foo.h
#include <iostream> class foo { public: foo() { std::cout<<"foo constructor "; } ~foo() { std::cout<<"foo destructor "; } void doit() { std::cout<<"foo doit "; } };
main.cpp
#include "foo.h"
extern "C"
{
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
}
int main()
{
int count = 0;
foo f;
pid_t pid = fork(); //fork是把进程当前的情况拷贝一份,fork只拷贝下一步要执行的代码到新的进程
if (pid < 0)
std::cout<<"error in fork"<<std::endl;
else if (pid == 0)
{
std::cout<<"i am child process"<<std::endl;
++count;
std::cout<<"child process id : "<<getpid()<<std::endl;
}
else
{
std::cout<<"i am parent process"<<std::endl;
++count;
std::cout<<"parent process id : "<<getpid()<<std::endl;
}
f.doit();
std::cout<<"count : "<<count<<std::endl;
return 0;
}
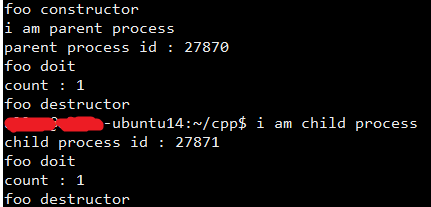
输出: