一、概述
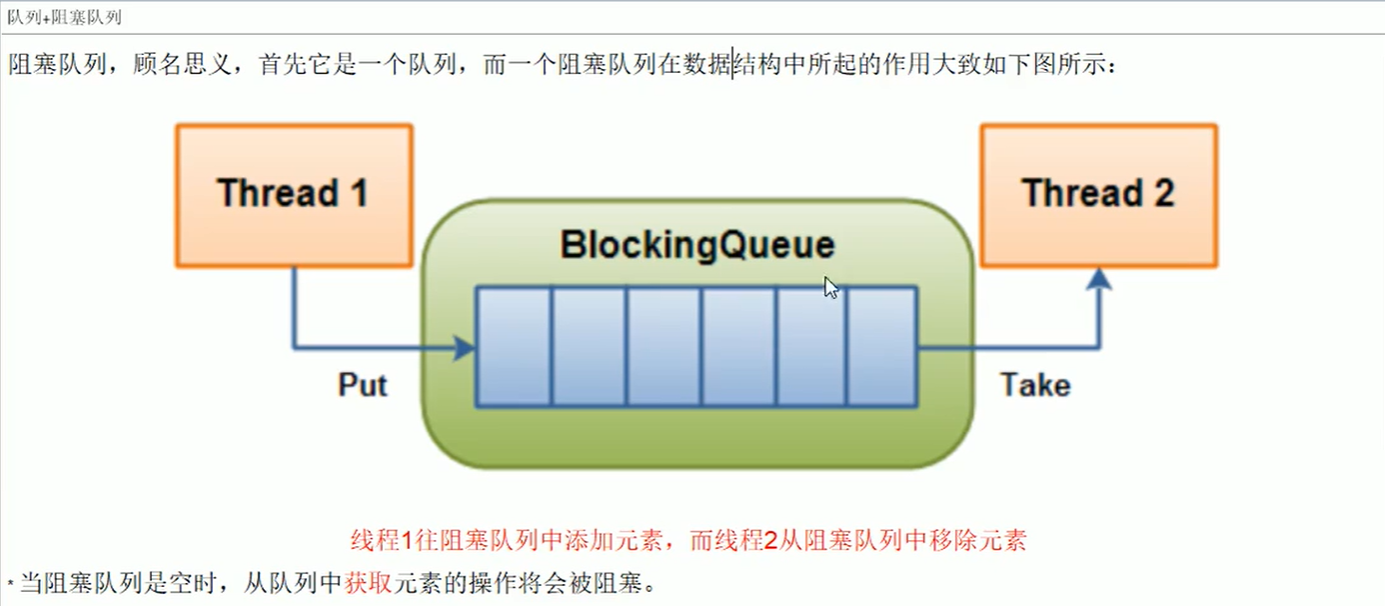


二、为什么用,有什么好处


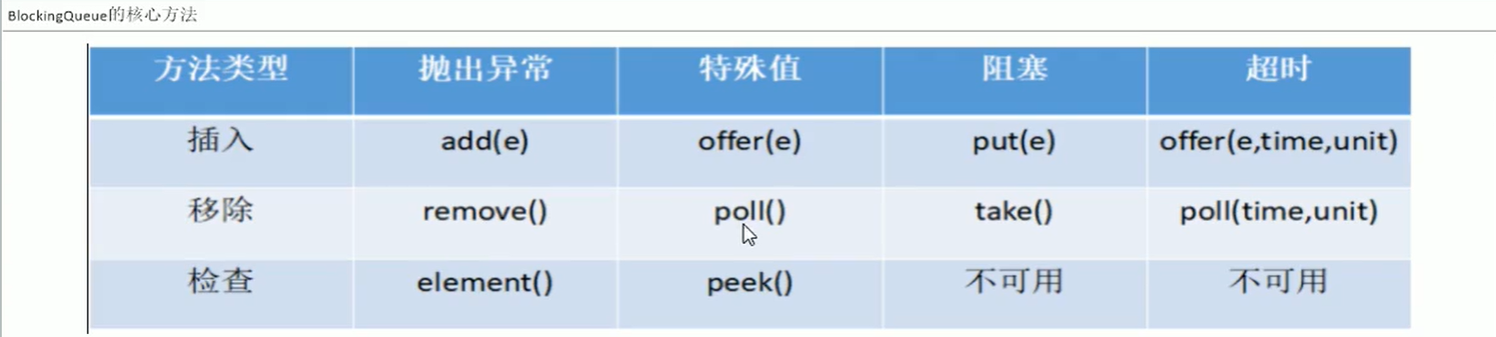
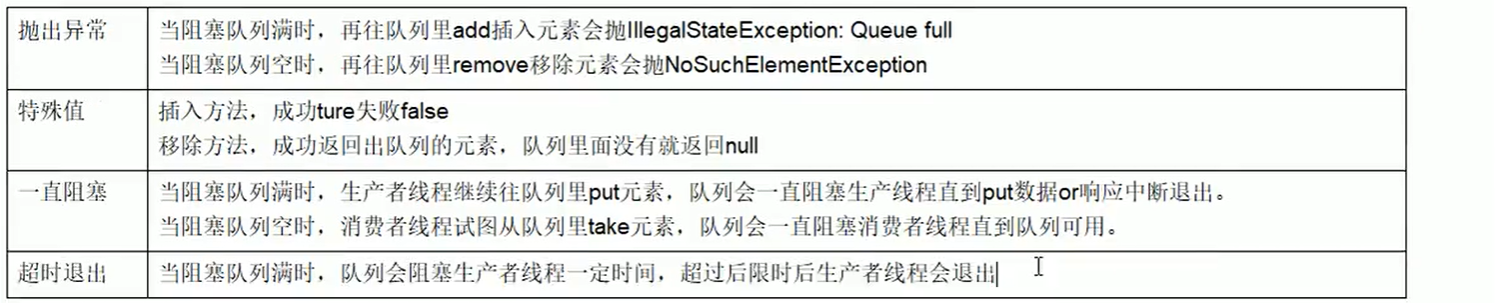
三、BlockingQueue的核心方法
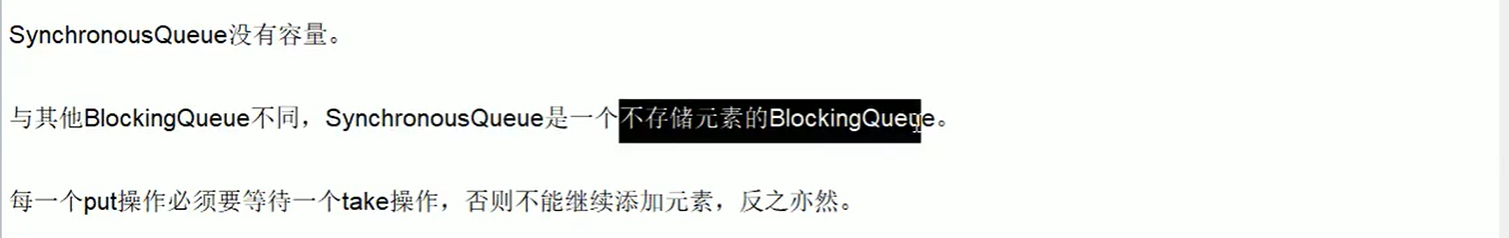
四、SynchronousQueue队列
理论
实操
public class SynchronousQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new SynchronousQueue<>();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " put 1");
blockingQueue.put("1");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " put 2");
blockingQueue.put("2");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " put 3");
blockingQueue.put("3");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"线程1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " get " + blockingQueue.take());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " get " + blockingQueue.take());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " get " + blockingQueue.take());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"线程2").start();
}
}
首先put1,因为该队列只能存放一个元素,所以后边的put2和put3只能等待;5s后,take1,取出元素,队列为空,然后put2,以此类推。
- 输出:
线程1 put 1
线程2 get 1
线程1 put 2
线程2 get 2
线程1 put 3
线程2 get 3
五、线程通信之生产者与消费者
传统版
/**
* TODO 一个初始值为0的变量,两个线程对其交替操作,一个加1,一个减1,来五轮。
*
* @author kakaluote
* @date 2021年6月30日 下午4:23:33
*
* 1、线程 操纵 资源类
* 2、判断 干活 唤醒通知
* 3、严防多线程下的虚假唤醒
*
* 深 透 明 细
*/
public class ProConsu_TraditionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShareData shareData = new ShareData();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
try {
shareData.increment();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
},"线程1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
try {
shareData.decrement();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
},"线程2").start();
}
}
//资源类
class ShareData{
private int number = 0;
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
public void increment() throws Exception{
lock.lock();
try{
//1 判断
while(number != 0){
//等待,不能生产
condition.await();
}
//2、干活
number ++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 生产 " + number);
//3、通知唤醒
condition.signalAll();
}catch(Exception e){
}finally{
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void decrement() throws Exception{
lock.lock();
try{
//1 判断
while(number == 0){
//等待,不能消费
condition.await();
}
//2、干活
number --;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 消费 " + number);
//3、通知唤醒
condition.signalAll();
}catch(Exception e){
}finally{
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
输出
线程1 生产 1
线程2 消费 0
线程1 生产 1
线程2 消费 0
线程1 生产 1
线程2 消费 0
线程1 生产 1
线程2 消费 0
线程1 生产 1
线程2 消费 0
阻塞队列版
public class ProdConsumer_BlockQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyResource myResource = new MyResource(new ArrayBlockingQueue<String>(10));
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 启动成功");
try {
myResource.myProd();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"生产者").start();
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 启动成功");
System.out.println();
try {
myResource.myConsumer();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"消费者").start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("5s时间到,大老板" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "叫停,活动结束");
myResource.stop();
}
}
class MyResource{
private volatile boolean FLAG = true;//默认开启,进行生产+消费
private AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger();
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = null;
public MyResource(BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue) {
this.blockingQueue = blockingQueue;
System.out.println(blockingQueue.getClass().getName());
}
public void myProd() throws Exception{
String data = null;
boolean retValue;
while(FLAG) {
//++i
data = atomicInteger.incrementAndGet() + "";
retValue = blockingQueue.offer(data,2L,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if(retValue) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 插入队列" + data + "成功!");
}else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 插入队列" + data + "失败!");
}
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 大老板说:FLAG=false,生产结束!");
}
public void myConsumer()throws Exception{
String result = null;
while(FLAG) {
result = blockingQueue.poll(2L,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if(null == result || result.equalsIgnoreCase("")) {
FLAG = false;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 超过2s没有取到,消费退出。");
return;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 消费队列" + result + "成功!");
}
}
public void stop(){
this.FLAG = false;
}
}
输出:
java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue
生产者 启动成功
消费者 启动成功
生产者 插入队列1成功!
消费者 消费队列1成功!
生产者 插入队列2成功!
消费者 消费队列2成功!
生产者 插入队列3成功!
消费者 消费队列3成功!
生产者 插入队列4成功!
消费者 消费队列4成功!
生产者 插入队列5成功!
消费者 消费队列5成功!
5s时间到,大老板main叫停,活动结束
生产者 大老板说:FLAG=false,生产结束!
消费者 超过2s没有取到,消费退出。
六、synchronized和lock的区别

