数据库的持久层总结框架图
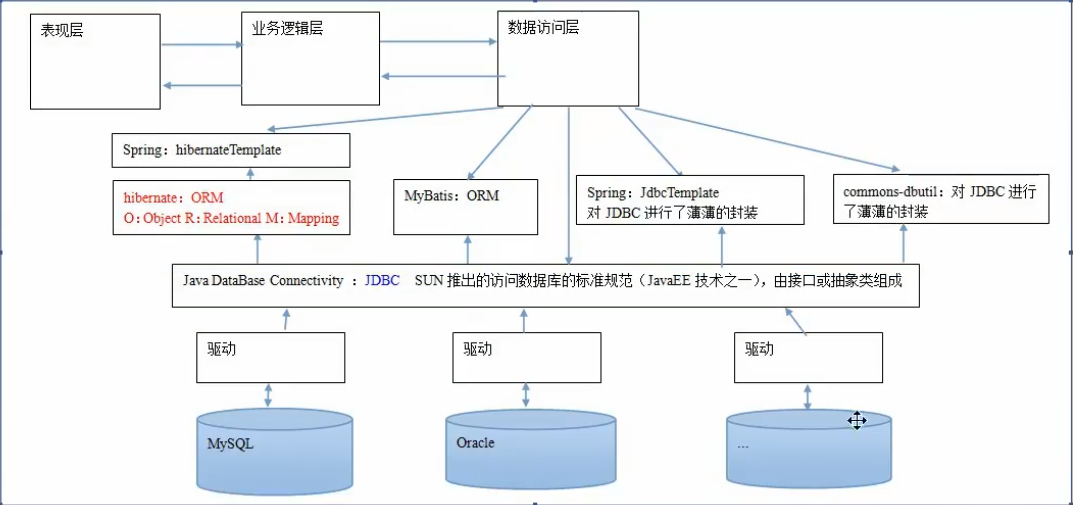
总结:
数据库 --> 各个数据库对应的驱动(厂商提供) -> JDBC ---> Spring hibernate || MyBatis || JdbcTemplate || commons-dbutil
- Spring hibernate || MyBatis || JdbcTemplate || commons-dbutil 这四个包都是再JDBC的基础上进行封装
在模板模式(Template Pattern)中,一个抽象类公开定义了执行它的方法的方式/模板。它的子类可以按需要重写方法实现,但调用将以抽象类中定义的方式进行。这种类型的设计模式属于行为型模式。
意图:定义一个操作中的算法的骨架,而将一些步骤延迟到子类中。模板方法使得子类可以不改变一个算法的结构即可重定义该算法的某些特定步骤。
1 Spring事务控制概述
常识:
1)Spring框架提供了一组事务控制的接口,这组接口在spring-tx依赖包中
2)Spring的事务控制也是基于AOP的,即可以使用编程的方式实现,也可以使用配置的方法实现。
<!--Spring的事务所依赖的包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>5.0.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
2 Spring事务管理的接口
事物管理定义:按照给定的事务规则来执行提交或者回滚操作
1)PlatformTransactionManager: (平台)事务管理器
2)TransactionDefinition: 事务定义信息(事务隔离级别、传播行为、超时、只读、回滚规则)
3)TransactionStatus: 事务运行状态
2-1 PlatformTransactionManager接口
public interface PlatformTransactionManager {
TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException;
void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
}
- 可以看到事务管理器接口要求实现事务的获取,提交以及回滚操作
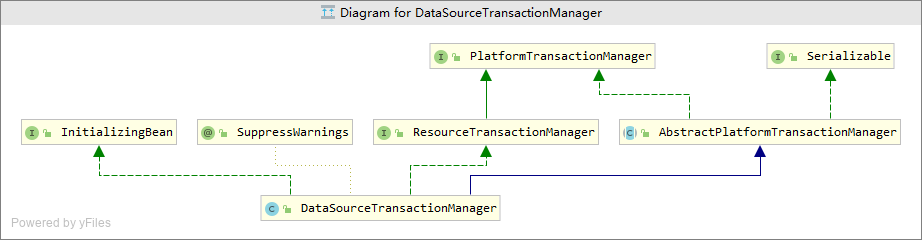
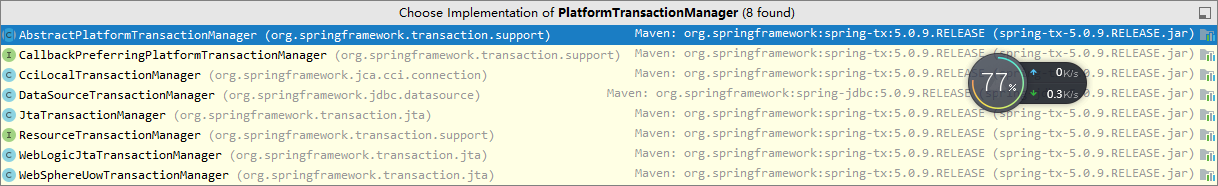
- 上图是JDBC对于PlatformTransactionManager接口的实现的类图,实际开发者我们通常使用别人写好的实现类。
- 下图是PlatformTransactionManager接口的实现类,可以看到提供了基于JDBC,JTA,JCA规范的事物管理器。
1)JTA规范,即Java Transaction API,JTA允许应用程序执行分布式事务处理——在两个或多个网络计算机资源上访问并且更新数据
2)J2EE提供JCA(Java Connector Architecture)规范来标准化对EIS(Enterprise Information System)的访问,CCI (Common Client Interface)是应用程序用来与连接器交互并与EIS通信的接口。同样还为本地事务划界提供了API。
3)JDBC,java 程序与数据库交互的一套规范,不同的数据库厂商根据自己的数据库实现这套规范,这就使得数据库相关的逻辑程序不用每个数据库都不同。
2-2 TranscationDefiniton接口
public interface TransactionDefinition {
/*事务的传播行为*/
int PROPAGATION_REQUIRED = 0;
int PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS = 1;
int PROPAGATION_MANDATORY = 2;
int PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW = 3;
int PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED = 4;
int PROPAGATION_NEVER = 5;
int PROPAGATION_NESTED = 6;
/*事务的隔离级别*/
int ISOLATION_DEFAULT = -1;
int ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED = Connection.TRANSACTION_READ_UNCOMMITTED;
int ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED = Connection.TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED;
int ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ = Connection.TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ;
int ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE = Connection.TRANSACTION_SERIALIZABLE;
int TIMEOUT_DEFAULT = -1; // 超时事件默认为-1,即没有事件限制,如果有的话,则以s为单位进行设置
int getPropagationBehavior(); // 获取事务传播行为
int getIsolationLevel(); // 获取事务隔离级别
int getTimeout(); // 获取事务超时时间
boolean isReadOnly(); // 获取事务是否可读,数据库在查询时可以设置为只读,其他设置为读写事务
@Nullable
String getName(); // 获取事务对象名称
}
事务的可读性isReadOnly
读写型事务:事务中包含有增删查改
只读型事务:事务中没有增删查改,对于只读查询,可以指定事务类型为readonly,即只读事务。由于只读事务不存在数据的修改,因此数据库将会为只读事务提供一些优化手段,例如Oracle对于只读事务,不启动回滚段,不记录回滚log。
事务的传播行为
定义:多个事务方法相互调用时,事务如何在这些方法间传播。
关于事务传播机制详细解释,参考01 Spring事务传播
1)required,required_new(后者确保事务都是新建的)
2)supports,not_supproted(后者确保非事务方法执行)
3)mandatory(强制的: [ˈmændətɔːri],要求方法调用者必须有事务,否则抛出异常)
4)never
5)nested
| 事务的传播行为 | 含义 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| PROPAGATION_REQUIRED(默认值) | 如果当前没有事务,则自己新建一个事务,如果当前存在事务,则加入这个事务 | 数据库增删改的场景使用 |
| PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS | 当前存在事务,则加入当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方法执行 | 数据库查询使用 |
| PROPAGATION_MANDATORY | 当前存在事务,则加入当前事务,如果当前事务不存在,则抛出异常。 | |
| PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW | 创建一个新事务,如果存在当前事务,则挂起该事务,(在执行时,不论当前是否存在事务,总是会新建一个事务。) | |
| PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED | 始终以非事务方式执行,如果当前存在事务,则挂起当前事务(不论当前是否存在事务,都会以非事务的方式运行) | |
| PROPAGATION_NEVER | 不使用事务,如果当前事务存在,则抛出异常 | |
| PROPAGATION_NESTED | 如果当前事务存在,则在嵌套事务中执行,否则REQUIRED的操作一样(开启一个事务) |
方法A调用方法B,方法B设置了上面的事务传播行为,当前指的是方法A。
Spring事物管理的特点:
-
Spring并不直接管理事务,而是提供了多种事务管理器
-
Spring 支持两种方式的事务管理
1)编程式事务管理:通过 TransactionTemplate或者TransactionManager手动管理事务
2)声明式事务管理:实际是通过 AOP实现(基于@Transactional 的全注解方式使用最多),实际开发中用的比较多。
2-3 TransactionStatus接口
public interface TransactionStatus extends SavepointManager, Flushable {
boolean isNewTransaction();
boolean hasSavepoint(); // 大型项目需要进行复杂的事务提交,事务的回滚可能是以存储点的方式进行的
void setRollbackOnly();
boolean isRollbackOnly();
@Override
void flush();
boolean isCompleted();
}
3 Spring声明式事务的使用方法
3-1 Spring基于xml的声明式事务控制
Dao层
接口
package com.springlearn.dao;
import com.springlearn.domain.Account;
import java.util.List;
public interface IAccountDao {
Account findAccountById(Integer accountId);
void updateAccount(Account account);
Account findAccountByName(String accountName);
}
实现类
package com.springlearn.dao.impl;
import com.springlearn.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.springlearn.domain.Account;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.support.JdbcDaoSupport;
import java.util.List;
public class AccountDao extends JdbcDaoSupport implements IAccountDao {
public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) {
List<Account> accounts = super.getJdbcTemplate().query("select * from account where id = ?", new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class),accountId);
return accounts.isEmpty() ? null : accounts.get(0);
}
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
super.getJdbcTemplate().update("update account set name = ?,money=? where id=?",account.getName(),account.getMoney(),account.getId());
}
public Account findAccountByName(String accountName) {
List<Account> accounts = super.getJdbcTemplate().query("select * from account where name = ?", new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class),accountName);
if(accounts.isEmpty()){
return null;
}else if(accounts.size() > 1){
throw new RuntimeException("结果集不唯一");
}
return accounts.get(0);
}
}
Service层
接口
package com.springlearn.service;
import com.springlearn.domain.Account;
import java.util.List;
public interface IAccountService {
Account findAccountById(Integer accountId);
void transfer(String sourceName, String targetName, float money);
}
实现类
package com.springlearn.service.impl;
import com.springlearn.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.springlearn.domain.Account;
import com.springlearn.service.IAccountService;
import java.util.List;
public class AccountService implements IAccountService {
IAccountDao accountDao;
/*这里类提供了事务控制
* 1)通过ThreadLocal保证线程安全性(配合线程池使用,注意及时remove)
* 2)实现了事务的开启,提交以及回滚操作
* */
public void setAccountDao(IAccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) {
