1. Pandas数据类型
pandas做数据处理,经常用到数据转换,得到正确类型的数据。
pandas与numpy之间的数据对应关系。
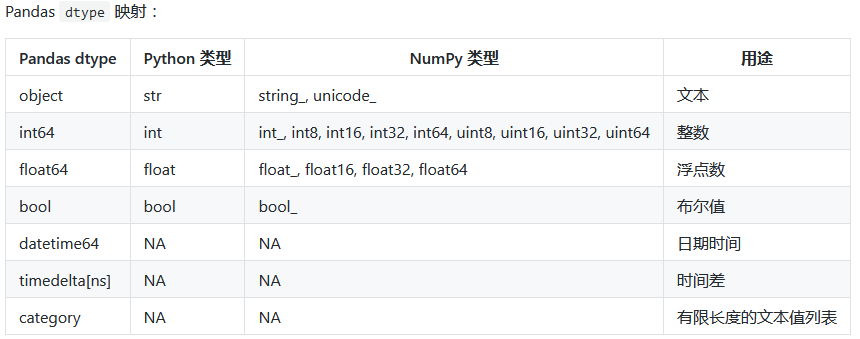
重点介绍object,int64,float64,datetime64,bool等几种类型,category与timedelta两种类型这里不做介绍。
import numpy as np import pandas as pd # 从csv文件读取数据,数据表格中只有5行,里面包含了float,string,int三种数据python类型,也就是分别对应的pandas的float64,object,int64 df = pd.read_csv("sales_data_types.csv", index_col=0) print(df)
Customer Number Customer Name 2016 2017 0 10002.0 Quest Industries $125,000.00 $162500.00 1 552278.0 Smith Plumbing $920,000.00 $101,2000.00 2 23477.0 ACME Industrial $50,000.00 $62500.00 3 24900.0 Brekke LTD $350,000.00 $490000.00 4 651029.0 Harbor Co $15,000.00 $12750.00 Percent Growth Jan Units Month Day Year Active 0 30.00% 500 1 10 2015 Y 1 10.00% 700 6 15 2014 Y 2 25.00% 125 3 29 2016 Y 3 4.00% 75 10 27 2015 Y 4 -15.00% Closed 2 2 2014 N
df.dtypes
Customer Number float64 Customer Name object 2016 object 2017 object Percent Growth object Jan Units object Month int64 Day int64 Year int64 Active object dtype: object
# 想得到2016年与2017年的数据总和,直接相加不是我们需要的答案,因为这两列中的数据类型是object,执行该操作之后,得到是一个更加长的字符串, # 通过df.info() 来获得关于数据框的更多的详细信息 df['2016']+df['2017']
0 $125,000.00$162500.00 1 $920,000.00$101,2000.00 2 $50,000.00$62500.00 3 $350,000.00$490000.00 4 $15,000.00$12750.00 dtype: object
df.info() # Customer Number 列是float64,然而应该是int64 # 2016 2017两列的数据是object,并不是float64或者int64格式 # Percent以及Jan Units 也是objects而不是数字格式 # Month,Day以及Year应该转化为datetime64[ns]格式 # Active 列应该是布尔值 # 如果不做数据清洗,很难进行下一步的数据分析,为了进行数据格式的转化,pandas里面有三种比较常用的方法 # 1. astype()强制转化数据类型 # 2. 通过创建自定义的函数进行数据转化 # 3. pandas提供的to_nueric()以及to_datetime()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'> Int64Index: 5 entries, 0 to 4 Data columns (total 10 columns): Customer Number 5 non-null float64 Customer Name 5 non-null object 2016 5 non-null object 2017 5 non-null object Percent Growth 5 non-null object Jan Units 5 non-null object Month 5 non-null int64 Day 5 non-null int64 Year 5 non-null int64 Active 5 non-null object dtypes: float64(1), int64(3), object(6) memory usage: 440.0+ bytes
2. Numpy中的astype()
astype()将第一列的数据转化为整数int类型。
# 这样的操作并没有改变原始的数据框,而只是返回的一个拷贝 df['Customer Number'].astype("int")
0 10002 1 552278 2 23477 3 24900 4 651029 Name: Customer Number, dtype: int32
# 想要真正的改变数据框,通常需要通过赋值来进行,比如 df["Customer Number"] = df["Customer Number"].astype("int") print(df) print ('{:-^70}'.format('转换后的类型:')) print(df.dtypes)
Customer Number Customer Name 2016 2017 0 10002 Quest Industries $125,000.00 $162500.00 1 552278 Smith Plumbing $920,000.00 $101,2000.00 2 23477 ACME Industrial $50,000.00 $62500.00 3 24900 Brekke LTD $350,000.00 $490000.00 4 651029 Harbor Co $15,000.00 $12750.00 Percent Growth Jan Units Month Day Year Active 0 30.00% 500 1 10 2015 Y 1 10.00% 700 6 15 2014 Y 2 25.00% 125 3 29 2016 Y 3 4.00% 75 10 27 2015 Y 4 -15.00% Closed 2 2 2014 N -------------------------------转换后的类型:-------------------------------- Customer Number int32 Customer Name object 2016 object 2017 object Percent Growth object Jan Units object Month int64 Day int64 Year int64 Active object dtype: object