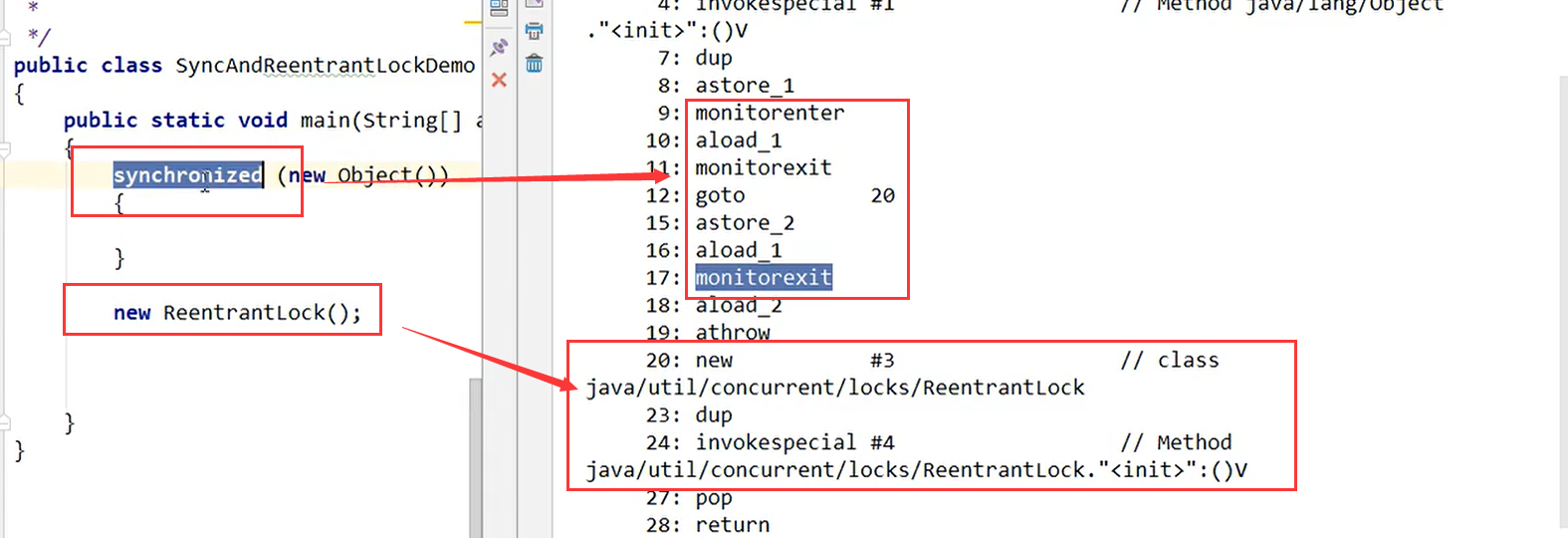



/**
* TODO 多线程之间按顺序调用,实现A->B->C三个线程启动,要求如下:
* AA打印5次,BB打印10次,CC打印15次
* 紧接着
* AA打印5次,BB打印10次,CC打印15次
* ...
* 来10轮
* @author kakaluote
* @date 2021年7月1日 上午10:52:33
*/
public class SyncAndReentrantLockDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShareResource shareResource = new ShareResource();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
shareResource.print5();
}
},"线程A").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
shareResource.print10();
}
},"线程B").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
shareResource.print15();
}
},"线程C").start();
}
}
class ShareResource{
private int number = 1;//a,1;b,2;c,3
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition c1 = lock.newCondition();
private Condition c2 = lock.newCondition();
private Condition c3 = lock.newCondition();
public void print5(){
lock.lock();
try{
while(number != 1){
c1.await();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + i);
}
number = 2;
c2.signal();
}catch(Exception e){
}finally{
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void print10(){
lock.lock();
try{
while(number != 2){
c2.await();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + i);
}
number = 3;
c3.signal();
}catch(Exception e){
}finally{
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void print15(){
lock.lock();
try{
while(number != 3){
c3.await();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 15; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + i);
}
number = 1;
c1.signal();
}catch(Exception e){
}finally{
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
七、Callable接口
demo (创建线程的第三种方式)
public class CallableDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//同一个FutureTask,多个线程同时启动,call方法只会执行一次
FutureTask<Integer> task = new FutureTask<Integer>(new MyThread());
new Thread(task,"AAA").start();
new Thread(task,"BBB").start();
//可以通过此方式判断任务是否执行完
while(task.isDone()){
}
try {
//get每次最好放在最后,因为他会阻塞后边的线程
Integer integer = task.get();
System.out.println(integer);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class MyThread implements Callable<Integer>{
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " :Callable");
return 777;
}
}
八、线程池
为什么用?优势?

