首先,我们看使用原生的JDBC来操作数据库的方式:
// 1. 获取JDBC Connection Connection connection = DbManager.getConnectoin(); // 2. 组装sql语句 String sql = "insert into temp(id, name) values(?,?)"; // 3. 构造 PreparedStatement PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 4. 为 PreparedStatement 设置参数 ps.setLong(1, 1L); ps.setString(2, "aaa"); // 5. 执行 PreparedStatement int count = ps.executeUpdate();
那么,MyBatis是如何对上面的过程进行封装的呢?
我们以update为例,看MyBatis是如何封装这几个步骤的:
sql执行的入口:
DefaultSqlSession.update(String statement, Object parameter) --> Executor.update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) -->
SimpleExecutor.doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter)
DefaultSqlSession.update(String, Object)
public int update(String statement, Object parameter) { try { dirty = true; MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement); // 将mapper中的sql解析成原生的JDBC能够识别的sql,其中包括MyBatis标签的解析,"#{key,JdbcType=XXX}"占位符替换成"?" return executor.update(ms, wrapCollection(parameter)); // 构造java.sql.PreparedStatement --> 往java.sql.PreparedStatement设置sql的参数 --> 执行sql语句 } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error updating database. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
可以看出,MyBatis将这个过程封装成了两步:
1. sql语句解析 (解析sql,替换占位符为"?")
2. sql语句执行 (设置sql中的参数,执行sql)
### 1. sql语句解析
configuration.getMappedStatement(statement)会去解析MyBatis的标签(比如:<foreach>、<if>等),并且将"#{key, JdbcType=XXX}"替换成原生的JDBC看的懂的占位符"?"。
流程如下:
Configuration.getMappedStatement(String, boolean) --> Configuration.buildAllStatements() --> MapperAnnotationBuilder.parseStatement(Method) --> MapperAnnotationBuilder.buildSqlSourceFromStrings(String[], Class<?>, LanguageDriver) --> RawLanguageDriver.createSqlSource(Configuration, String, Class<?>) --> XMLLanguageDriver.createSqlSource(Configuration, String, Class<?>)
20170721更新:(xml应该是如下)
Configuration.getMappedStatement(String, boolean) --> Configuration.buildAllStatements() --> XMLStatementBuilder.parseStatementNode() --> LanguageDriver.createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, XNode script, Class<?> parameterType) --> RawLanguageDriver.createSqlSource(Configuration, String, Class<?>) --> XMLLanguageDriver.createSqlSource(Configuration, String, Class<?>)
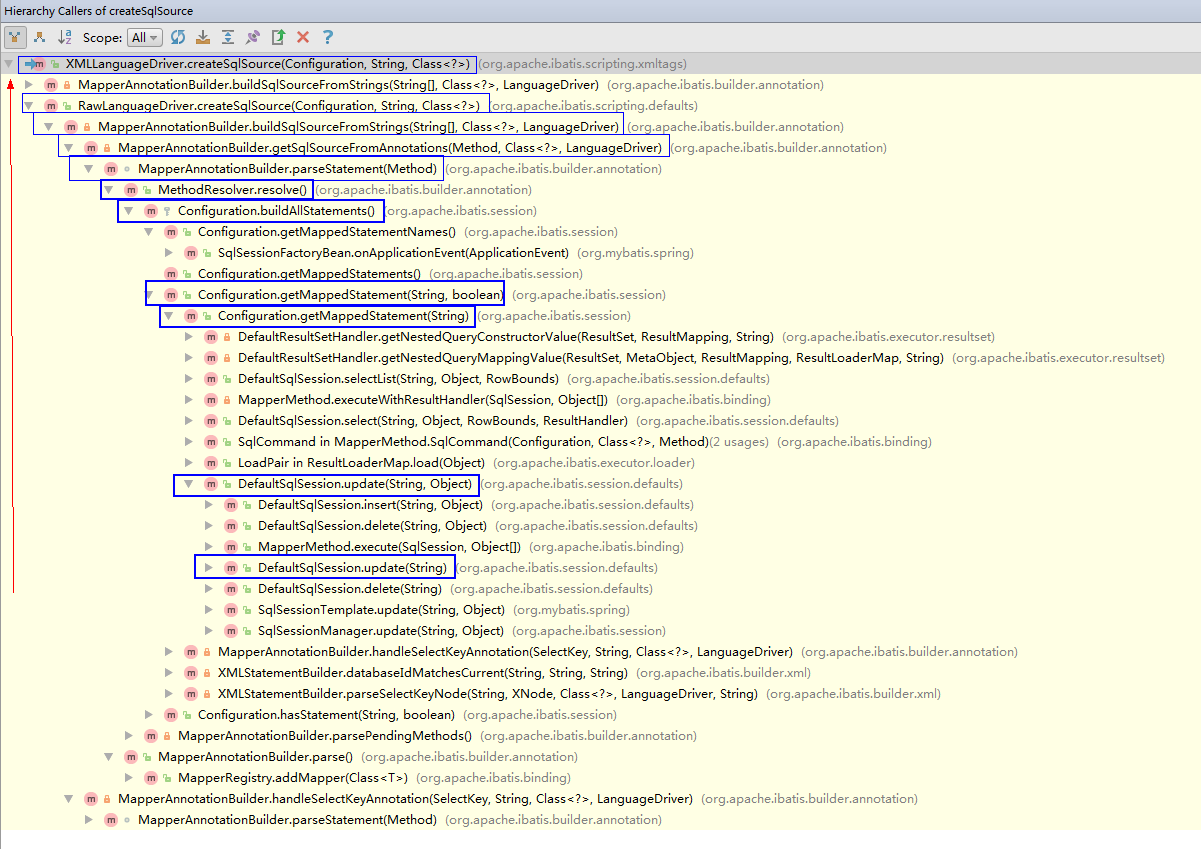
可以看出,MyBatis中的动态SQL解析是通过别名为 xml 语言驱动器 org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.XmlLanguageDriver 驱动解析的。
public class XMLLanguageDriver implements LanguageDriver { public ParameterHandler createParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) { return new DefaultParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql); } public SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, XNode script, Class<?> parameterType) { XMLScriptBuilder builder = new XMLScriptBuilder(configuration, script, parameterType); return builder.parseScriptNode(); } public SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String script, Class<?> parameterType) { if (script.startsWith("<script>")) { // issue #3 XPathParser parser = new XPathParser(script, false, configuration.getVariables(), new XMLMapperEntityResolver()); return createSqlSource(configuration, parser.evalNode("/script"), parameterType); } else { script = PropertyParser.parse(script, configuration.getVariables()); // issue #127 TextSqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode(script); if (textSqlNode.isDynamic()) { // 动态sql解析入口 return new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, textSqlNode); } else { return new RawSqlSource(configuration, script, parameterType); } } } }