# 然后像2016,2017 Percent Growth,Jan Units 这几列带有特殊符号的object是不能直接通过astype("flaot)方法进行转化的, # 这与python中的字符串转化为浮点数,都要求原始的字符都只能含有数字本身,不能含有其他的特殊字符 # 我们可以试着将将Active列转化为布尔值,看一下到底会发生什么,五个结果全是True,说明并没有起到什么作用
df["Active"].astype("bool")
0 True 1 True 2 True 3 True 4 True Name: Active, dtype: bool
df['2016'].astype('float')
ValueError: could not convert string to float: '$15,000.00'
以上说明:
- 如果数据是纯净的数据,可以转化为数字。
- astype 两种作用,数字转化为单纯字符串,单纯数字的字符串转化为数字,含非数字的字符串不能通过 astype 转化。
3. 自定义函数清理数据
通过下面函数将货币进行转化:
def convert_currency(var): """ convert the string number to a float _ 去除$ - 去除逗号, - 转化为浮点数类型 """ new_value = var.replace(",","").replace("$","") return float(new_value)
# 通过replace函数将$以及逗号去掉,然后字符串转化为浮点数,让pandas选择pandas认为合适的特定类型,float或者int,该例子中将数据转化为了float64 # 通过pandas中的apply函数将2016列中的数据全部转化 df["2016"].apply(convert_currency)
0 125000.0 1 920000.0 2 50000.0 3 350000.0 4 15000.0 Name: 2016, dtype: float64
# 当然可以通过lambda 函数将这个比较简单的函数一行带过 df["2016"].apply(lambda x: x.replace(",","").replace("$","")).astype("float64")
0 125000.0 1 920000.0 2 50000.0 3 350000.0 4 15000.0 Name: 2016, dtype: float64
#同样可以利用lambda表达式将PercentGrowth进行数据清理 df["Percent Growth"].apply(lambda x: x.replace("%","")).astype("float")/100
0 0.30 1 0.10 2 0.25 3 0.04 4 -0.15 Name: Percent Growth, dtype: float64
# 同样可以通过自定义函数进行解决,结果同上 # 最后一个自定义函数是利用np.where() function 将Active 列转化为布尔值。 df["Active"] = np.where(df["Active"] == "Y", True, False) df["Active"]
0 True 1 True 2 True 3 True 4 False Name: Active, dtype: bool
# 此时可查看一下数据格式 df["2016"]=df["2016"].apply(lambda x: x.replace(",","").replace("$","")).astype("float64") df["2017"]=df["2017"].apply(lambda x: x.replace(",","").replace("$","")).astype("float64") df["Percent Growth"]=df["Percent Growth"].apply(lambda x: x.replace("%","")).astype("float")/100 df.dtypes
Customer Number int32 Customer Name object 2016 float64 2017 float64 Percent Growth float64 Jan Units object Month int64 Day int64 Year int64 Active bool dtype: object
# 再次查看DataFrame # 此时只有Jan Units中格式需要转化,以及年月日的合并,可以利用pandas中自带的几个函数进行处理 print(df)
Customer Number Customer Name 2016 2017 Percent Growth 0 10002 Quest Industries 125000.0 162500.0 0.30 1 552278 Smith Plumbing 920000.0 1012000.0 0.10 2 23477 ACME Industrial 50000.0 62500.0 0.25 3 24900 Brekke LTD 350000.0 490000.0 0.04 4 651029 Harbor Co 15000.0 12750.0 -0.15 Jan Units Month Day Year Active 0 500 1 10 2015 True 1 700 6 15 2014 True 2 125 3 29 2016 True 3 75 10 27 2015 True 4 Closed 2 2 2014 False