线程池如何使用?
架构说明

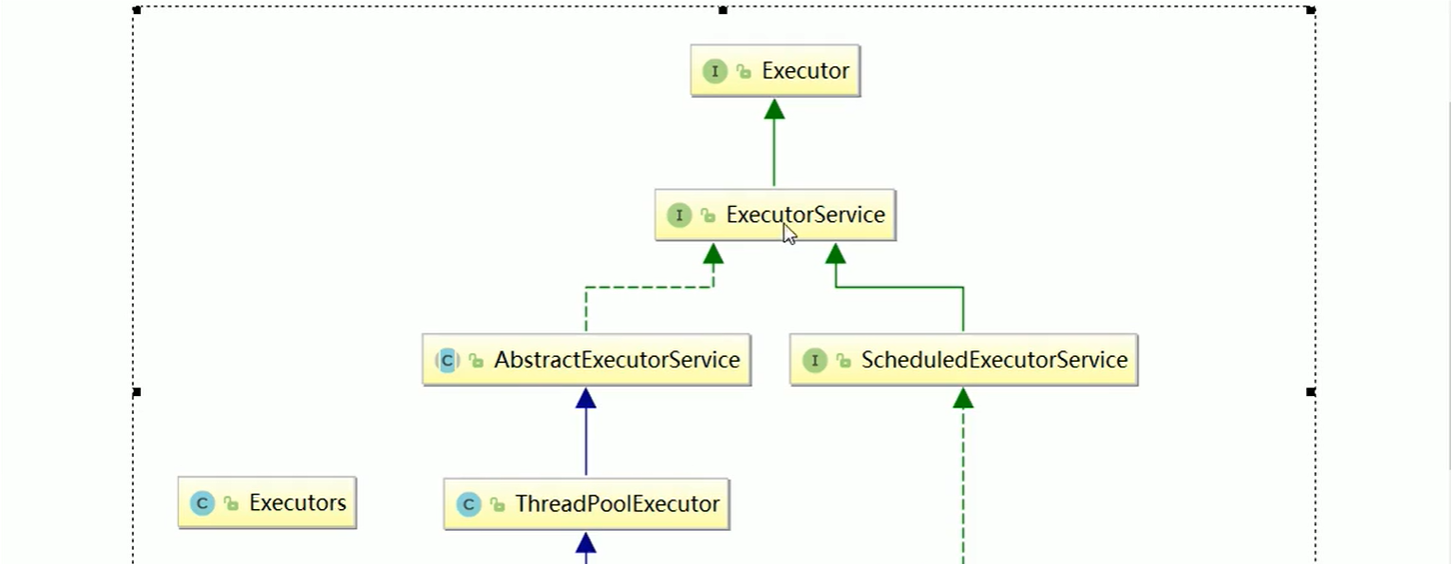

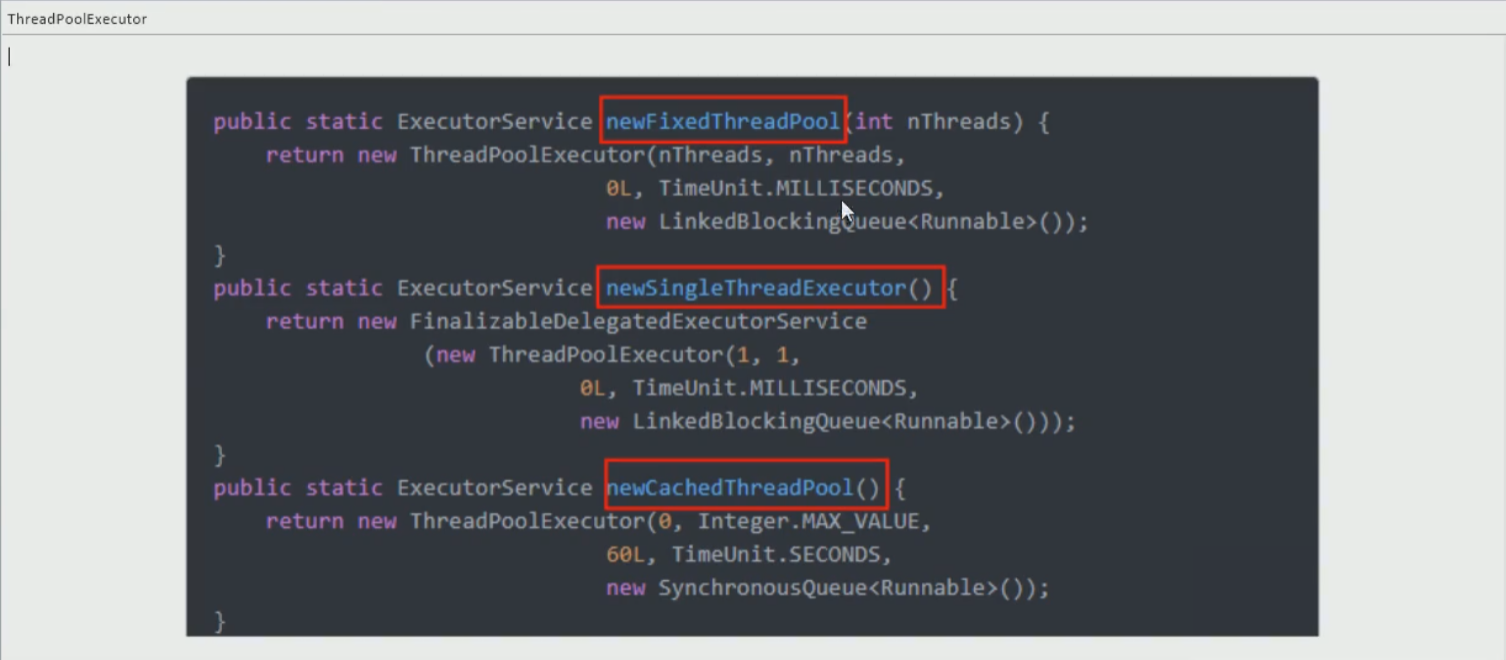
编码实现(三大常用线程池)
- Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5)
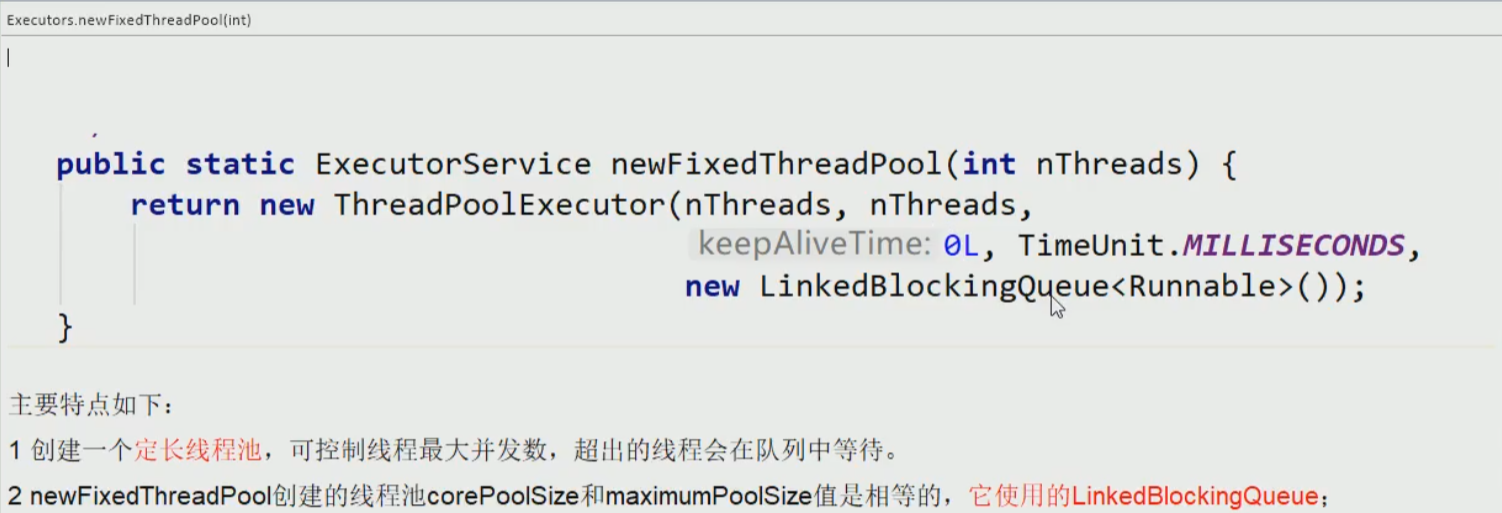
//模拟银行的五个窗口(1池五个处理线程)
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
try {
//模拟10个用户来办理业务,每个用户就是一个来自外部的请求线程
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
threadPool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 办理业务");
});
}
}catch(Exception e) {
}finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
输出:
pool-1-thread-1 办理业务
pool-1-thread-4 办理业务
pool-1-thread-3 办理业务
pool-1-thread-2 办理业务
pool-1-thread-3 办理业务
pool-1-thread-4 办理业务
