一、LocalStreamEnvironment
LocalStreamEnvironment 是 StreamExecutionEnvironment 的子类,它在本地、多线程、在实例化LocalStreamEnvironment的 JVM 中运行程序。
它在后台生成一个嵌入式 Flink 集群并在该集群上执行程序。
实例化此环境时,它使用默认并行性(默认值为1)。默认并行度可以通过 setParallelism(int) 设置。
我们通常会在写完 Stream API 后,调用 env.execute() 方法。如果在本地执行,则会调用 LocalStreamEnvironment#execute 方法,方法中的第一段源码为:
StreamGraph streamGraph = getStreamGraph();
streamGraph.setJobName(jobName);
接着继续跟踪 StreamExecutionEnvironment#getStreamGraph() 的源码:
/**
* Getter of the {@link org.apache.flink.streaming.api.graph.StreamGraph} of the streaming job.
*
* @return The streamgraph representing the transformations
*/
@Internal
public StreamGraph getStreamGraph() {
if (transformations.size() <= 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No operators defined in streaming topology. Cannot execute.");
}
return StreamGraphGenerator.generate(this, transformations);
}
这段源码也非常简单,生成 StreamGraph 的逻辑封装在 StreamGraphGenerator 中。
二、StreamGraphGenerator
继续跟踪代码,将 StreamExecutionEnvironment 的实例对象传递给 StreamGraphGenerator 并创建对象后,就调用了 StreamGraphGenerator#generateInternal 方法:
/**
* This starts the actual transformation, beginning from the sinks.
*/
private StreamGraph generateInternal(List<StreamTransformation<?>> transformations) {
for (StreamTransformation<?> transformation: transformations) {
transform(transformation);
}
return streamGraph;
}
这里遍历的 transformations 保存的是我在上一节《Flink执行计划第一层——StreamTransformation》中提到的由我们的 Stream API 代码生成的StreamTransformation集合。
2.1 transform
接下来我们来跟踪一下 StreamGraphGenerator#transform 的代码:
/**
* Transforms one {@code StreamTransformation}.
*
* <p>This checks whether we already transformed it and exits early in that case. If not it
* delegates to one of the transformation specific methods.
*/
private Collection<Integer> transform(StreamTransformation<?> transform) {
if (alreadyTransformed.containsKey(transform)) {
return alreadyTransformed.get(transform);
}
LOG.debug("Transforming " + transform);
if (transform.getMaxParallelism() <= 0) {
// if the max parallelism hasn't been set, then first use the job wide max parallelism
// from the ExecutionConfig.
int globalMaxParallelismFromConfig = env.getConfig().getMaxParallelism();
if (globalMaxParallelismFromConfig > 0) {
transform.setMaxParallelism(globalMaxParallelismFromConfig);
}
}
// call at least once to trigger exceptions about MissingTypeInfo
transform.getOutputType();
Collection<Integer> transformedIds;
if (transform instanceof OneInputTransformation<?, ?>) {
transformedIds = transformOneInputTransform((OneInputTransformation<?, ?>) transform);
} else if (transform instanceof TwoInputTransformation<?, ?, ?>) {
transformedIds = transformTwoInputTransform((TwoInputTransformation<?, ?, ?>) transform);
