一、position:fixed
锁定位置(相对于浏览器的位置),例如有些网站的右下角的弹出窗口。
二、position:absolute
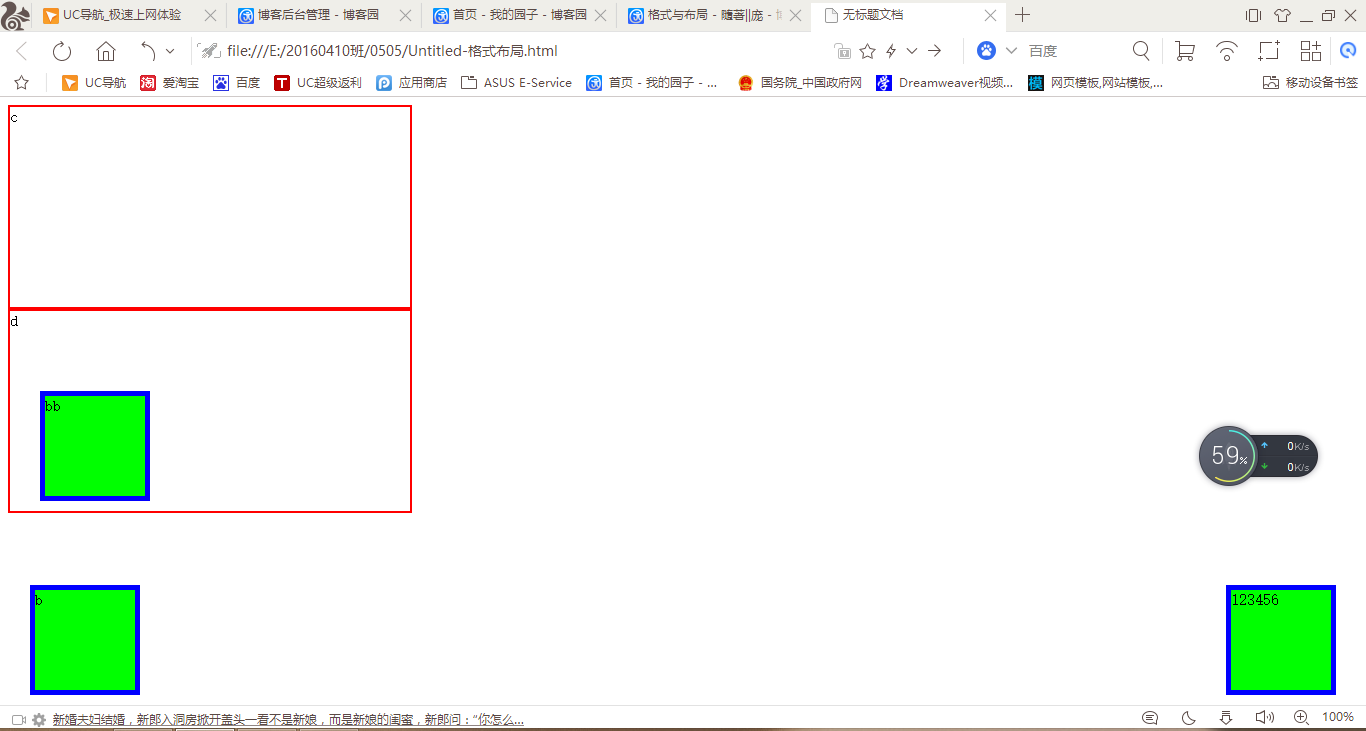
1.外层没有position:absolute(或relative);那么div相对于浏览器定位,如下图中b(距离浏览器右边框为50像素,距离下边框为20像素)。
2.外层有position:absolute(或relative);那么div相对于外层边框定位,如下图中bb(距离d的右边框50像素,距离d的下边框为20像素)。
示例:
1 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> 2 <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> 3 <head> 4 <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" /> 5 <title>无标题文档</title> 6 <style type="text/css"> 7 #a 8 { 9 border:5px solid blue; 10 background-color:#0F0; 11 width:100px; 12 height:100px; 13 margin:10px; 14 right:20px; 15 bottom:0px; 16 position:fixed;} 17 .b 18 { 19 border:5px solid blue; 20 background-color:#0F0; 21 width:100px; 22 height:100px; 23 margin:10px; 24 left:20px; 25 bottom:0px; 26 position:absolute;} 27 .c 28 { 29 width:400px; 30 height:200px; 31 border:2px double red;} 32 .d 33 { 34 width:400px; 35 height:200px; 36 border:2px double red; 37 position:absolute;} 38 </style> 39 </head> 40 41 <body><div id="a">123456</div> 42 <div class="c">c<div class="b">b</div></div> 43 <div class="d">d<div class="b">bb</div></div> 44 45 </body> 46 </html>
效果显示:
三、position:relative
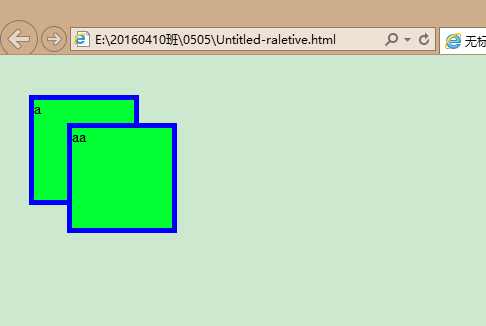
相对位置。
如下图,相对于把此div包含住的div的某个位置进行固定。如果外层没有包含他的,那就相对于浏览器进行相对位置的固定。
