教程 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/74597564
目录
一 图像变换与平面坐标系的关系
二 平面坐标系与齐次坐标系
三 单应性变换

一 图像变换与平面坐标系的关系
- 旋转:

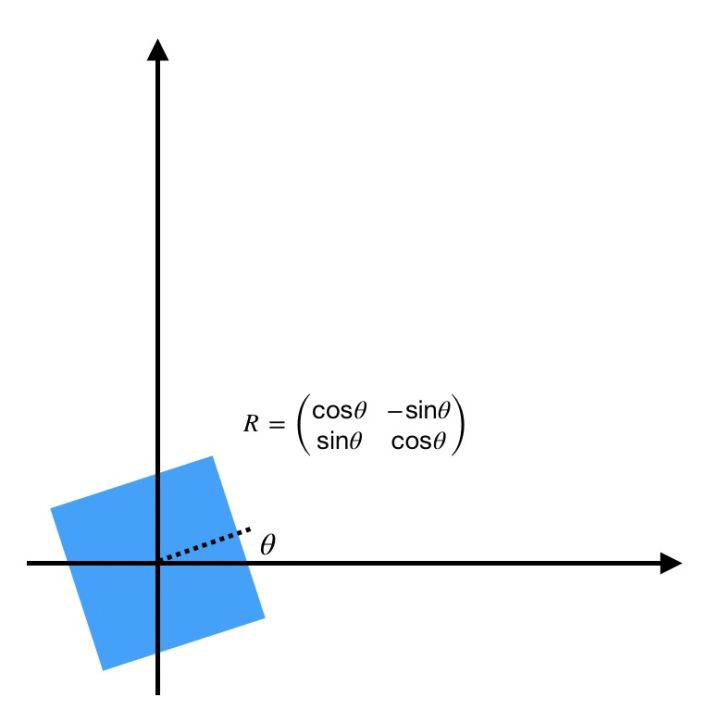
写成矩阵乘法形式:
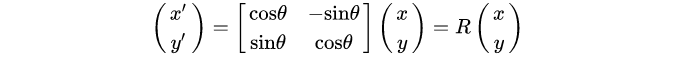
- 平移:

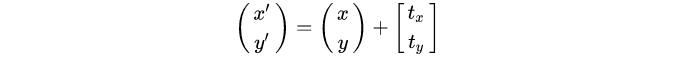
但是现在遇到困难了,平移无法写成和上面旋转一样的矩阵乘法形式。所以引入齐次坐标 ,再写成矩阵形式:
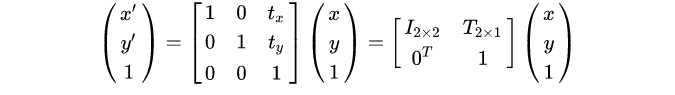
其中 表示单位矩阵,而
表示平移向量。
那么就可以把把旋转和平移统一写在一个矩阵乘法公式中,即刚体变换:
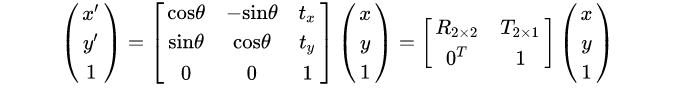
而旋转矩阵 是正交矩阵(
)。

刚体变换:旋转+平移(正方形-正方形)
作用:z轴距离不变 x y 和原来相等
仿射变换
作用:z轴距离不变 x y 各自被比例拉伸

其中 可以是任意2x2矩阵(与
一定是正交矩阵不同)。

仿射变换(正方形-平行四边形)
可以看到,相比刚体变换(旋转和平移),仿射变换除了改变目标位置,还改变目标的形状,但是会保持物体的“平直性”。
不同 和
矩阵对应的各种基本仿射变换:
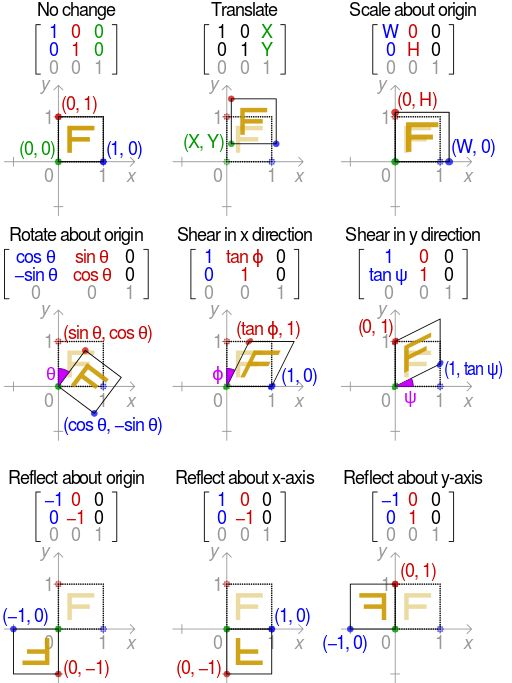
仿射变换(正方形-平行四边形)
可以看到,相比刚体变换(旋转和平移),仿射变换除了改变目标位置,还改变目标的形状,但是会保持物体的“平直性”。
不同 和
矩阵对应的各种基本仿射变换:

