前言
之前就有写过学习笔记: Asp.net core 学习笔记 Fluent Validation
但都是用一点记入一点,零零散散不好读, 这一篇来稍微整理一下.
主要参考:
Simple Use
要验证的类
public class Person { public string Email { get; set; } = ""; }
对应这个类的 Validator
public class PersonValidator : AbstractValidator<Person> { public PersonValidator() { RuleFor(e => e.Email).EmailAddress(); } }
继承 AbstractValidator, 然后再构造函数里添加上验证逻辑.
调用验证方式
public static async Task Main() { var person = new Person { Email = "test..." }; var personValidator = new PersonValidator(); var validationResult = personValidator.Validate(person); if (!validationResult.IsValid) { foreach (var error in validationResult.Errors) { Console.WriteLine(error.PropertyName); // Email Console.WriteLine(error.ErrorMessage); // 'Email' is not a valid email address. } } }
创建 validator 然后调用 validate, 把实例丢进去就会返回验证结果了.
如果是在 Web API controller 还可以直接 add to ModelState 哦.
validationResult.AddToModelState(ModelState, prefix: null);
常用 Validator (Build-in)
RuleFor(e => e.Email).Null(); // == null RuleFor(e => e.Email).NotNull(); // != null
常用 1
RuleFor(e => e.Email).Equal("some value"); // == "some value" RuleFor(e => e.Email).NotEqual("some value"); // != "some value" RuleFor(e => e.Email).Matches("regex expression", RegexOptions.IgnoreCase); // 正则表达式 RuleFor(e => e.Email).EmailAddress(); // 封装好的 email 正则, empty string 也是 invalid 哦
常用 2
RuleFor(e => e.Salary).LessThan(1); // < 1 RuleFor(e => e.Salary).LessThanOrEqualTo(1); // <= 1 RuleFor(e => e.Salary).GreaterThan(1); // > 1 RuleFor(e => e.Salary).GreaterThanOrEqualTo(1); // >= 1 RuleFor(e => e.Salary).ExclusiveBetween(from: 1, to: 100); // > 1 and < 100 RuleFor(e => e.Salary).InclusiveBetween(from: 1, to: 100); // >= 1 and <= 100
常用 3
RuleFor(e => e.Email).Length(10); // .Length == 10 (string, Array 都可以) RuleFor(e => e.Email).MinimumLength(10); // .Length > 10 RuleFor(e => e.Email).MaximumLength(10); // .Length < 10
decimal 专用
RuleFor(e => e.Salary).ScalePrecision(scale: 19, precision: 2, ignoreTrailingZeros: true);
允许 19 位数, 有 2 个位数可以是小数. ignoreTrailingZeros 指 15.0000 结尾 4 个 0 不会占据位数
理解 Emtpty
RuleFor(e => e.Email).Empty();
RuleFor(e => e.Email).NotEmpty();
Empty 的意思是, 不能是 default value, 不能 length = 0 (string 会先 trim 才看 length 哦)
int = 0 – failed
enum = first enum value – failed
int? = null – failed
string = "" – failed
string = " " – failed
List<string> = new() – failed
Date = default – failed
不常用的
// Credit Card Validator // Enum Validator // Enum Name Validator // Predicate Validator
Cross Field
直接用就可以了. 很直观
RuleFor(e => e.Salary).GreaterThan(e => e.Age);
Conditional
参考: Conditions
有 2 种 conditional
1. 当满足条件时才验证
RuleFor(e => e.Salary).LessThan(10).When(e => e.Email == "test");
2. if ... else 配置
When(e => e.Email == "test", () => {
// 这里不要乱放代码, 只放 setup validation 代码就好, 因为它一定会执行 RuleFor(e => e.Salary).LessThan(500); }).Otherwise(() => { RuleFor(e => e.Salary).InclusiveBetween(from: 1, to: 100); });
很可惜, 它没有提供 swtich 和 else if, 写起来不那么直观.
注: 它的运行机制是, validation setup 一定会跑 (和 if 概念不同哦, 所以不要乱吧代码放进 setup validation scope 里面), 在做 validation 的时候才调用 when 去判断是否要执行
Include Properties
var validationResult = personValidator.Validate( person, options => options.IncludeProperties("Email", "Salary") // params string[] properties );
适用于 partial update 场景.
Custom Validator
除了使用 build-in 的 validator, 想要自己写逻辑验证有 2 个方法.