} else if (transform instanceof SourceTransformation<?>) {
transformedIds = transformSource((SourceTransformation<?>) transform);
} else if (transform instanceof SinkTransformation<?>) {
transformedIds = transformSink((SinkTransformation<?>) transform);
} else if (transform instanceof UnionTransformation<?>) {
transformedIds = transformUnion((UnionTransformation<?>) transform);
} else if (transform instanceof SplitTransformation<?>) {
transformedIds = transformSplit((SplitTransformation<?>) transform);
} else if (transform instanceof SelectTransformation<?>) {
transformedIds = transformSelect((SelectTransformation<?>) transform);
} else if (transform instanceof FeedbackTransformation<?>) {
transformedIds = transformFeedback((FeedbackTransformation<?>) transform);
} else if (transform instanceof CoFeedbackTransformation<?>) {
transformedIds = transformCoFeedback((CoFeedbackTransformation<?>) transform);
} else if (transform instanceof PartitionTransformation<?>) {
transformedIds = transformPartition((PartitionTransformation<?>) transform);
} else if (transform instanceof SideOutputTransformation<?>) {
transformedIds = transformSideOutput((SideOutputTransformation<?>) transform);
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unknown transformation: " + transform);
}
// need this check because the iterate transformation adds itself before
// transforming the feedback edges
if (!alreadyTransformed.containsKey(transform)) {
alreadyTransformed.put(transform, transformedIds);
}
if (transform.getBufferTimeout() >= 0) {
streamGraph.setBufferTimeout(transform.getId(), transform.getBufferTimeout());
}
if (transform.getUid() != null) {
streamGraph.setTransformationUID(transform.getId(), transform.getUid());
}
if (transform.getUserProvidedNodeHash() != null) {
streamGraph.setTransformationUserHash(transform.getId(), transform.getUserProvidedNodeHash());
}
if (transform.getMinResources() != null && transform.getPreferredResources() != null) {
streamGraph.setResources(transform.getId(), transform.getMinResources(), transform.getPreferredResources());
}
return transformedIds;
}
transform 方法是会被递归调用的方法:
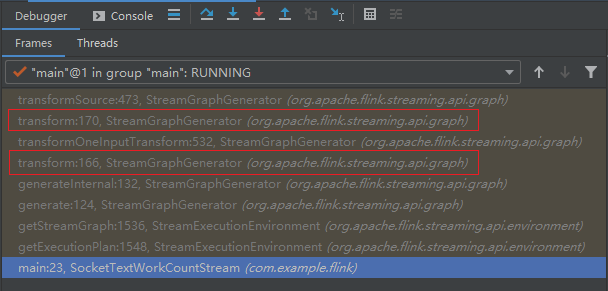
根据 《入门Flink的第一个程序——WordCount》 的例子,我画出了对应的示意图:
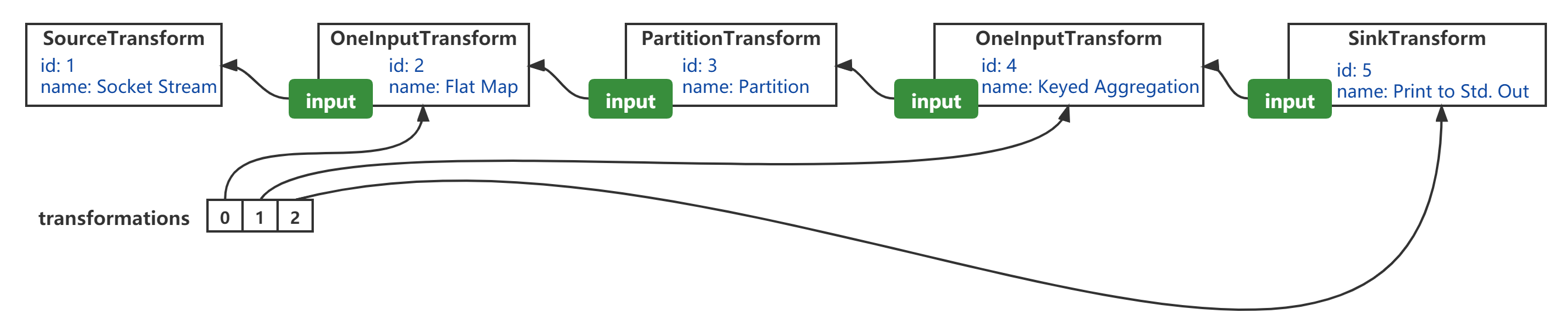
transformations表示的是StreamExecutionEnvironment的成员变量,同时也是StreamGraphGenerator#generateInternal(List<StreamTransformation<?>>)的方法参数;- 从“逻辑顺序”来看,
transform方法的转换顺序,实质上是从SourceTransformation“逆向”沿着input引用,经过OneInputTransformation(id=2)、PartitionTransformation、OneInputTransformation(id=4),到达SinkTransformation
2.2 transformSource
所以,我们现在可以按顺序来看源码了,所以首先看针对 SourceTransformation 的转换方法 transformSource :
/**
* Transforms a {@code SourceTransformation}.