Account account = accountDao.findAccountById(accountId);
return account;
}
public void transfer(String sourceName, String targetName, float money) {
/*基本步骤:1)查询两个账户 2)计算两个账户更新后的金额 3)更新两个账户记录*/
Account source = accountDao.findAccountByName(sourceName);
Account target = accountDao.findAccountByName(targetName);
source.setMoney(source.getMoney()-money);
target.setMoney(target.getMoney()+money);
int i = 1/0;
accountDao.updateAccount(source);
accountDao.updateAccount(target);
}
}
xml配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
https://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- 告知spring在创建容器时要扫描的包,配置所需要的标签不是在bean中,而是在名称为context的空间中-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.springlearn.service.impl.AccountService">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.springlearn.dao.impl.AccountDao">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 数据源参数的注入-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springlearn"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="123456"></property>
</bean>
<!-- spring基于xml配置事务管理器
step1:配置事务管理器
step2:配置事务的通知(需要导入xml约束)
step3:配置AOP的通用切入点表达式
step4:建立事务通知与切入点表达式的关系
step5:配置事务的属性(tx:advice标签内部配置)
-->
<bean id = "transactionManage" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置事务的通知,这个通知会通过AOP用于增强数据库的操作,事务管理器中提供了数据库事务的支持-->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManage">
<!--配置事务的属性:isolation隔离级别,progagation事务传播级别,timeout:事务超时时间
rollback-for:用于指定异常,产生指定异常则回滚
no-rollback-for:指定异常,该异常不会回滚
默认所有异常都回滚
-->
<tx:attributes>
<!--匹配所有方法-->
<tx:method name="*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" timeout="-1"></tx:method>
<!--匹配查询方法,要求数据库所有查询方法都以find开头才能匹配-->
<tx:method name="find*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="SUPPORTS" read-only="true" timeout="-1"></tx:method>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!-- 将AOP的切入点表达式(切入点表达式中指定增强的被代理类路径)与事务的通知整合在一起-->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="pt1" expression="execution(* com.springlearn.service.impl.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="pt1"></aop:advisor>
</aop:config>
</beans>
注意:将JDBC提供的事务管理器作为通知,利用Spring的AOP机制将该通知作为Service层方法的事务控制。
这里的思想与自己实现事务管理类作为通知用于事务控制是相一致的。
测试类
package com.springlearn.Test;
import com.springlearn.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.springlearn.domain.Account;
import com.springlearn.service.IAccountService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class JTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
IAccountService accountService = ac.getBean("accountService",IAccountService.class);
Account account = accountService.findAccountById(2);
System.out.println(account);
account = accountService.findAccountById(3);
System.out.println(account);
accountService.transfer("bbb","ccc",12f);
}
}
基于xml的声明式事务配置步骤
step1:配置事务管理器(将对应类放入容器)
step2:配置事务的通知(需要导入xml约束,tx:advice)
step3:配置AOP的通用切入点表达式(aop:pointcut)
step4:建立事务通知与切入点表达式的关系(aop:advisor)
step5:配置事务的属性(tx:advice标签内部配置)(tx:attributes)
3-2 Spring基于注解的声明式事务配置
Dao层
package com.springlearn.dao;
import com.springlearn.domain.Account;
public interface IAccountDao {
Account findAccountById(Integer accountId);
void updateAccount(Account account);
Account findAccountByName(String accountName);
}