1. Must
RuleFor(e => e.Email).Must((rootObject, propertyValue) => { return rootObject.Salary == 1 && propertyValue == "email@email.com"; });
直接写验证逻辑. 通过实例和属性值做判断.
2. PropertyValidator
public class MoneyValidator<T> : PropertyValidator<T, decimal> where T : Person { public override string Name => "MoneyValidator"; public override bool IsValid(ValidationContext<T> context, decimal propertyValue) { var person = context.InstanceToValidate; // 可以拿到 instance, 如果没有用到, 泛型 T 就好了, 不需要 where return propertyValue == 1; } }
使用
RuleFor(e => e.Salary).SetValidator(new MoneyValidator<Person>());
Friendly call
RuleFor(e => e.Salary).Money();
extension method
public static class ValidatorExtensions { public static IRuleBuilderOptions<T, decimal> Money<T>(this IRuleBuilder<T, decimal> ruleBuilder) { return ruleBuilder.SetValidator(new MoneyValidator<T>()); } public static IRuleBuilderOptions<T, decimal?> Money<T>(this IRuleBuilder<T, decimal?> ruleBuilder,) { return ruleBuilder.SetValidator(new MoneyValidator<T>()); } }
注: decimal 和 decimal? 要 2 个方法重载. 内部 set 同一个 validator 就可以了, 当遇到 null 的时候它会直接 pass, 估计内部有做了处理, 这个方式是源码学来的.
Dependency Injection
和 EF Core 类似的做法, 通过反射 Assembly 找出 Validator 然后 AddScope.
mvcBuilder.AddFluentValidation(options =>
{
options.RegisterValidatorsFromAssembly(assembly);
});
Web API Controller
private readonly CreateProjectDtoValidator _createProjectDtoValidator;public ProjectController(CreateProjectDtoValidator createProjectDtoValidator) { _createProjectDtoValidator = createProjectDtoValidator }
这样 Validator 就可以注入 DbContext 和其它 service 了.
Asynchronous
有几个方法都可以异步.
1. WhenAsync
WhenAsync((person, cancellationToken) => { return Task.FromResult(true); }, () => { RuleFor(e => e.Email).EmailAddress(); });
RuleFor(p => p.Email).EmailAddress().WhenAsync((person, cancellationToken) => Task.FromResult(true));
2. MustAsync
RuleFor(e => e.Email).MustAsync((rootObject, propertyValue, context, cancellationToken) => { return Task.FromResult(true); });
3. Customer AsyncValidator
public class MoneyAsyncValidator<T> : AsyncPropertyValidator<T, decimal> { public override string Name => "MoneyValidator"; public override Task<bool> IsValidAsync(ValidationContext<T> context, decimal propertyValue, CancellationToken cancellation) { return Task.FromResult(propertyValue == 1); } }
调用
RuleFor(e => e.Salary).SetAsyncValidator(new MoneyAsyncValidator<Person>());
4. ValidateAsync
如果验证规则里用到了 async, 那在调用 Validate 的时候要用 Async 版本哦.
var validationResult = await personValidator.ValidateAsync(person);
PropertyName, DisplayName
参考: Overriding the Property Name
参考之前的: ASP.NET Core – Case Style Conversion FluentValidation 的部分.
Manually set error with property name and display name
Fluent Validation 当有 Children 的时候, 它的返回是这样的

property name 会是一个 path 的形式. array 就配上 [n].
如果我们有需求动态添加 error 的话, 就必须符合它的格式哦. 比如:
var validator = new PersonValidator(); var person = new Person { Children = new List<Child> { new Child(), new Child() } }; var personResult = validator.Validate(person); for (int i = 0; i < person.Children.Count; i++) { var child = person.Children[i]; var childValidator = new ChildValidator(); var childResult = childValidator.Validate(child); foreach (var error in childResult.Errors) { var eExp = Expression.Parameter(person.GetType(), "e"); var eDotNameExp = Expression.Property(eExp, nameof(person.Children)); var lambda = Expression.Lambda(eDotNameExp, eExp); var propertyName = ValidatorOptions.Global.PropertyNameResolver(person.GetType(), person.GetType().GetProperty(nameof(person.Children)), lambda); error.PropertyName = $"{propertyName}[{i}].{error.PropertyName}"; personResult.Errors.Add(error); } } Console.WriteLine(JsonSerializer.Serialize(personResult.Errors.Select(e => new { e.PropertyName, e.ErrorMessage }), new JsonSerializerOptions { WriteIndented = true } ));
需要特别注意的是, PropertyName 必须经过正确的 ValidatorOptions.Global.PropertyNameResolver 处理.