示例:
1 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> 2 <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> 3 <head> 4 <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" /> 5 <title>无标题文档</title> 6 <style type="text/css"> 7 #a 8 { 9 border:5px solid blue; 10 background-color:#0F3; 11 width:100px; 12 height:100px; 13 left:30px; 14 top:40px; 15 position:fixed; 16 17 } 18 #aa 19 { 20 border:5px solid blue; 21 background-color:#0F3; 22 width:100px; 23 height:100px; 24 left:60px; 25 top:60px; 26 position:relative;} 27 </style> 28 29 30 </head> 31 32 <body> 33 <div id="a">a</div> 34 <div id="aa">aa</div> 35 </body> 36 </html>
效果显示:
四、分层(z-index)
在z轴方向分层,可以理解为分成一摞纸,层数越高越靠上。
在上面relative的示例中,我们看到了aa遮住了a,这是因为后写代码的显示级别越靠前,那么在不改变代码顺序的情况下如何让a盖住aa?如下:
示例:
1 <style type="text/css"> 2 #a 3 { 4 border:5px solid blue; 5 background-color:#0F3; 6 width:100px; 7 height:100px; 8 margin:0px; 9 left:30px; 10 top:40px; 11 position:fixed; 12 z-index:2;/*这里修改一下,默认情况下,层数是1*/ 13 } 14 #aa 15 { 16 border:5px solid blue; 17 background-color:#0F3; 18 width:100px; 19 height:100px; 20 margin:0px; 21 left:60px; 22 top:60px; 23 position:relative;} 24 </style>
效果图:

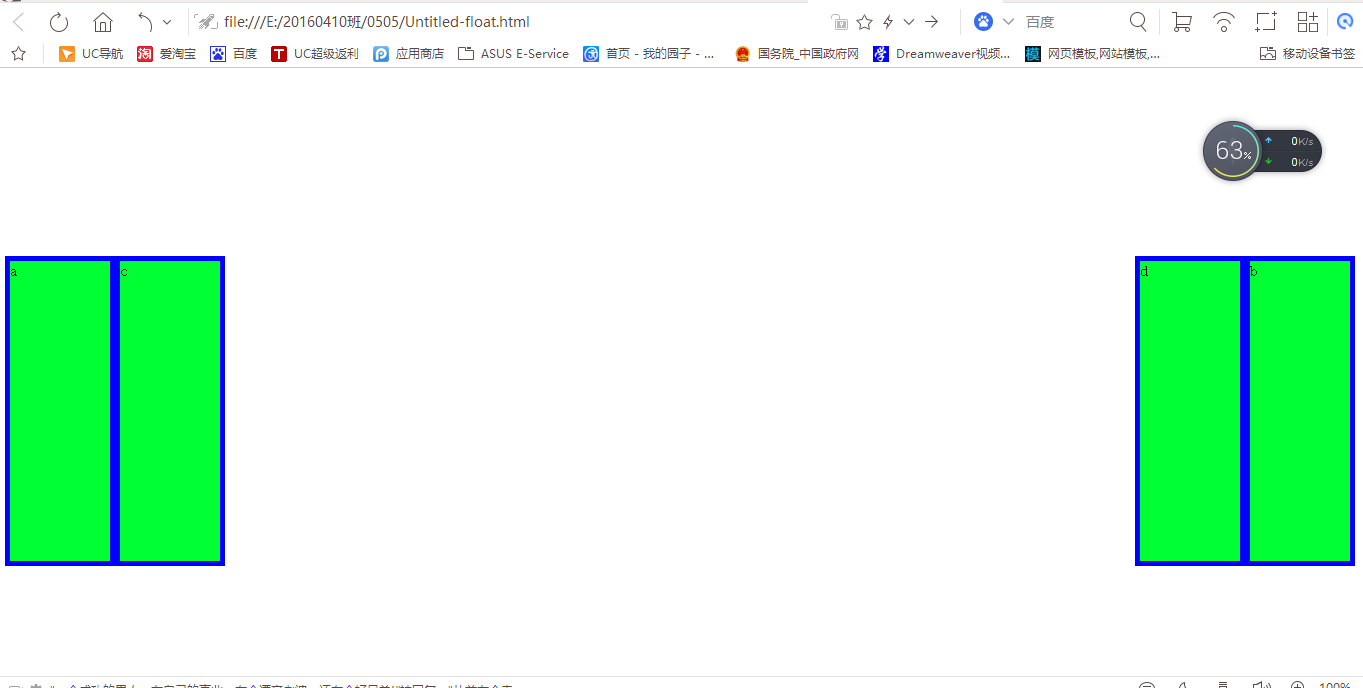
五、float:left、right
Left、right时不用给他规定位置(left、top),直接相对于浏览器。若外部被包裹,相对于外部div的除去一行的位置的左上或右上显示。