package com.springlearn.dao.impl;
import com.springlearn.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.springlearn.domain.Account;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.support.JdbcDaoSupport;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.List;
@Repository(value="accountDao")
public class AccountDao implements IAccountDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) {
List<Account> accounts = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account where id = ?", new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class),accountId);
return accounts.isEmpty() ? null : accounts.get(0);
}
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set name = ?,money=? where id=?",account.getName(),account.getMoney(),account.getId());
}
public Account findAccountByName(String accountName) {
List<Account> accounts = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account where name = ?", new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class),accountName);
if(accounts.isEmpty()){
return null;
}else if(accounts.size() > 1){
throw new RuntimeException("结果集不唯一");
}
return accounts.get(0);
}
}
Service层
package com.springlearn.service;
import com.springlearn.domain.Account;
public interface IAccountService {
Account findAccountById(Integer accountId);
void transfer(String sourceName, String targetName, float money);
}
package com.springlearn.service.impl;
import com.springlearn.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.springlearn.domain.Account;
import com.springlearn.service.IAccountService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
/*注解配置虽然使用方便,但是没法像xml方式那样通过*进行方法名的批量匹配,
* 因此如果方法较多,可能需要大量的注解配置
*
* */
@Service(value = "accountService")
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.SUPPORTS,readOnly = true)
public class AccountService implements IAccountService {
@Autowired
IAccountDao accountDao;
/*这里类提供了事务控制
* 1)通过ThreadLocal保证线程安全性(配合线程池使用,注意及时remove)
* 2)实现了事务的开启,提交以及回滚操作
* */
public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) {
Account account = accountDao.findAccountById(accountId);
return account;
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED,readOnly = false)
public void transfer(String sourceName, String targetName, float money) {
/*基本步骤:1)查询两个账户 2)计算两个账户更新后的金额 3)更新两个账户记录*/
Account source = accountDao.findAccountByName(sourceName);
Account target = accountDao.findAccountByName(targetName);
source.setMoney(source.getMoney()-money);
target.setMoney(target.getMoney()+money);
accountDao.updateAccount(source);
accountDao.updateAccount(target);
int i = 1/0;
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
https://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.springlearn"></context:component-scan>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 数据源参数的注入-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springlearn"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="123456"></property>
</bean>
<!--Spring中基于注解的声明式事务控制配置步骤
1)配置事务管理器
2)开启Spring对注解事务的支持
3)在需要事务支持的地方使用@Tranctional
-->
<bean id = "transactionManage" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManage"></tx:annotation-driven>
</beans>
测试类
package com.springlearn.Test;
import com.springlearn.domain.Account;