pool-1-thread-1 办理业务
pool-1-thread-5 办理业务
pool-1-thread-2 办理业务
- Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor()
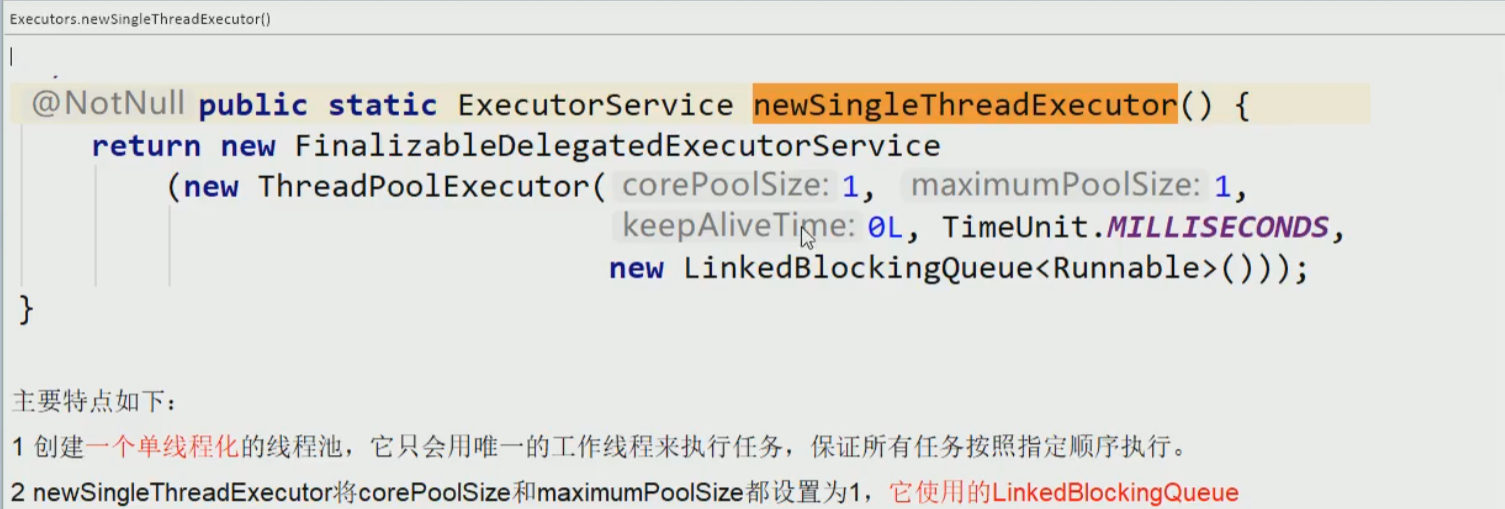
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
try {
//模拟10个用户来办理业务,每个用户就是一个来自外部的请求线程
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
threadPool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 办理业务");
});
}
}catch(Exception e) {
}finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
输出:
pool-1-thread-1 办理业务
pool-1-thread-1 办理业务
pool-1-thread-1 办理业务
pool-1-thread-1 办理业务
pool-1-thread-1 办理业务
pool-1-thread-1 办理业务
pool-1-thread-1 办理业务
pool-1-thread-1 办理业务
pool-1-thread-1 办理业务