*/
private <T> Collection<Integer> transformSource(SourceTransformation<T> source) {
String slotSharingGroup = determineSlotSharingGroup(source.getSlotSharingGroup(), Collections.emptyList());
streamGraph.addSource(source.getId(),
slotSharingGroup,
source.getCoLocationGroupKey(),
source.getOperator(),
null,
source.getOutputType(),
"Source: " + source.getName());
if (source.getOperator().getUserFunction() instanceof InputFormatSourceFunction) {
InputFormatSourceFunction<T> fs = (InputFormatSourceFunction<T>) source.getOperator().getUserFunction();
streamGraph.setInputFormat(source.getId(), fs.getFormat());
}
streamGraph.setParallelism(source.getId(), source.getParallelism());
streamGraph.setMaxParallelism(source.getId(), source.getMaxParallelism());
return Collections.singleton(source.getId());
}
StreamGraphGenerator#transformSource 最核心的逻辑就是 StreamGraph#addSource 方法,这个下一小节再讨论。
-
transformSource主要作用就是将SourceTransformation转换出StreamNode,用于组成StreamGraph。 -
transformSource方法执行完成后,继续回到transform方法,将当前转换好的SourceTransformation对象 put 到StreamGraphGenerator的成员变量alreadyTransformed: Map<StreamTransformation<?> Collection<Integer>>;
2.3 transformOneInputTransform
以下是 StreamGraphGenerator 的 transformOneInputTransform 的源码:
/**
* Transforms a {@code OneInputTransformation}.
*
* <p>This recursively transforms the inputs, creates a new {@code StreamNode} in the graph and
* wired the inputs to this new node.
*/
private <IN, OUT> Collection<Integer> transformOneInputTransform(OneInputTransformation<IN, OUT> transform) {
//
Collection<Integer> inputIds = transform(transform.getInput());
// the recursive call might have already transformed this
if (alreadyTransformed.containsKey(transform)) {
return alreadyTransformed.get(transform);
}
String slotSharingGroup = determineSlotSharingGroup(transform.getSlotSharingGroup(), inputIds);
streamGraph.addOperator(transform.getId(),
slotSharingGroup,
transform.getCoLocationGroupKey(),
transform.getOperator(),
transform.getInputType(),
transform.getOutputType(),
transform.getName());
if (transform.getStateKeySelector() != null) {
TypeSerializer<?> keySerializer = transform.getStateKeyType().createSerializer(env.getConfig());
streamGraph.setOneInputStateKey(transform.getId(), transform.getStateKeySelector(), keySerializer);
}
streamGraph.setParallelism(transform.getId(), transform.getParallelism());
streamGraph.setMaxParallelism(transform.getId(), transform.getMaxParallelism());
for (Integer inputId: inputIds) {
streamGraph.addEdge(inputId, transform.getId(), 0);
}
return Collections.singleton(transform.getId());
}
transformOneInputTransform 调用了 StreamGraph 的 addOperator 方法来创建 StreamNode,同时还调用了 addEdge 方法来添加 StreamEdge,这个在下一小节再分析。
2.4 transformPartition
接着再来看一下 StreamGraphGenerator 的 transformPartition 的源码:
/**
* Transforms a {@code PartitionTransformation}.
*
* <p>For this we create a virtual node in the {@code StreamGraph} that holds the partition
* property. @see StreamGraphGenerator
*/
private <T> Collection<Integer> transformPartition(PartitionTransformation<T> partition) {
StreamTransformation<T> input = partition.getInput();
List<Integer> resultIds = new ArrayList<>();
Collection<Integer> transformedIds = transform(input);
for (Integer transformedId: transformedIds) {
// 注意,这里生成了新的唯一id
int virtualId = StreamTransformation.getNewNodeId();
streamGraph.addVirtualPartitionNode(transformedId, virtualId, partition.getPartitioner());
resultIds.add(virtualId);
}
return resultIds;
}
transformPartition 又调用了 StreamGraph 的 addVirtualPartitionNode 方法,这个方法也在下一小节解析。
2.5 transformSink
最后,来看一下 StreamGraphGenerator 的 transformSink 的源码:
/**
* Transforms a {@code SourceTransformation}.
