Ioc容器BeanPostProcessor-Spring 源码系列(3)
目录:
Ioc容器beanDefinition-Spring 源码(1)
Ioc容器BeanPostProcessor-Spring 源码(3)
如果这个接口的某个实现类被注册到某个容器,那么该容器的每个受管Bean在调用初始化方法之前,都会获得该接口实现类的一个回调。容器调用接口定义的方法时会将该受管Bean的实例和名字通过参数传入方法,进过处理后通过方法的返回值返回给容器。
public class BeanPostProcessorTest implements BeanPostProcessor, Ordered { public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException { return o; } public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException { System.out.println("beanName:"+s); return o; } /** * 多个BeanPostProcessor 用order来排序 * @return */ public int getOrder() { return 0; } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { ApplicationContext appContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Spring-Customer.xml"); }
<bean class="aspect.test.spring.BeanPostProcessorTest" />
在 《定时任务管理中心》文中就是用这种方式讲需要管理的bean过滤出来的。
这篇就解析一下spring 源码是哪里触发的,如何完成的。
postProcessAfterInitialization的调用链如图:
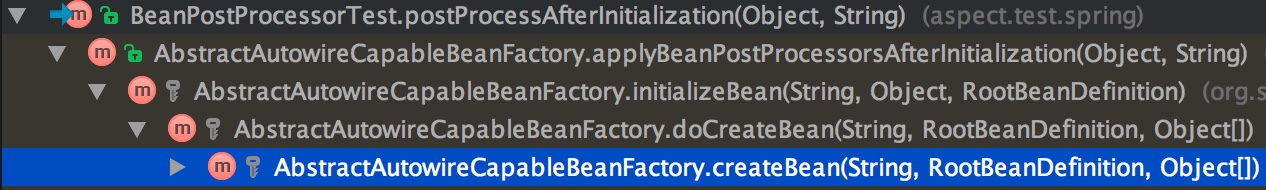
在上一篇中提到,doCreateBean就是创建bean的入口,在做线方法:populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);之后执行的initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);触发的,直接看initializeBean代码:
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) { if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() { @Override public Object run() { invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); return null; } }, getAccessControlContext()); } else { invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); } Object wrappedBean = bean; if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { // 执行ProcessorsBefore的方法 wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } try { invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException( (mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null), beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex); } if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { //执行ProcessorsAfter的方法 wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } return wrappedBean; }
这里就先只看applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization:
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException { Object result = existingBean; for (BeanPostProcessor beanProcessor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { result = beanProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName); if (result == null) { return result; } } return result; }
好了,到这里就调用到了所有BeanPostProcessors的实现。前面的代码其实有点像观察者模式的调用。
那么根据order顺序来执行BeanPostProcessors实现就是按顺序在放这个List<BeanPostProcessor>里,实现的代码如下:
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors( ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) { String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false); // Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when // a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when // a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors. int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length; beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount)); // Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered, // Ordered, and the rest. // 实现Ordered接口的 List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>(); // 未实现Ordered接口的 List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>(); List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>(); List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>(); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp); if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { //反而没有实现ordered的先放 internalPostProcessors.add(pp); } } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } else { nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } } // First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered. sortPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors); // Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered. List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>(); for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) { BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); orderedPostProcessors.add(pp); if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { internalPostProcessors.add(pp); } } sortPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors); // Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors. List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>(); for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) { BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp); if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { internalPostProcessors.add(pp); } } registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors); // Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors. sortPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors); beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext)); }
InitializingBean
InitializingBean是使用Spring的时候比较常用的。继承InitializingBean,实现afterPropertiesSet方法,就可以实现在这个bean创建好的时候触发做一些事情,比如读取必要的配置,缓存文件,初始化信息等操作。
InitializingBean接口:
public interface InitializingBean { /** * Invoked by a BeanFactory after it has set all bean properties supplied * (and satisfied BeanFactoryAware and ApplicationContextAware). * <p>This method allows the bean instance to perform initialization only * possible when all bean properties have been set and to throw an * exception in the event of misconfiguration. * @throws Exception in the event of misconfiguration (such * as failure to set an essential property) or if initialization fails. */ void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception; }
使用代码:
public class InitializingBeanTest implements InitializingBean { public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { System.out.println("afterPropertiesSet do something"); } }
这里看一下spring哪里出发执行的这个接口,其实我们在上篇中已经看见入口了,就是initializeBean方法中执行的applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization和applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization方法的中间就是初始化操作方法:invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
代码很明了:
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) throws Throwable { //bean是InitializingBean的实现类 boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean); if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'"); } if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { try { AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>() { @Override public Object run() throws Exception { ((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet(); return null; } }, getAccessControlContext()); } catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) { throw pae.getException(); } } else { // 执行afterPropertiesSet方法 ((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet(); } } if (mbd != null) { String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName(); // 这里判断是否设置了int-method属性,如果设置则执行invokeCustomInitMethod if (initMethodName != null && !(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) && !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) { invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd); } } }
上面代码最下面我们可以看到可以利用int-method属性一样可以实现初始化bean时进行一些操作,好处是不需要继承spring的接口,就不用和spring代码耦合在一起了。
----------------------
永远爱汀汀