Magic boy Bi Luo with his excited tree
Time Limit: 8000/4000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/131072 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1505 Accepted Submission(s): 456
Problem Description
Bi Luo is a magic boy, he also has a migic tree, the tree has N nodes , in each node , there is a treasure, it's value is V, and for each edge, there is a cost C, which means every time you pass the edge i , you need to pay C.
You may attention that every V can be taken only once, but for some C , you may cost severial times.
Now, Bi Luo define ans[i] as the most value can Bi Luo gets if Bi Luo starts at node i.
Bi Luo is also an excited boy, now he wants to know every ans[i], can you help him?
You may attention that every V can be taken only once, but for some C , you may cost severial times.
Now, Bi Luo define ans[i] as the most value can Bi Luo gets if Bi Luo starts at node i.
Bi Luo is also an excited boy, now he wants to know every ans[i], can you help him?
Input
First line is a positive integer T , represents there are T test cases.
Four each test:
The first line contain an integer N(N.
The next line contains N integers V, which means the treasure’s value of node i(1≤V.
For the next N lines, each contains three integers u,v,c , which means node u and node v are connected by an edge, it's cost is c(1≤c≤104).
You can assume that the sum of N will not exceed 106.
Four each test:
The first line contain an integer N(N.
The next line contains N integers V, which means the treasure’s value of node i(1≤V.
For the next N lines, each contains three integers u,v,c , which means node u and node v are connected by an edge, it's cost is c(1≤c≤104).
You can assume that the sum of N will not exceed 106.
Output
For the i-th test case , first output Case #i: in a single line , then output N lines , for the i-th line , output ans[i] in a single line.
Sample Input
1
5
4 1 7 7 7
1 2 6
1 3 1
2 4 8
3 5 2
Sample Output
Case #1:
15
10
14
9
15
Author
UESTC
细节!!!
啊啊啊啊!!!用了一天的时间终于调出来了啊!!!可恶的一道题!!!细节实在是太恶心了!!!
做了这个题之后 感觉整个人身体被掏空。。。QAQ。。。
不得不说那些一遍就能A的大佬们实在是太强了!!!
好了,说一说题目吧。其实拿到这道题目的时候,就想到了正确的方程。。。
每个点设f_up[maxn][0/1],f_down[maxn][0/1],然后先求出f_down,然后再求出f_up,就可以完美解决了!
想法很棒,实践极差!!!
这道题完全不止这么简单!!!
有超级多的细节需要你去考虑!!!
首先提一个最基础的细节,方程中0和1所表示的含义!
0的含义极好想懂,就是从这个点出发,向上或向下走最后返回这个的所可以走的最大价值;
但是1的含义就需要YY一下 了。
1表示从这个点出发向上或向下走最后不返回这个点所可以走的最大值;
听起来很容易。。。但要注意,比如一个点要向下走,他可以先在下面绕一圈转回来然后再向下走!!!
好吧,是挺容易的。
这样一来想必大家对于这个题目的转移方程就一目了然了。。
呵呵,你naive了!!!我一开始也是错在这个地方!!!
求f_up[i][1]是很难很难求的啊!!!
因为有这样几个细节:
1. 点i先走到他的父节点(或许没有),然后有两种情况。一种可以在上面绕一圈然后向下走(向下走之前也可以在下面绕圈QAQ),一种是可以在下面绕一圈然后向上走。
这样说起来可能有些难理解,画一幅图看看吧!
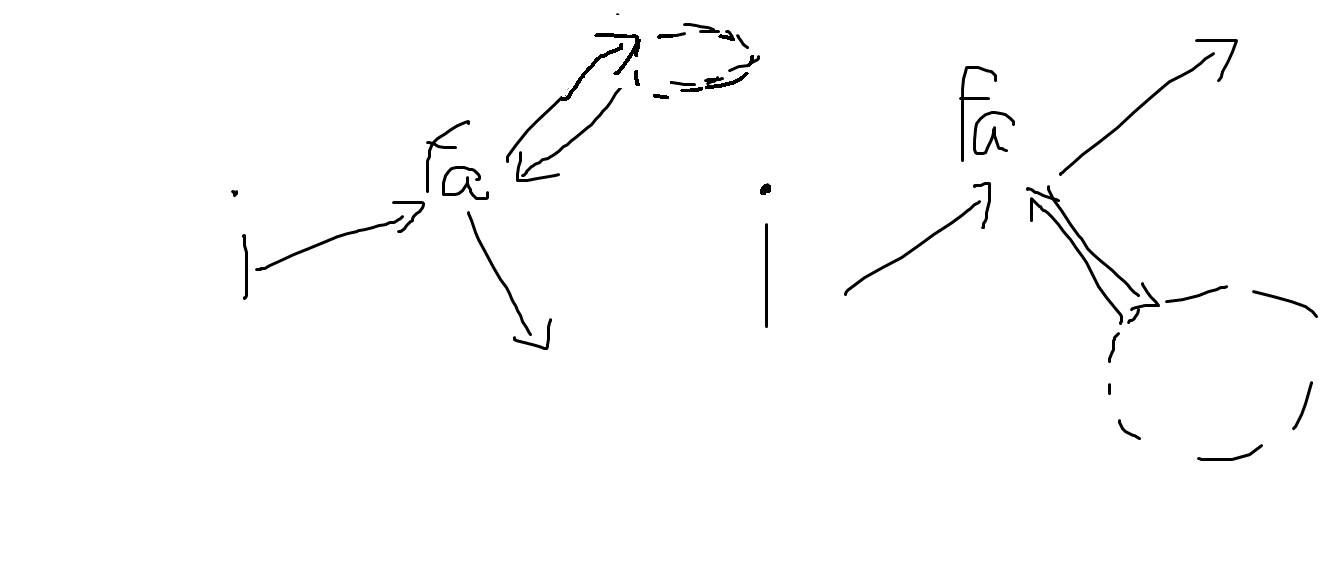
2. 十分显然,在第一种走法中间又有坑逼之处!!!就是i这个点在计算向下走的价值的时候要如何处理!!!