import com.springlearn.service.IAccountService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class JTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
IAccountService accountService = ac.getBean("accountService",IAccountService.class);
Account account = accountService.findAccountById(2);
System.out.println(account);
account = accountService.findAccountById(3);
System.out.println(account);
accountService.transfer("bbb","ccc",12f);
}
}
声明式主机的使用步骤
1)配置事务管理器(放入容器中)()
2)开启Spring对注解事务的支持(tx:annotation-driven)
3)在需要事务支持的地方使用@Tranctional
3-3 Spring纯注解的声明式事务配置
| 作用 | 对应注解 |
|---|---|
| 数据源参数的注入 | @PropertySource("jdbcConfig.properties") |
| 端口扫描 | @ComponentScan("com.springlearn") |
| 开启事务 | @EnableTransactionManagement |
| 主配置类导入其他配置类 | @Import({JdbcConfig.class,TransactionConfig.class}) |
主配置类
package com.springlearn.Config1;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.springlearn")
@Import({JdbcConfig.class,TransactionConfig.class})
@PropertySource("jdbcConfig.properties")
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class SpringConfiguration {
}
事务管理器配置类
package com.springlearn.Config1;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
public class TransactionConfig {
@Bean(value = "transactionManager")
public PlatformTransactionManager createTransactionManager(DataSource d){
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(d);
}
}
数据源配置类
package com.springlearn.Config1;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
/*
数据库连接相关的配置类
*/
public class JdbcConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.driver}")
private String driver;
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
@Bean
public DriverManagerDataSource createDataSource() {
DriverManagerDataSource ds = new DriverManagerDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName(driver);
ds.setUrl(url);
ds.setUsername(username);
ds.setPassword(password);
return ds;
}
@Bean(name="jdbcTemplate")
public JdbcTemplate createJdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource){
return new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
}
}
纯注解的容器启动:需要将主配置类的字节码作为容器的参数
package com.springlearn.Test;
import com.springlearn.Config1.SpringConfiguration;
import com.springlearn.domain.Account;
import com.springlearn.service.IAccountService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class JTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 传入配置类的字节码
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class);
IAccountService accountService = ac.getBean("accountService",IAccountService.class);
Account account = accountService.findAccountById(2);
System.out.println(account);
account = accountService.findAccountById(3);
System.out.println(account);
// accountService.transfer("bbb","ccc",12f);
}
}
补充:Spring中采用编程方式实现事务控制,需要将数据库操作代码封装到类中传递给框架提供的类,造成代码依旧比较冗余,实际开发中很少使用。
4 Spring事务知识点
Q1:spring事务的原理?
Spring事务的本质其实就是数据库对事务的支持,没有数据库的事务支持,spring是无法提供事务功能的。
那么,我们一般使用JDBC操作事务的时候,代码如下
(1)获取连接 Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection()
(2)开启事务con.setAutoCommit(true/false);
(3)执行CRUD
(4)提交事务/回滚事务 con.commit() / con.rollback();
(5)关闭连接 conn.close();
使用spring事务管理后,我们可以省略步骤(2)和步骤(4),就是让AOP帮你去做这些工作。关键类在TransactionAspectSupport这个切面里,大家有兴趣自己去翻。我就不列举了,因为公众号类型的文章,实在不适合写一些源码解析!