- Executors.newCachedThreadPool()
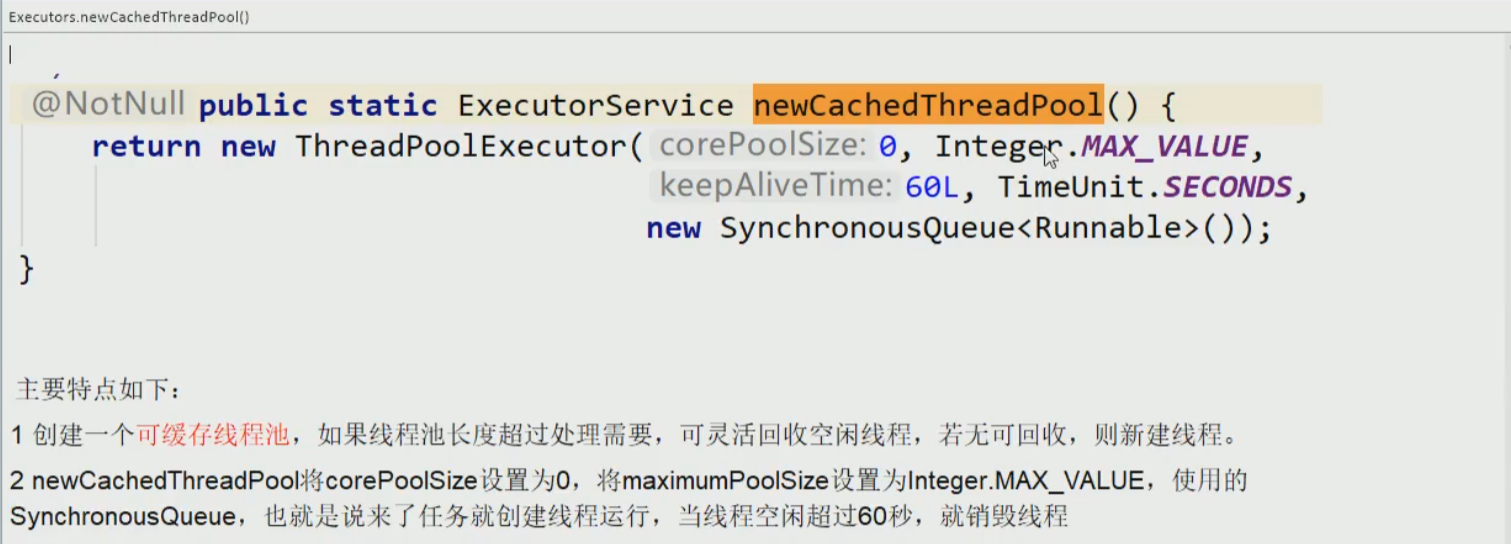
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
try {
//模拟10个用户来办理业务,每个用户就是一个来自外部的请求线程
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
threadPool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 办理业务");
});
}
}catch(Exception e) {
}finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
输出:
pool-1-thread-3 办理业务
pool-1-thread-6 办理业务
pool-1-thread-1 办理业务
pool-1-thread-4 办理业务
pool-1-thread-2 办理业务
pool-1-thread-7 办理业务
pool-1-thread-5 办理业务
pool-1-thread-8 办理业务
pool-1-thread-9 办理业务
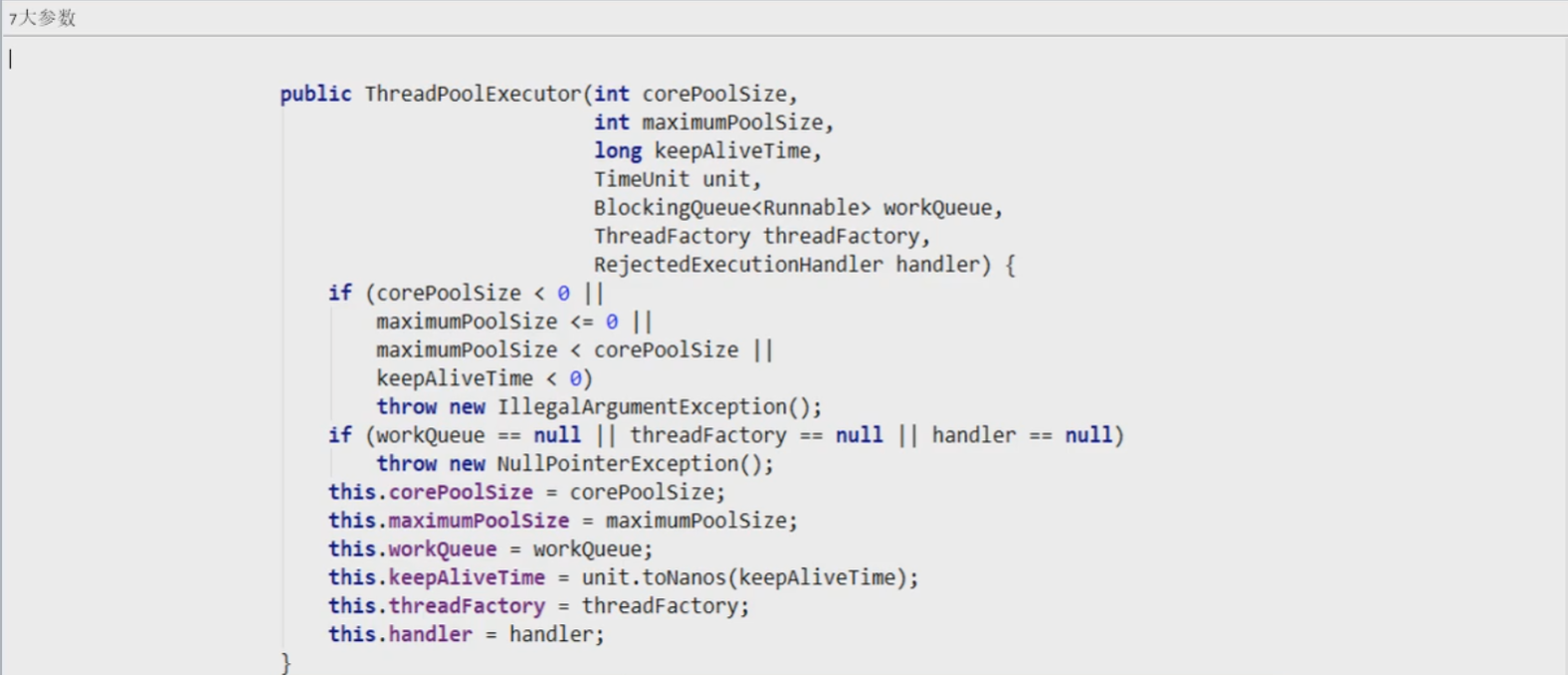
线程池的重要参数介绍(7大参数)
7大参数
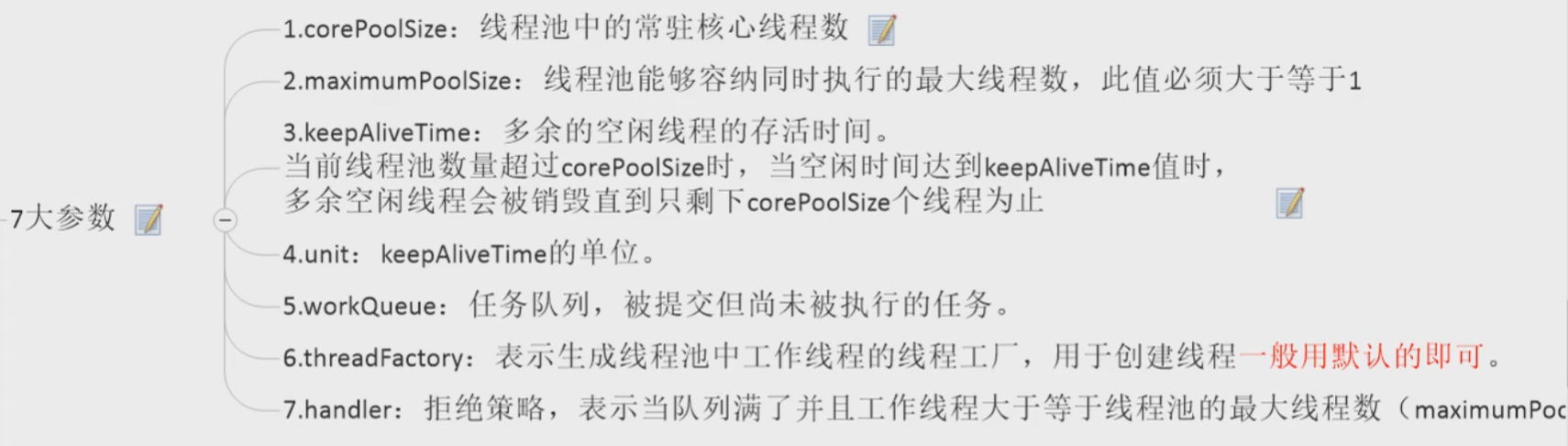

