1、https://www.cnblogs.com/sandyliu1999/p/4844664.html
XML是有层次结构的,序列化实际就是内存化,用连续的结构化的内存来存储表示一个对象,那么这两者之间就有区别了,查看下面的对应规则。
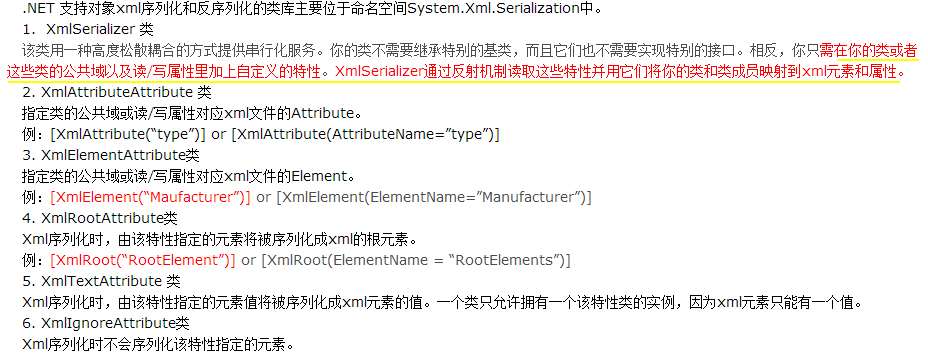
看上面链接里给出的例子应该就差不多可以看明白了。
下面看下XML格式的详解。
2、http://www.cnblogs.com/chenjiacheng/p/6522563.html --xml格式详解。


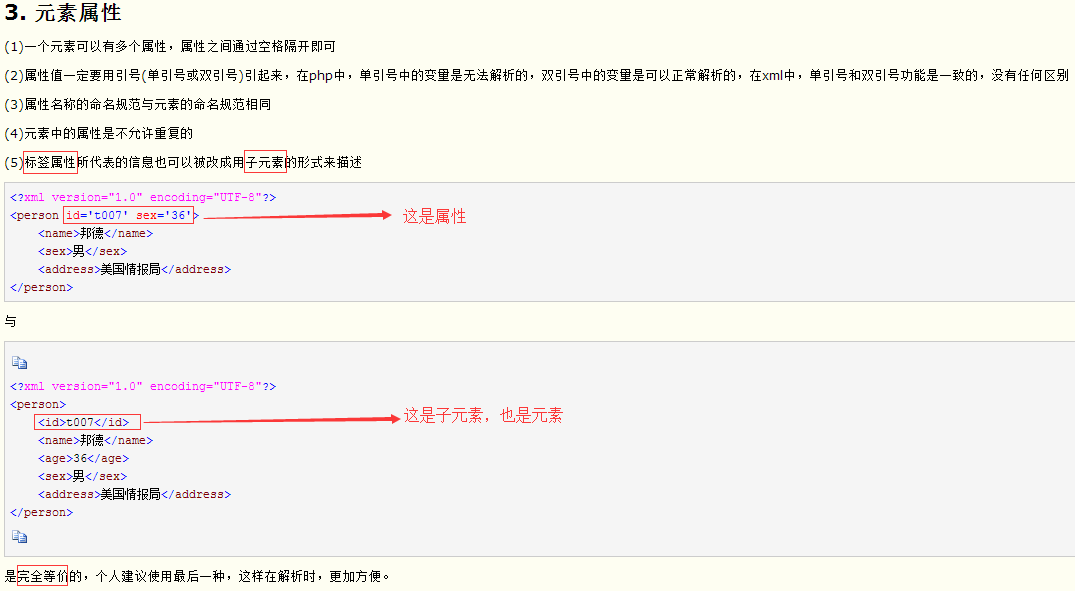
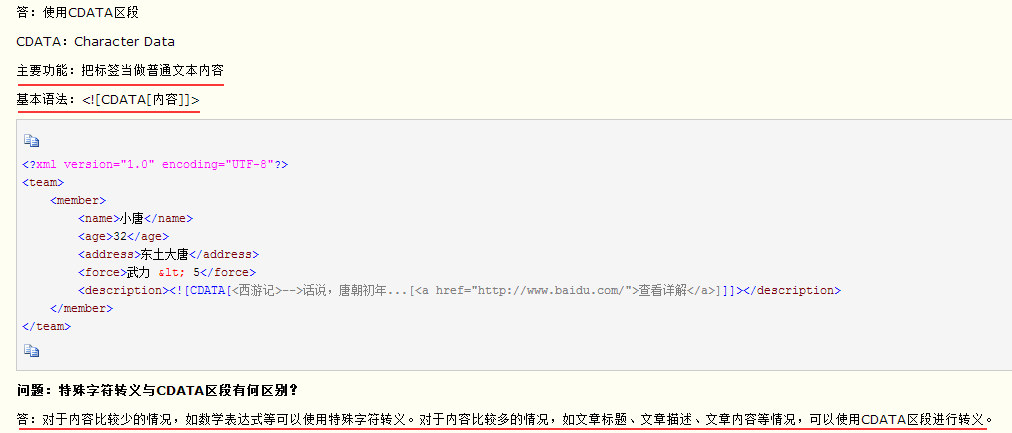
3、http://blog.csdn.net/com_ma/article/details/73277535
另一篇xml格式文档详解,摘取一点有用信息,开始标签和结束标签中间的是内容,一个元素可以有多个属性,格式如下:<元素名 属性名=“属性值” 属性名=“属性值”>
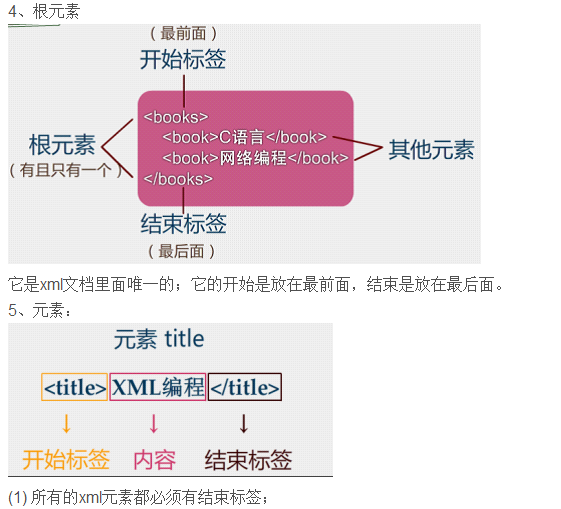

4、增加一个自己应用的实例
首先是xml文档,文档结构表明了需求数据结构。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <root> <ROOTITEMS> <RootItem> <NAME>system</NAME> <Items> <Item Value="sysDescr" OID="1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0" ></Item> <Item Value="sysUpTime" OID="1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0" ></Item> <Item Value="sysContact" OID="1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0" ></Item> <Item Value="sysName" OID="1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0" ></Item> <Item Value="sysLocation" OID="1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0" ></Item> <Item Value="sysServices" OID="1.3.6.1.2.1.1.7.0" ></Item> <Item Value="sysORLastChange" OID="1.3.6.1.2.1.1.8.0" ></Item> <Item Value="sysORTable" OID="1.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.0"></Item> </Items> </RootItem> </ROOTITEMS> </root>
然后是数据结构类,
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Xml.Serialization; namespace WindowsFormsApplication1 { [XmlRoot("root")] public class SnmpMIB { [XmlArray("ROOTITEMS"),XmlArrayItem("RootItem")] public RootItem[] oidItems { get; set; } } public class RootItem { [XmlElement("NAME")] public string rootName { set; get; } [XmlArray("Items"), XmlArrayItem("Item")] public Item[] items { set; get; } } public class Item { [XmlAttribute("Value")] public string name { set; get; } [XmlAttribute( "OID")] public string oid { set; get; } } }
序列化与反序列化类,
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.IO; using System.Xml.Serialization; namespace WindowsFormsApplication1 { class ConfigManager { private static SnmpMIB _snmpOids = null; public ConfigManager() { } public SnmpMIB Get(string path) { if (_snmpOids == null) { FileStream fs = null; try { XmlSerializer xs = new XmlSerializer(typeof(SnmpMIB)); fs = new FileStream(path, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read); _snmpOids = (SnmpMIB)xs.Deserialize(fs); fs.Close(); return _snmpOids; } catch { if (fs != null) fs.Close(); throw new Exception("Xml deserialization failed!"); } } else { return _snmpOids; } } public void Set(string path, SnmpMIB snmpOids) { if (snmpOids == null) throw new Exception("Parameter humanResource is null!"); FileStream fs = null; try { XmlSerializer xs = new XmlSerializer(typeof(SnmpMIB)); fs = new FileStream(path, FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write); xs.Serialize(fs, snmpOids); _snmpOids = null; fs.Close(); } catch { if (fs != null) fs.Close(); throw new Exception("Xml serialization failed!"); } } } }
最后就是应用类了。
ConfigManager config = new ConfigManager(); SnmpMIB snmpMib = null; try { snmpMib = config.Get("XMLFile1.xml"); } catch (Exception ex) { Console.WriteLine("Here is Error!"); } if (snmpMib != null) { RootItem[] items = snmpMib.oidItems; foreach(RootItem item in items) { Console.WriteLine(item.rootName); foreach (Item it in item.items) { Console.WriteLine(it.name + " " + it.oid); } } }
数据结构的定义是为了简化SNMP的MIB内容,所以需要自定义这样一个数据结构。关于SNMP协议,可以参见前一篇文档。