Q2:spring什么情况下进行事务回滚?
基本机制:当方法有异常抛出,事务才会自动进行回滚!
发生异常不会回滚的情况:1)代码中手动编码捕获异常没有抛出 2)事务只会对Error与RuntimeException及其子类这些异常,做出回滚。一般的Exception这些Checked异常不会发生回滚(如果一般Exception想回滚要做出配置
手动回滚的方式:(1)自己在代码里抛出一个自定义异常(常用) (2)通过编程代码回滚(不常用)
什么时候需要手动回滚? 事物执行没有异常,但不满足业务需求
Q3: 事物失效场景?
根本原因:AOP不起作用了,代理类没有发生作用
1)发生this自调用,this调用的不是代理类,是被代理类,自然调用的方法没有被增强
2)方法不是public的,被代理类的private方法没法被代理类增强,没有权限
3)发生了错误异常,就是有些异常发生了回滚了,但系统没有报错
4)数据库不支持事务
Q4:spring事务控制放在service层,在service方法中一个方法调用service中的另一个方法,默认开启几个事务?
1)spring的默认的传播行为是PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,如果外层有事务,则当前事务加入到外层事务,一块提交,一块回滚。如果外层没有事务,新建一个事务执行!
也就是说,默认情况下只有一个事务!
2)另外一个比较常用的是PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS,通常再查询的service设置
其他事物见定义
Q5:怎么保证spring事务内的连接唯一性?
spring底层是通过ThreadLocalMap将连接与线程绑定保证连接的唯一性
源码溯源:
// ================================01 JdbcTemplate.java的方法源码=================================================
public <T> T execute(ConnectionCallback<T> action) throws DataAccessException {
Assert.notNull(action, "Callback object must not be null");
// 获取数据库连接
Connection con = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(obtainDataSource());
try {
// Create close-suppressing Connection proxy, also preparing returned Statements.
Connection conToUse = createConnectionProxy(con);
return action.doInConnection(conToUse);
}
catch (SQLException ex) {
// Release Connection early, to avoid potential connection pool deadlock
// in the case when the exception translator hasn't been initialized yet.
String sql = getSql(action);
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, getDataSource());
con = null;
throw translateException("ConnectionCallback", sql, ex);
}
finally {
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, getDataSource());
}
}
//==============================02 DataSourceUtils.getConnection源码=============================================
public static Connection getConnection(DataSource dataSource) throws CannotGetJdbcConnectionException {
try {
return doGetConnection(dataSource);
}
catch (SQLException ex) {
throw new CannotGetJdbcConnectionException("Failed to obtain JDBC Connection", ex);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new CannotGetJdbcConnectionException("Failed to obtain JDBC Connection: " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
// =============================03 DataSourceUtils.doGetConnection源码================================
public static Connection doGetConnection(DataSource dataSource) throws SQLException {
Assert.notNull(dataSource, "No DataSource specified");
// 从TransactionSynchronizationManager获取连接
ConnectionHolder conHolder = (ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(dataSource);
if (conHolder != null && (conHolder.hasConnection() || conHolder.isSynchronizedWithTransaction())) {
conHolder.requested();
if (!conHolder.hasConnection()) {
logger.debug("Fetching resumed JDBC Connection from DataSource");
conHolder.setConnection(fetchConnection(dataSource));
}
return conHolder.getConnection();
}
// Else we either got no holder or an empty thread-bound holder here.
logger.debug("Fetching JDBC Connection from DataSource");
Connection con = fetchConnection(dataSource);
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {
logger.debug("Registering transaction synchronization for JDBC Connection");
// Use same Connection for further JDBC actions within the transaction.
// Thread-bound object will get removed by synchronization at transaction completion.