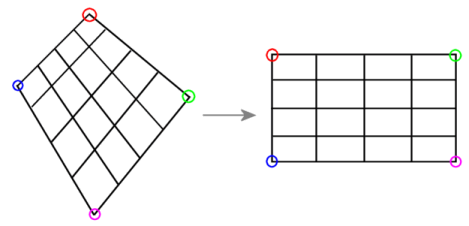
- 投影变换(单应性变换)
投影变换(单应性变换)
作用:z轴距离被拉伸 x y 被比例拉伸 z

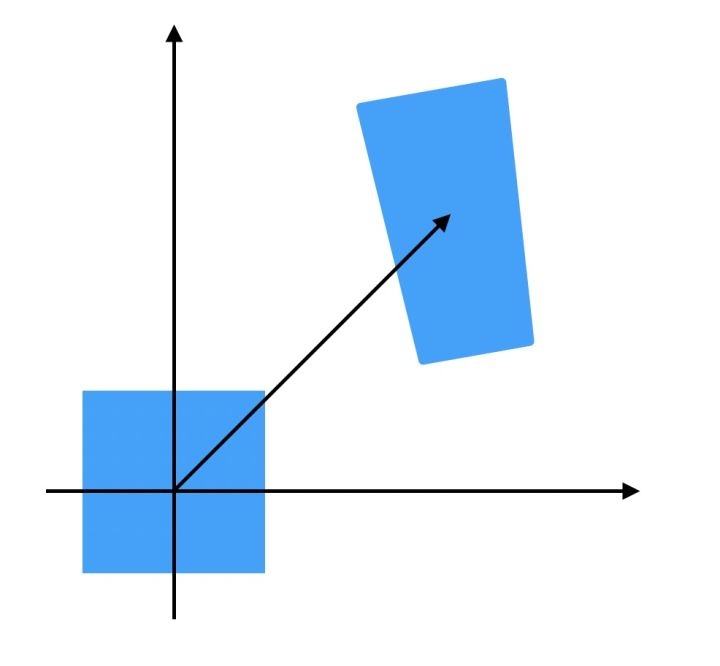
投影变换(正方形-任意四边形)
总结一下:
- 刚体变换:平移+旋转,只改变物体位置,不改变物体形状 x y z等于原来
- 仿射变换:改变物体位置和形状,但是保持“平直性” z不变 x y 被比例拉伸
- 投影变换:彻底改变物体位置和形状 z x y 都被比例拉伸
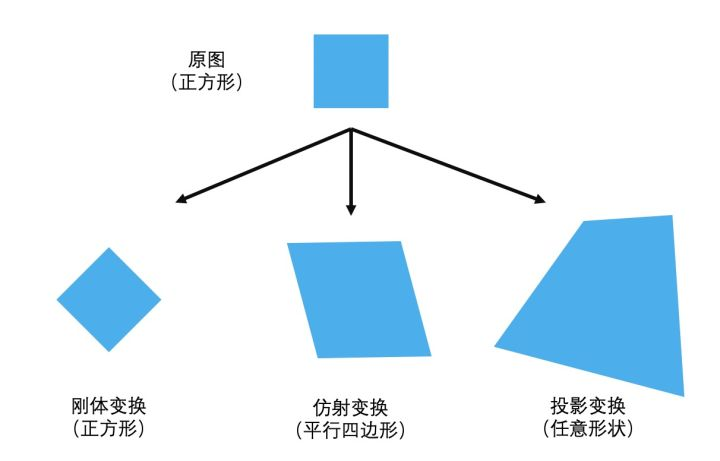
注:上图“投影变换”应该是“任意四边形”
我们来看看完整投影变换矩阵各个参数的物理含义:
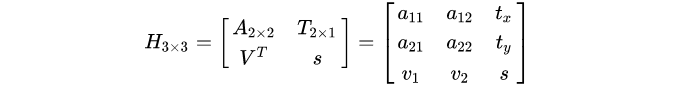
其中 代表仿射变换参数
代表平移变换参数
表示一种“变换后边缘交点“关系,如:
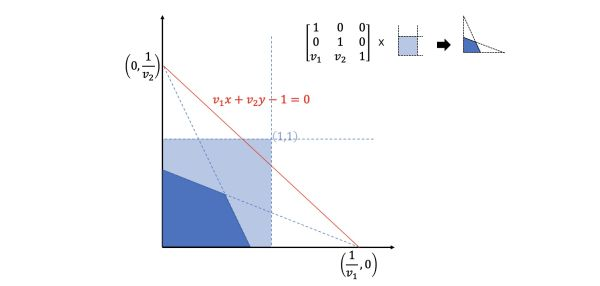
至于 则是一个与
相关的缩放因子。
一般情况下都会通过归一化使得 (原因见下文)。
二 平面坐标系与齐次坐标系
问题来了,齐次坐标到底是什么?
齐次坐标系 与常见的三维空间坐标系
不同,只有两个自由度:
而 (其中
)对应坐标
和
的缩放尺度。当
时:
特别的当 时,对应无穷远:
三 单应性变换
- 单应性是什么?
此处不经证明的给出:同一个 [无镜头畸变] 的相机从不同位置拍摄 [同一平面物体] 的图像之间存在单应性,可以用 [投影变换] 表示 。
注意:单应性成立是有条件的!