*/
private <T> Collection<Integer> transformSink(SinkTransformation<T> sink) {
Collection<Integer> inputIds = transform(sink.getInput());
String slotSharingGroup = determineSlotSharingGroup(sink.getSlotSharingGroup(), inputIds);
streamGraph.addSink(sink.getId(),
slotSharingGroup,
sink.getCoLocationGroupKey(),
sink.getOperator(),
sink.getInput().getOutputType(),
null,
"Sink: " + sink.getName());
streamGraph.setParallelism(sink.getId(), sink.getParallelism());
streamGraph.setMaxParallelism(sink.getId(), sink.getMaxParallelism());
for (Integer inputId: inputIds) {
streamGraph.addEdge(inputId,
sink.getId(),
0
);
}
if (sink.getStateKeySelector() != null) {
TypeSerializer<?> keySerializer = sink.getStateKeyType().createSerializer(env.getConfig());
streamGraph.setOneInputStateKey(sink.getId(), sink.getStateKeySelector(), keySerializer);
}
return Collections.emptyList();
}
transformSink 又调用了 StreamGraph 的 addSink 方法,同时也调用了 addEdge 方法,这些方法也将在下一小节解析。
三、StreamGraph
首先,这里用到了“图”(Graph) 这种数据结构。
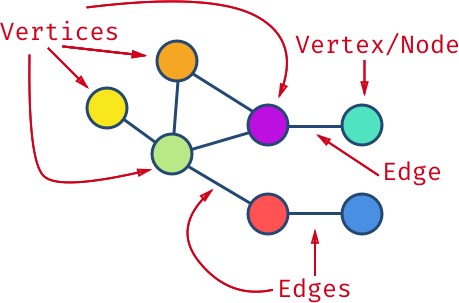
- 图包含若干个节点(Node);
- 两个节点相连的部分称为边(Edge);
- 节点也被称作顶点(Vertex);
3.1 addSource&addSink
我们来看一下 StreamGraph 的 addSource 和 addSink 源码:
public <IN, OUT> void addSource(Integer vertexID,
String slotSharingGroup,
@Nullable String coLocationGroup,
StreamOperator<OUT> operatorObject,
TypeInformation<IN> inTypeInfo,
TypeInformation<OUT> outTypeInfo,
String operatorName) {
addOperator(vertexID, slotSharingGroup, coLocationGroup, operatorObject, inTypeInfo, outTypeInfo, operatorName);
sources.add(vertexID);
}
public <IN, OUT> void addSink(Integer vertexID,
String slotSharingGroup,
@Nullable String coLocationGroup,
StreamOperator<OUT> operatorObject,
TypeInformation<IN> inTypeInfo,
TypeInformation<OUT> outTypeInfo,
String operatorName) {
addOperator(vertexID, slotSharingGroup, coLocationGroup, operatorObject, inTypeInfo, outTypeInfo, operatorName);
sinks.add(vertexID);
}
sources用来记录图中作为“数据源”的顶点的idsinks用来记录图中作为“终点”的顶点的id
两者调用了相同的方法 addOperator。
3.2 addOperator&&addNode
对 addOperator 的调用有三处:

源码如下:
public <IN, OUT> void addOperator(
Integer vertexID,
String slotSharingGroup,
@Nullable String coLocationGroup,
StreamOperator<OUT> operatorObject,
TypeInformation<IN> inTypeInfo,
TypeInformation<OUT> outTypeInfo,
String operatorName) {
if (operatorObject instanceof StoppableStreamSource) {
addNode(vertexID, slotSharingGroup, coLocationGroup, StoppableSourceStreamTask.class, operatorObject, operatorName);
} else if (operatorObject instanceof StreamSource) {
addNode(vertexID, slotSharingGroup, coLocationGroup, SourceStreamTask.class, operatorObject, operatorName);
} else {
addNode(vertexID, slotSharingGroup, coLocationGroup, OneInputStreamTask.class, operatorObject, operatorName);
}
TypeSerializer<IN> inSerializer = inTypeInfo != null && !(inTypeInfo instanceof MissingTypeInfo) ? inTypeInfo.createSerializer(executionConfig) : null;
TypeSerializer<OUT> outSerializer = outTypeInfo != null && !(outTypeInfo instanceof MissingTypeInfo) ? outTypeInfo.createSerializer(executionConfig) : null;
setSerializers(vertexID, inSerializer, null, outSerializer);
