原理
先看个例子,存储字符串abc、ab、abm、abcde、pm可以利用以下方式存储
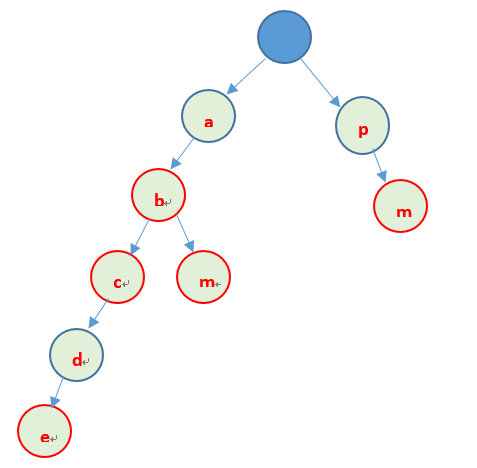
上边就是Trie树的基本原理:利用字串的公共前缀来节省存储空间,最大限度的减少无谓的字串比较。
应用
Trie树又称单词查找树,典型的应用是用于统计,排序和保存大量的字符串(不仅用于字符串),所以经常被搜索引擎系统用于文本词频的统计。
设计
trie,又称前缀树或字典树,是一种有序树,用于保存关联数组,其中的键通常是字符串。与二叉查找树不同,键不是直接保存在节点中,而是由节点在树中的位置决定。一个节点的所有子孙都有相同的前缀,也就是这个节点对应的字符串,而根节点对应空字符串。一般情况下,不是所有的节点都有对应的值,只有叶子节点和部分内部节点所对应的键才有相关的值。
结点可以设计成这样:
class trieNode { public: trieNode() : terminableSize(0), nodeSize(0) { for(int i = 0; i < Size; ++i) children[i] = NULL; } ~trieNode() { for(int i = 0; i < Size; ++i) { delete children[i]; children[i] = NULL; } } public: int terminableSize; //存储以此结点为结尾的字串的个数 int nodeSize; //记录此结点孩子的个数 trieNode* children[Size]; //该数组记录指向孩子的指针 };
图示
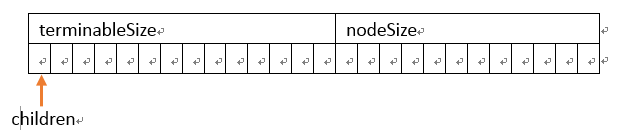
树设计成这样:
template<int Size, class Type> class trie { public: typedef trieNode<Size> Node; typedef trieNode<Size>* pNode; trie() : root(new Node) {} template<class Iterator> void insert(Iterator beg, Iterator end); void insert(const char *str); template<class Iterator> bool find(Iterator beg, Iterator end); bool find(const char *str); template<class Iterator> bool downNodeAlone(Iterator beg); template<class Iterator> bool erase(Iterator beg, Iterator end); bool erase(const char *str); int sizeAll(pNode); int sizeNoneRedundant(pNode); public: pNode root; private: Type index; };
index字串索引利用(char % 26) 得到,这样'a' % 26 = 19, 'b' % 26 = 20
实现
插入
以插入abc、ab为例
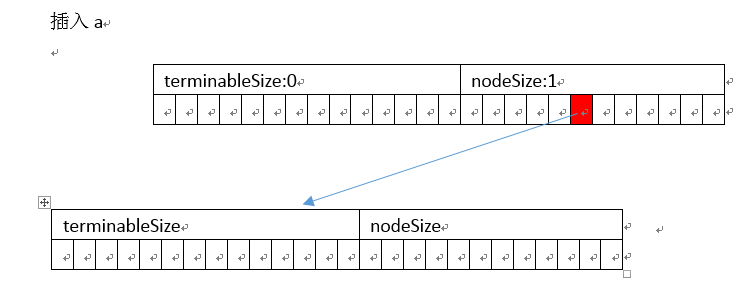 ]
]
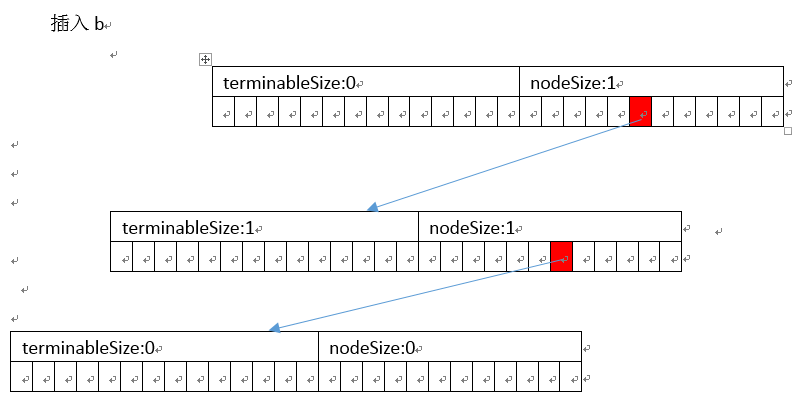
删除
删除结点,首先查找此字串是否在树中,如果在树中,再查找此结点以下的部分是不是都是只有一个孩子,并且每个结点只有叶子结点是结束结点,如果不是继续往下重复上边过程。
统计字串个数
分两种情况
- 计算重复的字串的个数:是结束结点,此时加的是terminabel的个数
- 计算不重复的字串的个数:是结束结点,此时加的是1(当terminabel>0)的个数
参考代码
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> using namespace std; template<int Size> class trieNode { public: trieNode() : terminableSize(0), nodeSize(0) { for(int i = 0; i < Size; ++i) children[i] = NULL; } ~trieNode() { for(int i = 0; i < Size; ++i) { delete children[i]; children[i] = NULL; } } public: int terminableSize; int nodeSize; trieNode* children[Size]; }; template<int Size, class Type> class trie { public: typedef trieNode<Size> Node; typedef trieNode<Size>* pNode; trie() : root(new Node) {} template<class Iterator> void insert(Iterator beg, Iterator end); void insert(const char *str); template<class Iterator> bool find(Iterator beg, Iterator end); bool find(const char *str); template<class Iterator> bool downNodeAlone(Iterator beg); template<class Iterator> bool erase(Iterator beg, Iterator end); bool erase(const char *str); int sizeAll(pNode); int sizeNoneRedundant(pNode); public: pNode root; private: Type index; }; template<int Size, class Type> template<class Iterator> void trie<Size, Type>::insert(Iterator beg, Iterator end) { pNode cur = root; pNode pre; for(; beg != end; ++beg) { if(!cur->children[index[*beg]]) { cur->children[index[*beg]] = new(Node); ++cur->nodeSize; } pre = cur; cur = cur->children[index[*beg]]; } ++pre->terminableSize; } template<int Size, class Type> void trie<Size, Type>::insert(const char *str) { return insert(str, str + strlen(str)); } template<int Size, class Type> template<class Iterator> bool trie<Size, Type>::find(Iterator beg, Iterator end) { pNode cur = root; pNode pre; for(; beg != end; ++beg) { if(!cur->children[index[*beg]]) { return false; break; } pre = cur; cur = cur->children[index[*beg]]; } if(pre->terminableSize > 0) return true; return false; } template<int Size, class Type> bool trie<Size, Type>::find(const char *str) { return find(str, str + strlen(str)); } template<int Size, class Type> template<class Iterator> bool trie<Size, Type>::downNodeAlone(Iterator beg) { pNode cur = root; int terminableSum = 0; while(cur->nodeSize != 0) { terminableSum += cur->terminableSize; if(cur->nodeSize > 1) return false; else //cur->nodeSize = 1 { for(int i = 0; i < Size; ++i) { if(cur->children[i]) cur = cur->children[i]; } } } if(terminableSum == 1) return true; return false; } template<int Size, class Type> template<class Iterator> bool trie<Size, Type>::erase(Iterator beg, Iterator end) { if(find(beg, end)) { pNode cur = root; pNode pre; for(; beg != end; ++beg) { if(downNodeAlone(cur)) { delete cur; return true; } pre = cur; cur = cur->children[index[*beg]]; } if(pre->terminableSize > 0) --pre->terminableSize; return true; } return false; } template<int Size, class Type> bool trie<Size, Type>::erase(const char *str) { if(find(str)) { erase(str, str + strlen(str)); return true; } return false; } template<int Size, class Type> int trie<Size, Type>::sizeAll(pNode ptr) { if(ptr == NULL) return 0; int rev = ptr->terminableSize; for(int i = 0; i < Size; ++i) rev += sizeAll(ptr->children[i]); return rev; } template<int Size, class Type> int trie<Size, Type>::sizeNoneRedundant(pNode ptr) { if(ptr == NULL) return 0; int rev = 0; if(ptr->terminableSize > 0) rev = 1; if(ptr->nodeSize != 0) { for(int i = 0; i < Size; ++i) rev += sizeNoneRedundant(ptr->children[i]); } return rev; } template<int Size> class Index { public: int operator[](char vchar) { return vchar % Size; } }; int main() { trie<26, Index<26> > t; t.insert("hello"); t.insert("hello"); t.insert("h"); t.insert("h"); t.insert("he"); t.insert("hel"); cout << "SizeALL:" << t.sizeAll(t.root) << endl; cout << "SizeALL:" << t.sizeNoneRedundant(t.root) << endl; t.erase("h"); cout << "SizeALL:" << t.sizeAll(t.root) << endl; cout << "SizeALL:" << t.sizeNoneRedundant(t.root) << endl; }
结果

技术实现细节
1. 对树的删除,并不是树销毁结点,而是通过结点自身的析构函数实现
2. 模版类、模版函数、非类型模版可以参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/kaituorensheng/p/3601495.html
3. 字母的存储并不是存储的字母,而是存储的位置,如果该位置的指针为空,则说明此处没有字母;反之有字母。
4. terminableNum存储以此结点为结束结点的个数,这样可以避免删除时,不知道是否有多个相同字符串的情况。