简单说就是:
其中 是Left view图片上的点,
是Right view图片上对应的点。
- 那么这个
单应性矩阵如何求解呢?
更一般的,每一组匹配点 有
由平面坐标与齐次坐标对应关系 ,上式可以表示为:
进一步变换为:
写成矩阵 形式:
也就是说一组匹配点 可以获得2组方程。
- 单应性矩阵8自由度
注意观察:单应性矩阵 与
其实完全一样(其中
),例如:
即点 无论经过
还是
映射,变化后都是
。
如果使 ,那么有:
所以单应性矩阵 虽然有9个未知数,但只有8个自由度。
在求 时一般添加约束
(也有用
约束),所以还有
共8个未知数。由于一组匹配点
对应2组方程,那么只需要
组不共线的匹配点即可求解
的唯一解。

可以看到:
- 红框所在平面上内容基本对齐,但受到镜头畸变影响无法完全对齐;
- 平面外背景物体不符合单应性原理,偏离很大,完全无法对齐。
- 传统方法估计单应性矩阵
一般传统方法估计单应性变换矩阵,需要经过以下4个步骤:
- 提取每张图SIFT/SURF/FAST/ORB等特征点
- 提取每个特征点对应的描述子
- 通过匹配特征点描述子,找到两张图中匹配的特征点对(这里可能存在错误匹配)
- 使用RANSAC算法剔除错误匹配
- 求解方程组,计算Homograph单应性变换矩阵
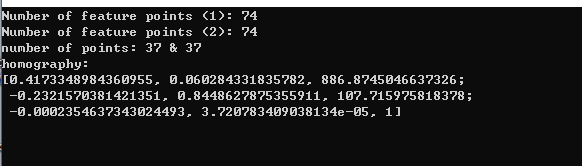
样例1 输入两张图+特征检测+自动匹配+自动求解单应矩阵+根据单应矩阵变换图像+输出拼接图
opencv 349+vs2015 opencv编译了扩展库及其sfft库 使用sift角点
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <opencv2/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/features2d.hpp>
#include <opencv2/calib3d.hpp>
#include <opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp>
#include <opencv2/stitching.hpp>
#define PARLIAMENT01 "x1.bmp"
#define PARLIAMENT02 "x2.bmp"
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Mat image1 = imread(PARLIAMENT01, 0);
Mat image2 = imread(PARLIAMENT02, 0);
if (!image1.data || !image2.data)
return 0;
//namedWindow("Image 1", 1);
//namedWindow("Image 2", 1);
//imshow("Image 1", image1);
//imshow("Image 2", image2);
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints1;
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints2;
Mat descriptors1, descriptors2;
//创建SIFT检测器
Ptr<Feature2D> ptrFeature2D = xfeatures2d::SIFT::create(74);
//检测SIFT特征并生成描述子
ptrFeature2D->detectAndCompute(image1, noArray(), keypoints1, descriptors1);
ptrFeature2D->detectAndCompute(image2, noArray(), keypoints2, descriptors2);
cout << "Number of feature points (1): " << keypoints1.size() << endl;
cout << "Number of feature points (2): " << keypoints2.size() << endl;
//使用欧氏距离和交叉匹配策略进行图像匹配
BFMatcher matcher(NORM_L2, true);
vector<DMatch> matches;
matcher.match(descriptors1, descriptors2, matches);
Mat imageMatches;
drawMatches(image1, keypoints1, // 1st image and its keypoints
image2, keypoints2, // 2nd image and its keypoints
matches, // the matches
imageMatches, // the image produced
Scalar(255, 255, 255), // color of the lines
Scalar(255, 255, 255), // color of the keypoints
vector<char>(),
2);
// namedWindow("Matches (pure rotation case)", 0);
// imshow("Matches (pure rotation case)", imageMatches);
//将keypoints类型转换为Point2f
vector<Point2f> points1, points2;
for (vector<DMatch>::const_iterator it = matches.begin();
it != matches.end(); ++it)
{
float x = keypoints1[it->queryIdx].pt.x;
float y = keypoints1[it->queryIdx].pt.y;
points1.push_back(Point2f(x, y));
x = keypoints2[it->trainIdx].pt.x;
y = keypoints2[it->trainIdx].pt.y;
points2.push_back(Point2f(x, y));
}
cout << "number of points: " << points1.size() << " & " << points2.size() << endl;
//使用RANSAC算法估算单应矩阵
vector<char> inliers;
Mat homography = findHomography(
points1, points2, // corresponding points
