介绍一下Java里简单常用的输入输出方法。
Java的输出函数很简单,直接调用System类的out对象的print函数即可。
代码:
System.out.print(a);//输出变量a的值 System.out.print("214214");//输出字符串 System.out.print("123"+a);//混合输出字符串和变量值 /* 当然也可以使用System.out.println();表示换行输出,相当于System.out.print(" "); 其中System是一个类,out是java.io.PrintStream的对象,也就是System这个类中含有java.io.PrintStream的对象out。 print()是java.io.PrintStream类里的一个方法,也就是out对象的一个方法。 */
Java的输入比较麻烦,找了好多书都讲的不详细,网上也看了些方法,像BufferedReader类和InputStreamReader类法,Scanner类法等等。综合发现还是Scanner类最好用,它既可以读字符,也可以读字符串和整数。
代码:
import java.util.Scanner; public static void main(String [] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入你的姓名:"); String name = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println("请输入你的年龄:"); int age = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("请输入你的工资:"); float salary = sc.nextFloat(); System.out.println("你的信息如下:"); System.out.println("姓名:"+name+" "+"年龄:"+age+" "+"工资:"+salary); }
另外,该对象的next()方法和nextLine()方法的区别:
在java中,next()方法是不接收空格的,在接收到有效数据前,所有的空格或者tab键等输入被忽略,若有有效数据,则遇到这些键退出。nextLine()可以接收空格或者tab键,其输入应该以enter键结束。
在学习Java的输入时,有个有趣的发现,感兴趣的朋友可以往下看。
Java版的getchar()函数:(char)System.in.read()
当时想的是,既然输出用的是out对象,那么必然有个in对象的方法能完成输入的功能。于是就发现了System.in.read()这个东东,它实现的功能是:从键盘读一个字符。好嘛^_^,那么就输下这个东东
System.out.println(System.in.read());
运行结果:

结果很意外,输入5,输出53 13 10;输入a,输出97 13 10;什么也不输直接回车,输出13 10。即输出了输入字符、回车控制字符和换行控制字符的ASCLL码!!
不,我不要ASCLL码数字,我要字符型!那么就强转一下吧。改下代码:
System.out.println((char)System.in.read());
果然如愿输出了字符型,而且回车控制字符和换行控制字符都不见了!而且经测试,结果完全符合算法题中的输入的要求,即在Java中实现了类似C++中的getchar()函数:(char)System.in.read()
再进一步思考,加个while(true)能否用字符数组形式输出字符串呢?
代码如下:
import java.io.IOException; public class dd { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { while(true){ System.out.print((char)System.in.read()); } } }
运行结果:
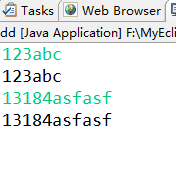
成功得到了字符串是不是?
实际并没有。。
这个方法有极大的缺陷:
System.out.println((char)System.in.read());
实际就相当于:
InputStream a=System.in; char ch=(char)a.read(); System.out.print(ch);
果然还是没有摆脱缓冲区的束缚,把刚才输出字符串的代码的while(true)换成for循环:
import java.io.IOException; public class dd { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //while(true){ for(int i=0;i<5;i++){ System.out.print((char)System.in.read()); //} } } }
运行结果:
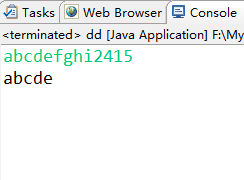
只能读for循环限制的5个字符。。while(true)只是用一个死循环把输入缓冲区的字符都读完了而已,才造成了这种方法能读字符串的假象,
再回到C/C++想想,这个真的和getchar()一样。。
参考下面代码:
#include<stdio.h> int main() { while(1) { char a=getchar(); printf("%c",a); } return 0; }
运行结果:
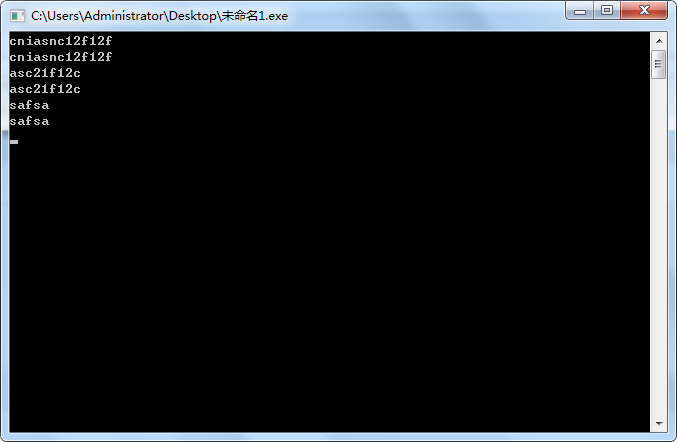
曾经,getchar()是否给了你它能输出字符串的假象呢?