一、作用域
依赖有效性/范围
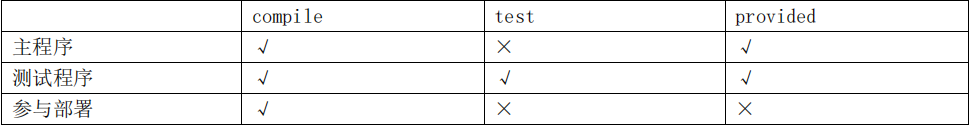
依赖传递性
A 依赖 B,B 依赖 C,A 能否使用 C 呢?那要看 B 依赖 C 的范围是不是 compile,如果是则可用,否则不 可用。

二、父子工程
1、在子工程中引用父工程
<parent> <groupId>com.baker.learning</groupId> <artifactId>base-java</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <!-- 指定从当前子工程的pom.xml文件出发,查找父工程的pom.xml的路径 --> <relativePath>../Parent/pom.xml</relativePath> </parent>
此时如果子工程的 groupId 和 version 如果和父工程重复则可以删除。
2、在父工程中管理依赖
将 Parent 项目中的 dependencies 标签,用 dependencyManagement 标签括起来
<dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.9</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement>
在子项目中重新指定需要的依赖,删除范围和版本号
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies>
3、父工程提取子工程公共jar包(所有子工程自动引入)
<dependencies> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.9</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencies>
三、聚合
将多个工程拆分为模块后,需要手动逐个安装到仓库后依赖才能够生效。修改源码后也需要逐个手动进。行 clean 操作。而使用了聚合之后就可以批量进行 Maven 工程的安装、清理工作。
在总的聚合工程中使用 modules/module 标签组合,指定模块工程的相对路径即可
<modules> <module>learn-springretry</module> <module>learn-springaop</module> <module>learn-resourceloader</module> <module>learn-globalexception</module> <module>learn-custom-annotation</module> <module>learn-websocket</module> <module>learn-spring-security</module> <module>learn-shiro-jwt</module> </modules>