C语言中为什么会有结构体
主要是基本数据类型没有办法展现我们需要的实体。比如我们要表现一个实体————人,那么我们需要姓名name,年龄age,性别sex,家庭关系如父母parent等等。
C语言如何定义结构体
在C语言中,可以使用结构体(Struct)来存放一组不同类型的数据。结构体的定义形式为:
struct 结构体名{
结构体所包含的变量或数组
};
结构体是一种集合,它里面包含了多个变量或数组,它们的类型可以相同,也可以不同,每个这样的变量或数组都称为结构体的成员(Member)。请看下面的一个例子:
struct Person {
char* name; // 姓名
int age; // 年龄
int sex; // 姓名
Person* parent; // 父母
};
注意点1:以分号结尾
注意大括号后面的分号;不能少,这是一条完整的语句。
如果不加这个分号,会出现编译错误: error C2628: “Person”后面接“int”是非法的(是否忘记了“;”?)
注意点2:结构体成员类型为自身
当结构体内的成员变量的类型是自身时,需要用指针。
比如Person中引用Person类型的变量parent,此时需要用指针来保存引用。否则会出现编译错误:error C2460: “Person::parent”: 使用正在定义的“Person”
C语言结构体的大小
我们先在32位编译模式下编译以下程序:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct A {
char c1;
char c2;
int i;
};
struct B {
char c1;
int i;
char c2;
};
int main()
{
printf("Size of A: %d bytes.
", sizeof(A));
printf("Size of B: %d bytes.
", sizeof(B));
A a = {'a', 'b', 1024};
printf("&a.c1:0x%08X
&a.c2:0x%08X
&a.i:0x%08X
", &a.c1, &a.c2, &a.i);
B b = {'A', 65536, 'B'};
printf("&b.c1:0x%08X
&b.i:0x%08X
&b.c2:0x%08X
", &b.c1, &b.i, &b.c2);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
&是取地址符,可以获取变量的内存地址%08X表示以16进制表示,字母大写,最小宽度为8,如果不足8位,以0补足。
一次实验的输出结果如下:
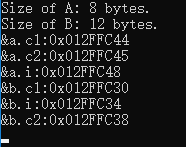
- 结构体A与结构体B的大小不等。结构体A的大小为8字节,结构体B的大小为12字节。

- 上图中一个单元格表示一个字节单元;
- 每个字节单元都对应一个内存地址;
- 内存地址由下向上依次增加;
成员的获取与赋值
1. 定义变量
Person person1;
struct Person person2;
这两种方式均可,前面可以写struct,也可以不写
2. 给结构体成员赋值
Person person1;
person1.age = 10;
3. 访问结构体成员
printf("%d", person1.age);
4. 整体赋值
之前用到的这两条语句就是整体赋值的例子:
A a = {'a', 'b', 1024};
B b = {'A', 65536, 'B'};
- 不过整体赋值仅限于定义结构体变量的时候,在使用过程中只能对成员逐一赋值,这和数组的赋值非常类似。
5. 定义结构体和定义变量结合
struct Student {
char *name; //姓名
int num; //学号
int age; //年龄
char group; //所在小组
float score; //成绩
} stu1, stu2 = { "Tom", 12, 18, 'A', 136.5 };
上面这段代码相当于把定义结构体和定义变量的代码组合起来了:
// 定义结构体Student
struct Student {
char *name; //姓名
int num; //学号
int age; //年龄
char group; //所在小组
float score; //成绩
};
并且,变量stu1没有赋值,而变量stu2进行了整体赋值:
// 定义变量
Student stu1;
Student stu2 = { "Tom", 12, 18, 'A', 136.5 };
typedef struct
typedef struct Student {...} Stu;与struct Student {...} stu;不同,前者Stu表示的是类型(相当于Student的别名),后者stu表示的是变量;typedef struct Student {...} Stu;相当于定义结构体语句struct Student {...};与定义类型语句typedef Student Stu;的组合;struct Student {...} stu;相当于定义结构体语句struct Student {...};与定义变量语句Student stu的组合;
我们再来看一个 typedef struct 的复杂例子:
typedef struct Student {
char *name; //姓名
int num; //学号
int age; //年龄
char group; //所在小组
float score; //成绩
} Stu, *PStu;
然后,我们可以用 PStu 来表示指针类型:
PStu stu1 = (PStu)malloc(sizeof(PStu));
stu1->age = 11;
上面这段代码就等同于
Stu* stu1 = (Stu*)malloc(sizeof(Stu));
stu1->age = 11;
Learn More
《C语言结构体详解,C语言struct用法详解》阅读