教程http://www.mamicode.com/info-detail-1779393.html 参看如何制作
http://www.cnblogs.com/houkai/archive/2013/06/05/3119513.html 参看如何现实和隐式的调用
分类
dll
.h
lib
1动态链接库的制作
我们先来演示如何使用VS2015创建一个动态链接库。
1.新建一个“Win32控制台应用程序”,“名称”为MathFuncsDll,“解决方案名称”为DynamicLibrary,单击“确定”。
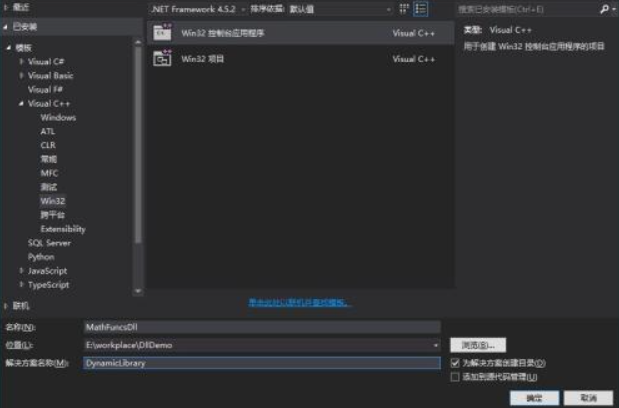
2.单击“下一步”,“应用程序类型”选择“DLL”,“附加选项”勾选“空项目”,单击“完成”。

3.为解决方案“DynamicLibrary”下的项目“MathFuncsDll”添加头文件MathFuncsDll.h,代码如下:
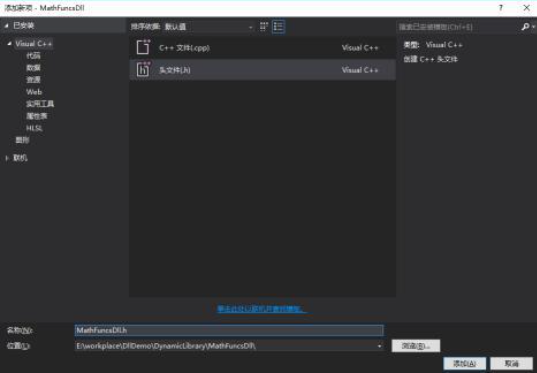
//testdll.h
#ifdef TESTDLL_EXPORTS
#define TESTDLL_API __declspec(dllexport)
#else
#define TESTDLL_API __declspec(dllimport)
#endif
namespace MathFuncs
{
// This class is exported from the testdll.dll
class MyMathFuncs
{
public:
// Returns a + b
static TESTDLL_API double Add(double a, double b);
// Returns a - b
static TESTDLL_API double Subtract(double a, double b);
// Returns a * b
static TESTDLL_API double Multiply(double a, double b);
// Returns a / b
// Throws const std::invalid_argument& if b is 0
static TESTDLL_API double Divide(double a, double b);
};
}
// testdll.cpp : 定义 DLL 应用程序的导出函数。
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "testdll.h"
#include <stdexcept>
using namespace std;
namespace MathFuncs
{
double MyMathFuncs::Add(double a, double b)
{
return a + b;
}
double MyMathFuncs::Subtract(double a, double b)
{
return a - b;
}
double MyMathFuncs::Multiply(double a, double b)
{
return a * b;
}
double MyMathFuncs::Divide(double a, double b)
{
if (b == 0)
{
throw invalid_argument("b cannot be zero!");
}
return a / b;
}
}
编译就会生成对应的dll文件,同时也会生成对应的lib文件
2动态链接库的调用
2.1隐式链接
采用静态加载的方式,比较简单,需要.h、.lib、.dll三件套。新建“控制台应用程序”或“空项目”。配置如下:
项目->属性->配置属性->VC++ 目录-> 在“包含目录”里添加头文件testdll.h所在的目录
项目->属性->配置属性->VC++ 目录-> 在“库目录”里添加头文件testdll.lib所在的目录
项目->属性->配置属性->链接器->输入-> 在“附加依赖项”里添加“testdll.lib”(若有多个 lib 则以空格隔开)
现在可以编译通过了,但是程序运行就报错,还需要将testdll.dll复制到当前项目生成的可执行文件所在的目录。
//mydll.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "testdll.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
double a = 7.4;
int b = 99;
cout << "a + b = " <<
MathFuncs::MyMathFuncs::Add(a, b) << endl;
cout << "a - b = " <<
MathFuncs::MyMathFuncs::Subtract(a, b) << endl;
cout << "a * b = " <<
MathFuncs::MyMathFuncs::Multiply(a, b) << endl;
cout << "a / b = " <<
MathFuncs::MyMathFuncs::Divide(a, b) << endl;
try
{
cout << "a / 0 = " <<
MathFuncs::MyMathFuncs::Divide(a, 0) << endl;
}
catch (const invalid_argument &e)
{
cout << "Caught exception: " << e.what() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
2.2显式链接
是应用程序在执行过程中随时可以加载DLL文件,也可以随时卸载DLL文件,这是隐式链接所无法作到的,所以显式链接具有更好的灵活性,对于解释性语言更为合适。
新建项目,不需要特殊配置,添加cpp文件
/*
*作者:侯凯
*说明:显式调用DLL
*日期:2013-6-5
*/
#include<Windows.h> //加载的头文件
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
typedef double (*pAdd)(double a, double b);
typedef double (*pSubtract)(double a, double b);
HMODULE hDLL = LoadLibrary("testdll.dll"); //加载dll文件
if(hDLL != NULL)
{
pAdd fp1 = pAdd(GetProcAddress(hDLL, MAKEINTRESOURCE(1))); //得到dll中的第一个函数
if(fp1 != NULL)
{
cout<<fp1(2.5, 5.5)<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<"Cannot Find Function "<<"add"<<endl;
}
pSubtract fp2 = pSubtract(GetProcAddress(hDLL, "?Subtract@MyMathFuncs@MathFuncs@@SANNN@Z")); //得到dll中标示为"?..."的函数,C++编译器考虑了函数的参数
if(fp2 != NULL)
{
cout<<fp2(5.5, 2.5)<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<"Cannot Find Function "<<"Subtract"<<endl;
}
FreeLibrary(hDLL);
}
else
{
std::cout<<"Cannot Find "<<"testdll"<<std::endl;
}
return 1;
}
显式调用的问题:在DLL文件中,dll工程中函数名称在编译生成DLL的过程中发生了变化(C++编译器),在DLL文件中称变化后的字符为“name标示”。GetProcAddress中第二个参数可以由DLL文件中函数的顺序获得,或者直接使用DLL文件中的”name标示”,这个标示可以通过Dumpbin.exe小程序查看。如果C++编译器下,想让函数名更规范(和原来工程中一样),具体方法详见:http://blog.csdn.net/btwsmile/article/details/6676802。
当然,为了让函数名更规范,最常用的方式是:创建dll过程中使用C编译器来编译函数,这样DLL文件中的函数名和原dll工程中的函数名就一致了。