inliers, // outputed inliers matches
RANSAC, // RANSAC method
1.); // max distance to reprojection point
//画出局内匹配项
drawMatches(image1, keypoints1, // 1st image and its keypoints
image2, keypoints2, // 2nd image and its keypoints
matches, // the matches
imageMatches, // the image produced
Scalar(255, 255, 255), // color of the lines
Scalar(255, 255, 255), // color of the keypoints
inliers,
2);
namedWindow("Homography inlier points", 0);
imshow("Homography inlier points", imageMatches);
//用单应矩阵对图像进行变换
Mat result;
warpPerspective(image1, // input image
result, // output image
homography, // homography
Size(2 * image1.cols, image1.rows)); // size of output image
cout << "homography:" << endl;
cout << homography << endl;
//拼接
Mat half(result, Rect(0, 0, image2.cols, image2.rows));
image2.copyTo(half);
namedWindow("Image mosaic", 0);
imshow("Image mosaic", result);
waitKey();
return 0;
}
样例2 变换矩阵如何实现变换
上面是调用库函数实现,从源码查看自己怎么实现
dst(x,y) = src((M11x+M12y+M13)/(M31x+M32y+M33), (M21x+M22y+M23)/(M31x+M32y+M33))
- void mywarpPerspective(Mat src,Mat &dst,Mat T) {
//此处注意计算模型的坐标系与Mat的不同
//图像以左上点为(0,0),向左为x轴,向下为y轴,所以前期搜索到的特征点 存的格式是(图像x,图像y)---(rows,cols)
//而Mat矩阵的是向下为x轴,向左为y轴,所以存的方向为(图像y,图像x)----(cols,rows)----(width,height)
//这个是计算的时候容易弄混的
//创建原图的四个顶点的3*4矩阵(此处我的顺序为左上,右上,左下,右下)
Mat tmp(3, 4, CV_64FC1, 1);
tmp.at < double >(0, 0) = 0;
tmp.at < double >(1, 0) = 0;
tmp.at < double >(0, 1) = src.cols;
tmp.at < double >(1, 1) = 0;
tmp.at < double >(0, 2) = 0;
tmp.at < double >(1, 2) = src.rows;
tmp.at < double >(0, 3) = src.cols;
tmp.at < double >(1, 3) = src.rows;
//获得原图四个顶点变换后的坐标,计算变换后的图像尺寸
Mat corner = T * tmp; //corner=(x,y)=(cols,rows)
int width = 0, height = 0;
double maxw = corner.at < double >(0, 0)/ corner.at < double >(2,0);
double minw = corner.at < double >(0, 0)/ corner.at < double >(2,0);
double maxh = corner.at < double >(1, 0)/ corner.at < double >(2,0);
double minh = corner.at < double >(1, 0)/ corner.at < double >(2,0);
for (int i = 1; i < 4; i++) {
maxw = max(maxw, corner.at < double >(0, i) / corner.at < double >(2, i));
minw = min (minw, corner.at < double >(0, i) / corner.at < double >(2, i));
maxh = max(maxh, corner.at < double >(1, i) / corner.at < double >(2, i));
minh = min (minh, corner.at < double >(1, i) / corner.at < double >(2, i));
}
//创建向前映射矩阵 map_x, map_y
//size(height,width)
dst.create(int(maxh - minh), int(maxw - minw), src.type());
Mat map_x(dst.size(), CV_32FC1);
Mat map_y(dst.size(), CV_32FC1);
Mat proj(3,1, CV_32FC1,1);
Mat point(3,1, CV_32FC1,1);
T.convertTo(T, CV_32FC1);
//本句是为了令T与point同类型(同类型才可以相乘,否则报错,也可以使用T.convertTo(T, point.type() );)
Mat Tinv=T.inv();
for (int i = 0; i < dst.rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < dst.cols; j++) {
point.at<float>(0) = j + minw ;
point.at<float>(1) = i + minh ;
proj = Tinv * point;
map_x.at<float>(i, j) = proj.at<float>(0)/ proj.at<float>(2) ;
map_y.at<float>(i, j) = proj.at<float>(1) / proj.at<float>(2) ;
}
}
remap(src,dst,map_x,map_y, CV_INTER_LINEAR);
}