ConnectionHolder holderToUse = conHolder;
if (holderToUse == null) {
holderToUse = new ConnectionHolder(con);
}
else {
holderToUse.setConnection(con);
}
holderToUse.requested();
TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization(
new ConnectionSynchronization(holderToUse, dataSource));
holderToUse.setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
if (holderToUse != conHolder) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(dataSource, holderToUse);
}
}
return con;
}
TransactionSynchronizationManager部分源码:
- 可以看到很多的ThreadLocal静态实例对象
public abstract class TransactionSynchronizationManager {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(TransactionSynchronizationManager.class);
private static final ThreadLocal<Map<Object, Object>> resources =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Transactional resources");
private static final ThreadLocal<Set<TransactionSynchronization>> synchronizations =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Transaction synchronizations");
private static final ThreadLocal<String> currentTransactionName =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Current transaction name");
private static final ThreadLocal<Boolean> currentTransactionReadOnly =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Current transaction read-only status");
private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> currentTransactionIsolationLevel =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Current transaction isolation level");
private static final ThreadLocal<Boolean> actualTransactionActive =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Actual transaction active");
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Management of transaction-associated resource handles
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Return all resources that are bound to the current thread.
* <p>Mainly for debugging purposes. Resource managers should always invoke
* {@code hasResource} for a specific resource key that they are interested in.
* @return a Map with resource keys (usually the resource factory) and resource
* values (usually the active resource object), or an empty Map if there are
* currently no resources bound
* @see #hasResource
*/
public static Map<Object, Object> getResourceMap() {
Map<Object, Object> map = resources.get();
return (map != null ? Collections.unmodifiableMap(map) : Collections.emptyMap());
}
/**
* Check if there is a resource for the given key bound to the current thread.
* @param key the key to check (usually the resource factory)
* @return if there is a value bound to the current thread
* @see ResourceTransactionManager#getResourceFactory()
*/
public static boolean hasResource(Object key) {
Object actualKey = TransactionSynchronizationUtils.unwrapResourceIfNecessary(key);
Object value = doGetResource(actualKey);
return (value != null);
}
/**
* Retrieve a resource for the given key that is bound to the current thread.
* @param key the key to check (usually the resource factory)
* @return a value bound to the current thread (usually the active
* resource object), or {@code null} if none
* @see ResourceTransactionManager#getResourceFactory()
*/
@Nullable
public static Object getResource(Object key) {
Object actualKey = TransactionSynchronizationUtils.unwrapResourceIfNecessary(key);
Object value = doGetResource(actualKey);
if (value != null && logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Retrieved value [" + value + "] for key [" + actualKey + "] bound to thread [" +
Thread.currentThread().getName() + "]");
}
return value;
}
/**
* Actually check the value of the resource that is bound for the given key.
*/
@Nullable
private static Object doGetResource(Object actualKey) {
Map<Object, Object> map = resources.get();
if (map == null) {
return null;
}
Object value = map.get(actualKey);
// Transparently remove ResourceHolder that was marked as void...
if (value instanceof ResourceHolder && ((ResourceHolder) value).isVoid()) {
map.remove(actualKey);
// Remove entire ThreadLocal if empty...
if (map.isEmpty()) {
resources.remove();
}
value = null;
}
return value;
}
/**
* Bind the given resource for the given key to the current thread.
* @param key the key to bind the value to (usually the resource factory)
* @param value the value to bind (usually the active resource object)
* @throws IllegalStateException if there is already a value bound to the thread
* @see ResourceTransactionManager#getResourceFactory()
*/
public static void bindResource(Object key, Object value) throws IllegalStateException {
Object actualKey = TransactionSynchronizationUtils.unwrapResourceIfNecessary(key);
Assert.notNull(value, "Value must not be null");
Map<Object, Object> map = resources.get();
// set ThreadLocal Map if none found
if (map == null) {
map = new HashMap<>();
resources.set(map);
}
Object oldValue = map.put(actualKey, value);
// Transparently suppress a ResourceHolder that was marked as void...
if (oldValue instanceof ResourceHolder && ((ResourceHolder) oldValue).isVoid()) {
oldValue = null;
}
if (oldValue != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Already value [" + oldValue + "] for key [" +
actualKey + "] bound to thread [" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "]");
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Bound value [" + value + "] for key [" + actualKey + "] to thread [" +
Thread.currentThread().getName() + "]");
}
}
...