第 1 个参数是 root class type, 第 2 个参数是 last depth PropertyInfo, 最后一个是从 Root 到 deepest propertyInfo 的路径 lambda 表达式
这样它才能 generate 到对的 Property Name
FluentValidation parse expression 的源码是这样的
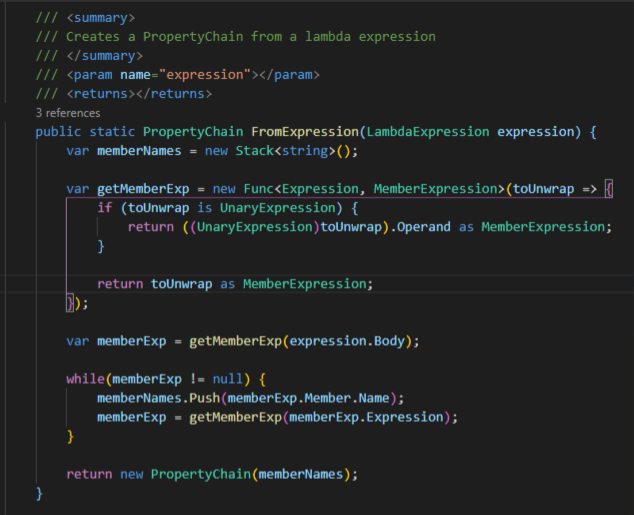
就这样看的话, 应该是没有 cover 到 Children[0].Name 这种 [0] 的处理的. 所以估计它是通过外部累加做到的. 所以使用 PropertyNameResolver 的时候, 可不要放入 [0] 这种 expression 哦.
Cascade mode
默认情况下, 当一个错误发生以后, 其它的验证依然会执行, 然后返回所有的错误.
有时候这不一定是我们期望的模式.
举例, email address 正则验证
当 empty string 的时候, 算不算 invalid email address ?
通常是不算的, 都没有填, 验个毛. 应该要跑错 required 必填.
那怎样处理?
3 个思路.
1. email validator 遇到 emtpy string 算 pass
2. email validator + when string.IsNullOrEmpty(value)
3. 当 1 个 error 发生, 停止后续的验证.
cascade mode 就是只第 3 种情况.
RuleFor(e => e.Email).Cascade(CascadeMode.Stop).NotEmpty().EmailAddress();
另一种写法是 depend rule, 当 a rule ok 了才执行 b rule, 这也可以算一种 Conditional 的手法.
RuleFor(e => e.Email).NotEmpty().DependentRules(() => { RuleFor(e => e.Email).EmailAddress(); });
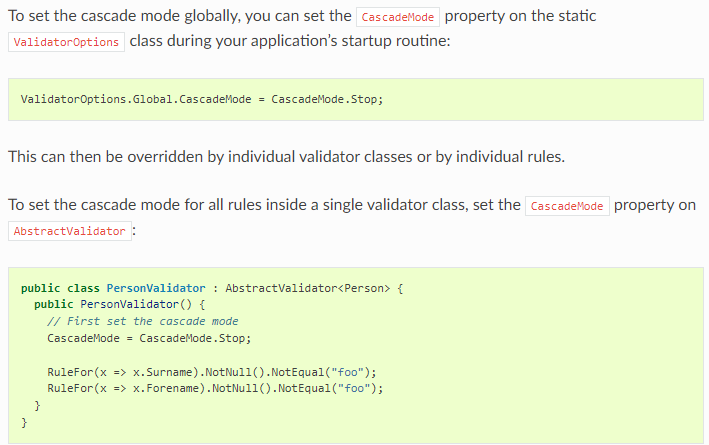
要 set global 或者 by validator 就这样:
Error Message
WithMessage
RuleFor(e => e.EmailSalary).EmailAddress().WithMessage("{PropertyName} {PropertyValue} is no ok!");
ValidationContext
在 Must, CustomPropertyValidator 内操作 context 也可以设置更多的参数.
RuleFor(e => e.Email).Must((rootObject, propertyValue, context) => { context.MessageFormatter.AppendArgument("MyValue", "value"); return false; }).WithMessage("{MyValue}");
customer property validator default message template
public class MoneyValidator<T> : PropertyValidator<T, decimal> { public override string Name => "MoneyValidator"; public override bool IsValid(ValidationContext<T> context, decimal value) { return true; } protected override string GetDefaultMessageTemplate(string errorCode) // errorCode 都是 null, 不清楚怎么用 { return "{MyValue} is wrong."; } }