if (operatorObject instanceof OutputTypeConfigurable && outTypeInfo != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
OutputTypeConfigurable<OUT> outputTypeConfigurable = (OutputTypeConfigurable<OUT>) operatorObject;
// sets the output type which must be know at StreamGraph creation time
outputTypeConfigurable.setOutputType(outTypeInfo, executionConfig);
}
if (operatorObject instanceof InputTypeConfigurable) {
InputTypeConfigurable inputTypeConfigurable = (InputTypeConfigurable) operatorObject;
inputTypeConfigurable.setInputType(inTypeInfo, executionConfig);
}
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("Vertex: {}", vertexID);
}
}
这段方法,首先就是要创建节点(addNode),然后对节点进行设置。
protected StreamNode addNode(Integer vertexID,
String slotSharingGroup,
@Nullable String coLocationGroup,
Class<? extends AbstractInvokable> vertexClass,
StreamOperator<?> operatorObject,
String operatorName) {
if (streamNodes.containsKey(vertexID)) {
throw new RuntimeException("Duplicate vertexID " + vertexID);
}
StreamNode vertex = new StreamNode(environment,
vertexID,
slotSharingGroup,
coLocationGroup,
operatorObject,
operatorName,
new ArrayList<OutputSelector<?>>(),
vertexClass);
// 顶点id映射顶点对象
streamNodes.put(vertexID, vertex);
return vertex;
}
3.3 addEdge
StreamGraph 的 addEdge 方法的源码很简单,主要逻辑还是在 addEdgeInternal 中:
public void addEdge(Integer upStreamVertexID, Integer downStreamVertexID, int typeNumber) {
addEdgeInternal(upStreamVertexID,
downStreamVertexID,
typeNumber,
null,
new ArrayList<String>(),
null);
}
而 addEdgeInternal 是一个可以递归调用的方法:
private void addEdgeInternal(Integer upStreamVertexID,
Integer downStreamVertexID,
int typeNumber,
StreamPartitioner<?> partitioner,
List<String> outputNames,
OutputTag outputTag) {
if (virtualSideOutputNodes.containsKey(upStreamVertexID)) {
int virtualId = upStreamVertexID;
upStreamVertexID = virtualSideOutputNodes.get(virtualId).f0;
if (outputTag == null) {
outputTag = virtualSideOutputNodes.get(virtualId).f1;
}
addEdgeInternal(upStreamVertexID, downStreamVertexID, typeNumber, partitioner, null, outputTag);
} else if (virtualSelectNodes.containsKey(upStreamVertexID)) {
int virtualId = upStreamVertexID;
upStreamVertexID = virtualSelectNodes.get(virtualId).f0;
if (outputNames.isEmpty()) {
// selections that happen downstream override earlier selections
outputNames = virtualSelectNodes.get(virtualId).f1;
}
addEdgeInternal(upStreamVertexID, downStreamVertexID, typeNumber, partitioner, outputNames, outputTag);
} else if (virtualPartitionNodes.containsKey(upStreamVertexID)) {
int virtualId = upStreamVertexID;
upStreamVertexID = virtualPartitionNodes.get(virtualId).f0;
if (partitioner == null) {
partitioner = virtualPartitionNodes.get(virtualId).f1;
}
addEdgeInternal(upStreamVertexID, downStreamVertexID, typeNumber, partitioner, outputNames, outputTag);
} else {
StreamNode upstreamNode = getStreamNode(upStreamVertexID);
StreamNode downstreamNode = getStreamNode(downStreamVertexID);
// If no partitioner was specified and the parallelism of upstream and downstream
// operator matches use forward partitioning, use rebalance otherwise.