就是这个东西卡了我一个下午!!!QAQ!!!
给点提醒吧,
1 在求f_down[i][1]的时候,要把最后向下的边(edge1)给记下来,还要记下如果没有(edge1)那么f_down[i][1]的最后向下的边是哪一条!!!
2 在计算1(就是上面那玩儿)的时候,比如求到了点s[i].v最好判断一下点s[i].v能不能在保证有价值的情况下返回i点。
#include<cstdio> #include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #define maxn 100100 << 1 using namespace std; int n,head[maxn],tot,u,v,val,dian[maxn],fir[maxn],sec[maxn]; int f_down[maxn][3],f_up[maxn][3],f_edge[maxn]; // 0表示返回原点,1表示不返回原点 struct st{ int v,val,next; st in(int a,int b,int c) { v = a; val = b; next = c; } }s[maxn]; inline void add(int u,int v,int val) { tot++; s[tot].in(v,val,head[u]); head[u] = tot; } void dfs(int fa,int now) { f_down[now][0] = f_down[now][1] = dian[now]; int k = 0,ma = 0; int pos; for(int i=head[now];i;i=s[i].next) { if(s[i].v != fa) { f_edge[s[i].v] = s[i].val; dfs(now,s[i].v); f_down[now][0] += max(f_down[s[i].v][0] - 2 * s[i].val,0); f_down[now][1] += max(f_down[s[i].v][0] - 2 * s[i].val,0); if(k < f_down[s[i].v][1] + f_edge[s[i].v] - f_down[s[i].v][0] && f_down[s[i].v][0] - 2 * s[i].val > 0) { k = f_down[s[i].v][1] + f_edge[s[i].v] - f_down[s[i].v][0]; sec[now] = s[i].v; if(k > ma) { swap(k,ma); swap(sec[now],fir[now]); } pos = fir[now]; } if(f_down[s[i].v][0] - 2 * s[i].val <= 0 && f_down[s[i].v][1] - s[i].val > 0) { if(k == 0) { k = f_down[s[i].v][1] - s[i].val; sec[now] = s[i].v; if(k > ma) { swap(k,ma); swap(sec[now],fir[now]); } pos = fir[now]; } else if(k < f_down[s[i].v][1] - s[i].val) { k = f_down[s[i].v][1] - s[i].val; sec[now] = s[i].v; if(k > ma) { swap(k,ma); swap(sec[now],fir[now]); } pos = fir[now]; } } } } if(ma != 0) f_down[now][1] = f_down[now][1] + ma; } int get_up(int fa,int now) { int ans = f_up[fa][1] - dian[fa] + f_down[fa][0] - dian[fa]; if(f_down[now][0] - 2 * f_edge[now] > 0) ans -= f_down[now][0] - 2 * f_edge[now]; return ans; } int get_down(int fa,int now) { int ans = f_up[fa][0] - dian[fa] + f_down[fa][1] - dian[fa]; if(fir[fa] == now) { int k = sec[fa]; ans -= f_down[now][1] - f_edge[now]; ans = ans - max(0,f_down[k][0] - 2 * f_edge[k]) + f_down[k][1] - f_edge[k]; } else if(f_down[now][0] - 2 * f_edge[now] > 0) ans -= f_down[now][0] - 2 * f_edge[now]; return ans; } void find(int fa,int now) { f_up[now][0] = f_up[now][1] = dian[now]; int k = f_down[fa][0]; if(fa) { if(f_down[now][0] - 2 * f_edge[now] > 0) k -= f_down[now][0] - 2 * f_edge[now]; f_up[now][0] += max(0,k - 2 * f_edge[now] + f_up[fa][0] - dian[fa]); f_up[now][1] += max(0,max(get_up(fa,now),get_down(fa,now)) - f_edge[now] + dian[fa]); } for(int i=head[now];i;i=s[i].next) { if(s[i].v != fa) find(now,s[i].v); } } int main(){ int t; cin >> t; for(int qwer=1;qwer<=t;qwer++) { tot = 0; memset(head,0,sizeof(head)); scanf("%d",&n); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",&dian[i]),fir[i] = sec[i] = 0; for(int i=1;i<n;i++) { scanf("%d%d%d",&u,&v,&val); add(u,v,val); add(v,u,val); } dfs(0,1); find(0,1); printf("Case #%d: ",qwer); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) printf("%d ",max(f_down[i][0] + f_up[i][1],f_down[i][1] + f_up[i][0]) - dian[i]); } } /* 3 4 5 3 4 4 1 2 1 1 3 2 1 4 1 8 13 13 13 13 13 13 13 13 1 2 5 1 3 6 2 4 7 2 5 8 2 6 9 3 7 5 3 8 5 5 4 1 7 7 7 1 2 6 1 3 1 2 4 8 3 5 2 */