- corePoolSize
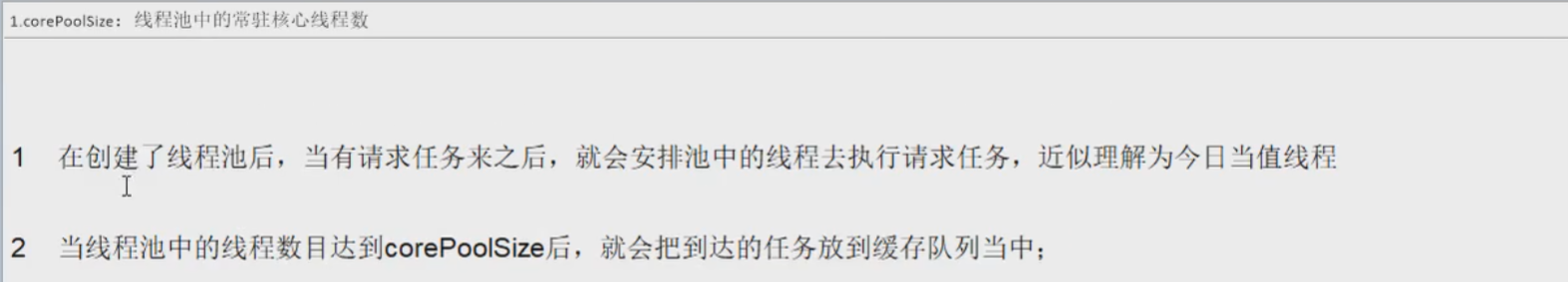
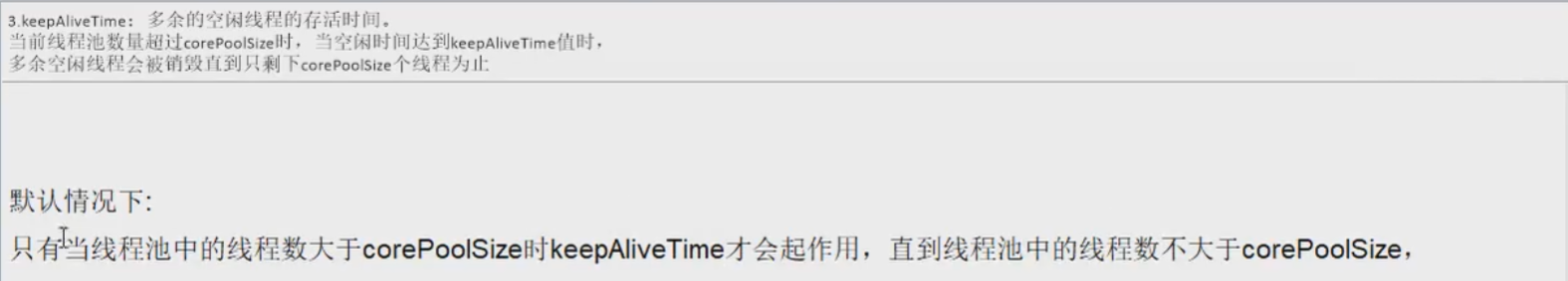
- keepAliveTime
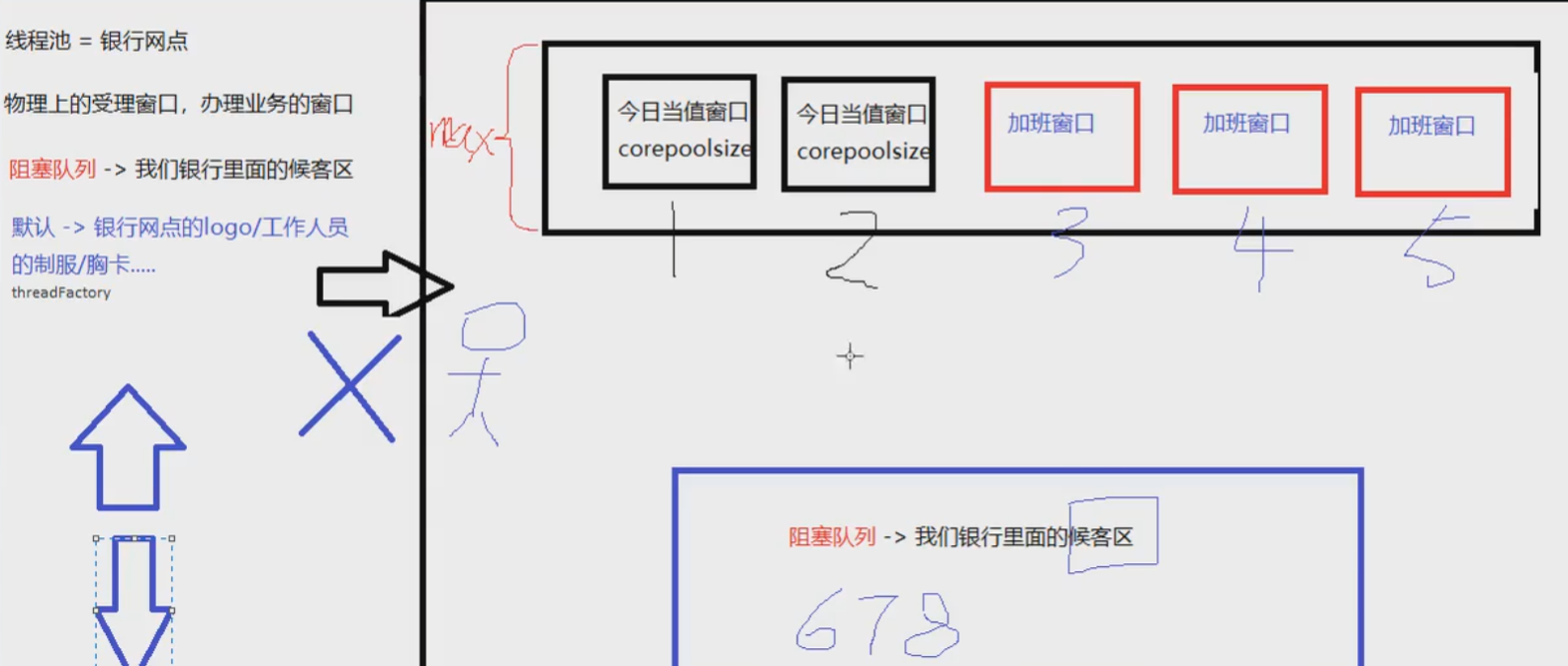
线程池的底层工作原理