if (partitioner == null && upstreamNode.getParallelism() == downstreamNode.getParallelism()) {
partitioner = new ForwardPartitioner<Object>();
} else if (partitioner == null) {
partitioner = new RebalancePartitioner<Object>();
}
if (partitioner instanceof ForwardPartitioner) {
if (upstreamNode.getParallelism() != downstreamNode.getParallelism()) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Forward partitioning does not allow " +
"change of parallelism. Upstream operation: " + upstreamNode + " parallelism: " + upstreamNode.getParallelism() +
", downstream operation: " + downstreamNode + " parallelism: " + downstreamNode.getParallelism() +
" You must use another partitioning strategy, such as broadcast, rebalance, shuffle or global.");
}
}
StreamEdge edge = new StreamEdge(upstreamNode, downstreamNode, typeNumber, outputNames, partitioner, outputTag);
getStreamNode(edge.getSourceId()).addOutEdge(edge);
getStreamNode(edge.getTargetId()).addInEdge(edge);
}
}
3.4 创建图的过程
- addNode 创建 StreamNode(id=1):

- addNode 创建 StreamNode(id=2):

- addEdge 创建 StreamNode(id=1)和 StreamNode(id=2)之间的边 StreamEdge,然后添加到 StreamNode(id=1)的 outEdges 列表以及 StreamNode(id=2)的 inEdges 列表:
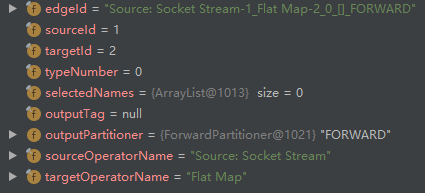
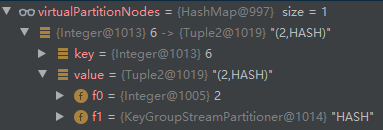
- addVirtualPartitionNode 新增 id=6 的虚拟节点,输入节点 id=2:
- addNode 创建 StreamNode(id=4):

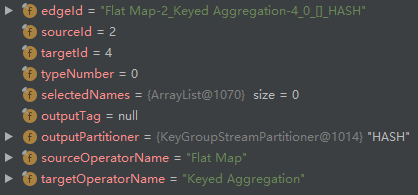
- addEdge 创建 StreamNode(id=2)和 StreamNode(id=4)之间的边 ,然后添加到 StreamNode(id=2)的 outEdges 列表以及 StreamNode(id=4)的 inEdges 列表:
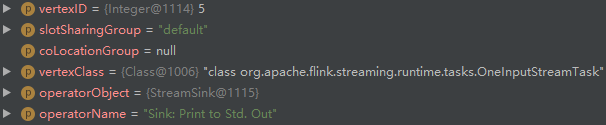
- addNode 创建 StreamNode(id=5):
- addEdge 创建 StreamNode(id=4)和 StreamNode(id=5)之间的边 ,然后添加到 StreamNode(id=4)的 outEdges 列表以及 StreamNode(id=5)的 inEdges 列表:
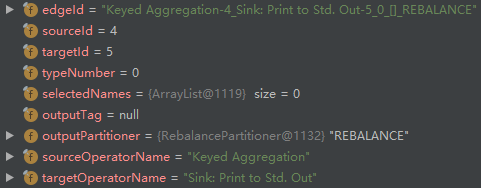
观察对比第3步和第8步,可以发现 outputPartitioner 不相同,一个是 ForwardPartitioner,另一个是 RebalancePartitioner,如果两个节点的 parallelism 相等,使用前者,不相等则使用后者。
判断逻辑的源码如下:
// If no partitioner was specified and the parallelism of upstream and downstream
// operator matches use forward partitioning, use rebalance otherwise.
if (partitioner == null && upstreamNode.getParallelism() == downstreamNode.getParallelism()) {
partitioner = new ForwardPartitioner<Object>();
} else if (partitioner == null) {
partitioner = new RebalancePartitioner<Object>();
}
四、小结
StreamExecutionEnvironment 的 getExecutionPlan 方法返回类型正是 StreamGraph,在《Flink执行计划第一层——StreamTransformation》 已经展示过执行计划的可视化功能了,最后再摆一次这张图:
