ // 向下转型 Mouse mouse = (Mouse) usb; mouse.click(); } else if (usb instanceof KeyBoard){ KeyBoard keyBoard = (KeyBoard) usb; keyBoard.tap(); } usb.disable(); } }
// main()
public class DemoCase { public static void main(String[] args) { MacBookPro book = new MacBookPro(); USB mouse = new Mouse(); // 多态写法,向上转型 KeyBoard keyBoard = new KeyBoard(); // 自动发生了向上转型 book.powerOn(); // powerOn book.useDevice(mouse); // enable mouse, click on the event, disable mouse // 也可以直接传匿名对象 new KeyBoard() book.useDevice(keyBoard); // enable key board, tap on a event, disable key board book.powerOff(); // powerOff } }
# 参考廖雪峰教程
Java的方法调用总是作用于运行期对象的实际类型,这种行为称为多态;
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // 给一个有普通收入、工资收入和享受国务院特殊津贴的小伙伴算税: Income[] incomes = new Income[] { new Income(3000), new Salary(7500), new StateCouncilSpecialAllowance(15000) }; System.out.println(totalTax(incomes)); } public static double totalTax(Income... incomes) { double total = 0; for (Income income: incomes) { total = total + income.getTax(); } return total; } } class Income { protected double income; public Income(double income) { this.income = income; } public double getTax() { return income * 0.1; // 税率10% } } class Salary extends Income { public Salary(double income) { super(income); } @Override public double getTax() { if (income <= 5000) { return 0; } return (income - 5000) * 0.2; } } class StateCouncilSpecialAllowance extends Income { public StateCouncilSpecialAllowance(double income) { super(income); } @Override public double getTax() { return 0; } }
ending ~
