VULNERABILITY_SCANNER
How to discover a vulnerability in a web application?
1. Go into every possible page.
2. Look for ways to send data to web application(URL + Forms).
3. Send payloads to discover vulnerabilities.
4. Analyze the response to check of the website is vulnerable.
->General steps are the same regardless of the vulnerability.
Class Scanner.
#!/usr/bin/env python import requests import re from urllib.parse import urljoin class Scanner: def __init__(self, url): self.target_url = url self.target_links = [] def extract_links_from(self, url): response = requests.get(url) return re.findall('(?:href=")(.*?")', response.content.decode()) def crawl(self, url): href_links = self.extract_links_from(url) for link in href_links: link = urljoin(url, link) if "#" in link: link = link.split("#")[0] if self.target_url in link and link not in self.target_links: self.target_links.append(link) print(link) self.crawl(link)
Vulnerability scanner.
#!/usr/bin/env python import scanner target_url = "http://10.0.0.45/mutillidae/" vuln_scanner = scanner.Scanner(target_url) vuln_scanner.crawl(target_url)
The Python program runs fine.
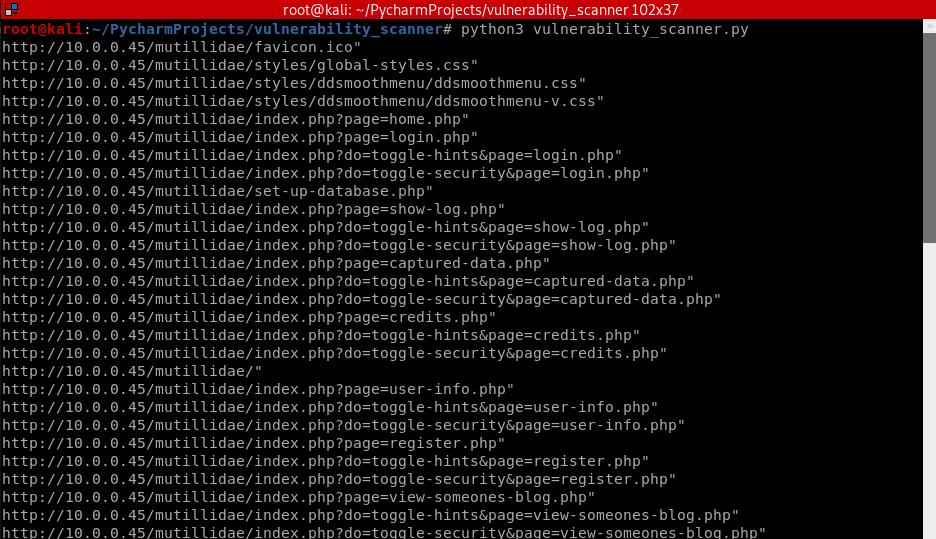
Polish the Python code using Default Parameters.
Class Scanner.
#!/usr/bin/env python import requests import re from urllib.parse import urljoin class Scanner: def __init__(self, url): self.target_url = url self.target_links = [] def extract_links_from(self, url): response = requests.get(url) return re.findall('(?:href=")(.*?")', response.content.decode()) def crawl(self, url=None): if url == None: url = self.target_url href_links = self.extract_links_from(url) for link in href_links: link = urljoin(url, link) if "#" in link: link = link.split("#")[0] if self.target_url in link and link not in self.target_links: self.target_links.append(link) print(link) self.crawl(link)
Vuln_scanner:
#!/usr/bin/env python import scanner target_url = "http://10.0.0.45/mutillidae/" vuln_scanner = scanner.Scanner(target_url) vuln_scanner.crawl()