生产上合理设置线程池参数
线程池的拒绝策略
- 是什么

- JDK内置的拒绝策略




- 四种拒绝策略都实现了 RejectedExecutionHandler
不能用固定,单个,可缓存的线程池创建


工作中使用线程池,自定义
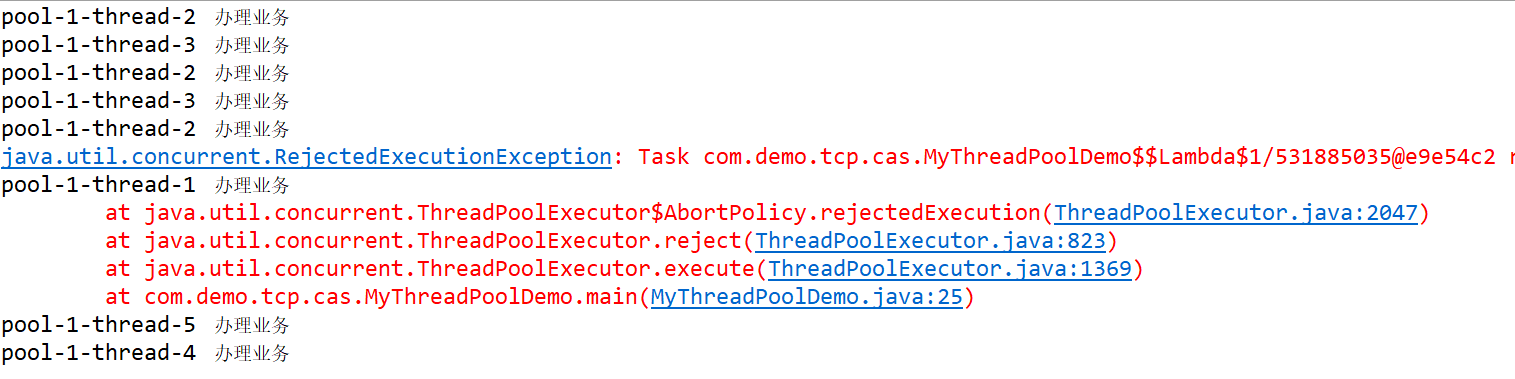
- ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy(),直接抛出异常
ExecutorService threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 5, 1L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(3),Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
try {
//模拟10个用户来办理业务,每个用户就是一个来自外部的请求线程
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
threadPool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 办理业务");
});
}
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
- ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy(),将某些任务回退到调用者

- ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy(),直接丢弃(只能完成max+队列个数)

- ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy(),抛弃等待最久的

合理配置线程池(针对的是maxPoolSize)
cpu核数:Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()
如果是CPU密集型

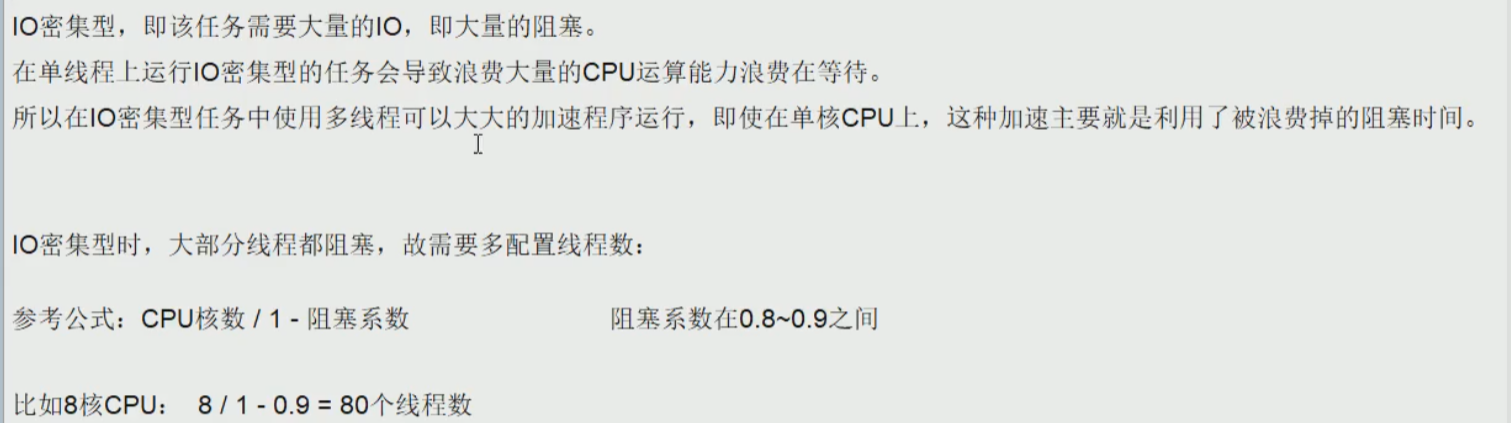
如果是IO密集型(有两种情况)
- 1

- 2
九、死锁编码以及定位分析
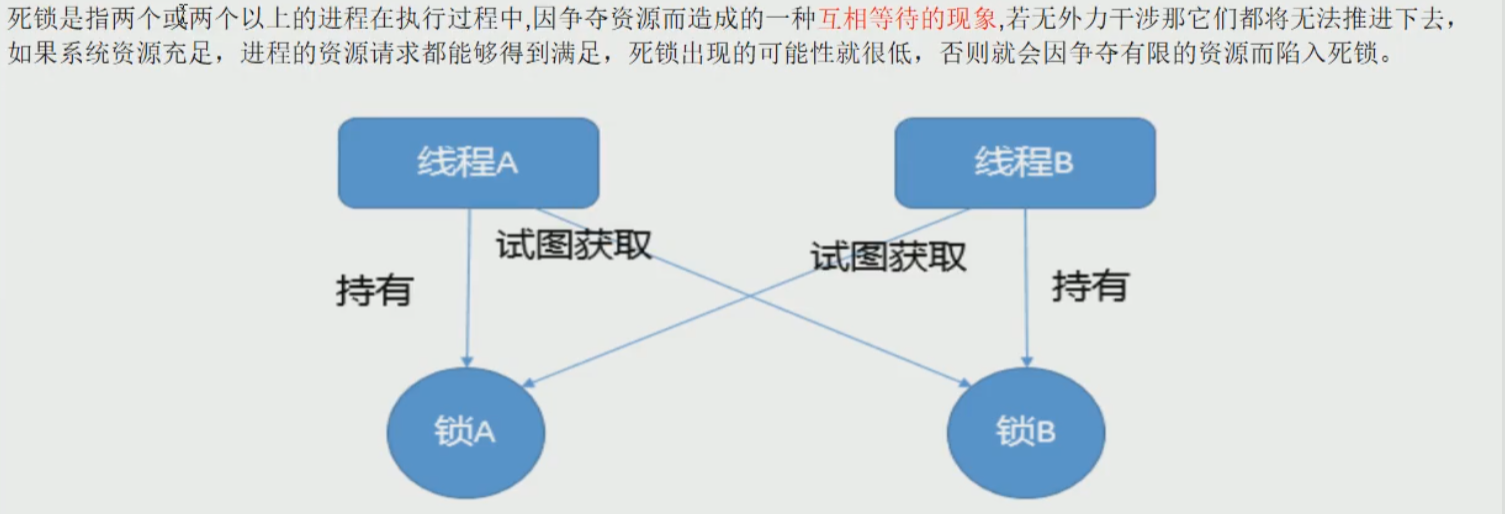
是什么
产生死锁的原因

代码
public class DeadLockDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String lockA = "lock1";
String lockB = "lock2";
new Thread(new HoldLockThread(lockA,lockB),"Thread_AAA").start();
new Thread(new HoldLockThread(lockB,lockA),"Thread_BBB").start();
}
}
class HoldLockThread implements Runnable{
private String lockA;
private String lockB;
public HoldLockThread(String lockA, String lockB) {
this.lockA = lockA;
this.lockB = lockB;
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lockA) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 自己持有:" + lockA + " 尝试获得:" + lockB);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (lockB) {
}
}
}
}
输出:

解决
定位死锁