4. pandas进行处理
# pandas中pd.to_numeric()处理Jan Units中的数据 pd.to_numeric(df["Jan Units"],errors='coerce').fillna(0)
0 500.0 1 700.0 2 125.0 3 75.0 4 0.0 Name: Jan Units, dtype: float64
# 最后利用pd.to_datatime()将年月日进行合并 pd.to_datetime(df[['Month', 'Day', 'Year']])
0 2015-01-10 1 2014-06-15 2 2016-03-29 3 2015-10-27 4 2014-02-02 dtype: datetime64[ns]
# 做到这里不要忘记重新赋值,否则原始数据并没有变化 df["Jan Units"] = pd.to_numeric(df["Jan Units"],errors='coerce') df["Start_date"] = pd.to_datetime(df[['Month', 'Day', 'Year']])
df
| Customer Number | Customer Name | 2016 | 2017 | Percent Growth | Jan Units | Month | Day | Year | Active | Start_date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10002 | Quest Industries | 125000.0 | 162500.0 | 0.30 | 500.0 | 1 | 10 | 2015 | True | 2015-01-10 |
| 1 | 552278 | Smith Plumbing | 920000.0 | 1012000.0 | 0.10 | 700.0 | 6 | 15 | 2014 | True | 2014-06-15 |
| 2 | 23477 | ACME Industrial | 50000.0 | 62500.0 | 0.25 | 125.0 | 3 | 29 | 2016 | True | 2016-03-29 |
| 3 | 24900 | Brekke LTD | 350000.0 | 490000.0 | 0.04 | 75.0 | 10 | 27 | 2015 | True | 2015-10-27 |
| 4 | 651029 | Harbor Co | 15000.0 | 12750.0 | -0.15 | NaN | 2 | 2 | 2014 | False | 2014-02-02 |
df.dtypes
Customer Number int32 Customer Name object 2016 float64 2017 float64 Percent Growth float64 Jan Units float64 Month int64 Day int64 Year int64 Active bool Start_date datetime64[ns] dtype: object
# 将这些转化整合在一起 def convert_percent(val): """ Convert the percentage string to an actual floating point percent - Remove % - Divide by 100 to make decimal """ new_val = val.replace('%', '') return float(new_val) / 100 df_2 = pd.read_csv("sales_data_types.csv",dtype={"Customer_Number":"int"},index_col=0,converters={ "2016":convert_currency, "2017":convert_currency, "Percent Growth":convert_percent, "Jan Units":lambda x:pd.to_numeric(x,errors="coerce"), "Active":lambda x: np.where(x=="Y",True,False) })
df_2.dtypes
Customer Number float64 Customer Name object 2016 float64 2017 float64 Percent Growth float64 Jan Units float64 Month int64 Day int64 Year int64 Active object dtype: object
df_2
| Customer Number | Customer Name | 2016 | 2017 | Percent Growth | Jan Units | Month | Day | Year | Active | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10002.0 | Quest Industries | 125000.0 | 162500.0 | 0.30 | 500.0 | 1 | 10 | 2015 | True |
| 1 | 552278.0 | Smith Plumbing | 920000.0 | 1012000.0 | 0.10 | 700.0 | 6 | 15 | 2014 | True |
| 2 | 23477.0 | ACME Industrial | 50000.0 | 62500.0 | 0.25 | 125.0 | 3 | 29 | 2016 | True |
| 3 | 24900.0 | Brekke LTD | 350000.0 | 490000.0 | 0.04 | 75.0 | 10 | 27 | 2015 | True |
| 4 | 651029.0 | Harbor Co | 15000.0 | 12750.0 | -0.15 | NaN | 2 | 2 | 2014 | False |
来自:https://github.com/xitu/gold-miner/blob/master/TODO1/pandas-dtypes.md