示例:
1 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> 2 <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> 3 <head> 4 <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" /> 5 <title>无标题文档</title> 6 <style> 7 #a 8 { 9 border:5px solid blue; 10 background-color:#0F3; 11 width:100px; 12 height:300px; 13 float:left; 14 cursor:pointer;} 15 #b 16 { 17 border:5px solid blue; 18 background-color:#0F3; 19 width:100px; 20 height:300px; 21 float:right;} 22 </style> 23 24 </head> 25 26 <body><br /> 27 <br /> 28 <br /> 29 <br /> 30 <br /> 31 <br /> 32 <br /> 33 <br /> 34 <br /> 35 <br /> 36 37 <div id="a">a</div> 38 <div id="b">b</div> 39 <div id="a">c</div> 40 <div id="b">d</div> 41 </body> 42 </html>
效果图:
overflow:hidden; //超出部分隐藏;scroll,显示出滚动条;
<div style="clear:both"></div> //截断流
设置超链接的样式示例:
1 <style type="text/css"> 2 a:link/*超链接被点前状态*/ 3 { 4 text-decoration:none; 5 color:#000;} 6 a:visited/*超链接点击后状态*/ 7 { 8 text-decoration:none; 9 color:#000; 10 } 11 a:hover/*悬停在超链接时*/ 12 { 13 text-decoration:underline; 14 color:#F00;} 15 a:active/*点击超链接时*/ 16 { 17 text-decoration:underline; 18 color:#F60;} 19 </style>
附:cursor:pointer 鼠标指到上面时的形状
© 版权符号©
半透明效果:
<div class="box">透明区域<div>
在样式表中的代码为:
.box
{
opacity:0.5; -moz-opacity:0.5 ; filter:alpha(opacity=50)
}