DynamicSqlSource.java
public class DynamicSqlSource implements SqlSource { private Configuration configuration; private SqlNode rootSqlNode; public DynamicSqlSource(Configuration configuration, SqlNode rootSqlNode) { this.configuration = configuration; this.rootSqlNode = rootSqlNode; } public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) { DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, parameterObject); // 构造DynamicContext,并将DynamicContext中的属性ContextMap bindings赋值 rootSqlNode.apply(context); // 处理sql中的标签,比如:<foreach>、<if>等 SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration); Class<?> parameterType = parameterObject == null ? Object.class : parameterObject.getClass(); SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings()); // 将占位符"#{key, jdbcType=XXX}"替换成占位符"?"。也就是原生的java.sql.PreparedStatement支持的占位符。(具体是通过GenericTokenParser#parse(String text)来实现的) BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject); // 构造BoundSql for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : context.getBindings().entrySet()) { boundSql.setAdditionalParameter(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()); // 将参数的key和value存放至BoundSql的MetaObject metaParameters;中 } return boundSql; } }
####2. sql语句执行
通过SimpleExecutor.java 去执行sql语句。其中,最重要的两步是 1. prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); 2. handler.update(stmt);
public class SimpleExecutor extends BaseExecutor { public SimpleExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) { super(configuration, transaction); } // 所有的数据库更新操作,都会调用doUpdate(),包括insert、update、delete public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null; try { Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null); // 构造执行Statement的StatementHandler stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); // 通过java.sql.Connection拿到java.sql.PreparedStatement,并且为 java.sql.PreparedStatement 设置sql中的参数 return handler.update(stmt); // 代理执行 java.sql.PreparedStatement (PreparedStatementHandler.update(Statement)) } finally { closeStatement(stmt); } } // 所有的数据库查询操作,都用调用doQuery() public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null; try { Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler); } finally { closeStatement(stmt); } } public List<BatchResult> doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) throws SQLException { return Collections.emptyList(); } private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException { Statement stmt; Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog); stmt = handler.prepare(connection); // 通过 java.sql.Connection 拿到 java.sql.PreparedStatement (PreparedStatementHandler.instantiateStatement(Connection)) handler.parameterize(stmt); // 为 java.sql.PreparedStatement 设置sql中的参数。(DefaultParameterHandler.setParameters(PreparedStatement)) return stmt; } }
至此,MyBatis的封装就一目了然了。^_^
附:
MyBatis开发文档: http://www.mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/dynamic-sql.html