一、LinkedList的继承关系
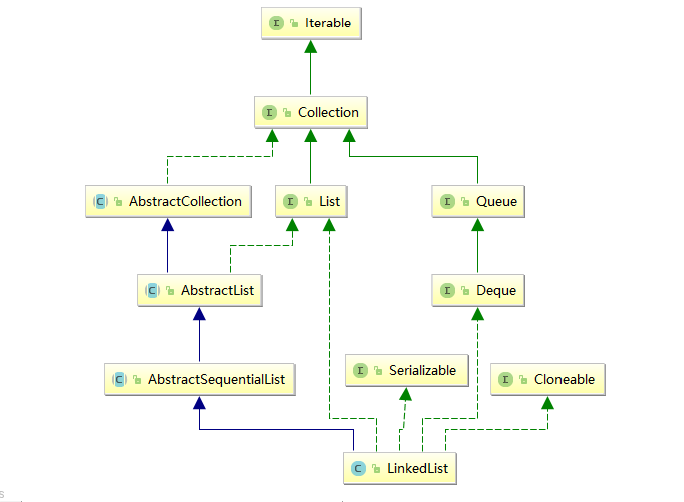
LinkedList实现了Collection,List,Serializable,Deque等接口
二、LinkedList的结构
通过查看源码发现linkedlist有个静态的内部类Node,Node里面有prev和next成员,说明linkedlist是一个双向链表的结构。代码如下
private static class Node<E> { E item; Node<E> next; Node<E> prev; Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { this.item = element; this.next = next; this.prev = prev; } }
因此linkedlist结构图如下

这里写了一个MyLinkedList类似于LinkedList 的结构,MyLinkedList还有很多方法没有实现
/** * 模仿java.util.LinkedList的MyLinkedList * @param <E> */ public class MyLinkedList<E> { private int size; Node<E> first;//头结点 Node<E> last; // 尾结点 private static class Node<E>{ // 从这可以看出 java.util.LinkedList是双向链表 private Node<E> prev; private Node<E> next; private E element; Node(Node<E> prev,E item,Node<E> next){ this.prev = prev; this.next = next; element = item; } } }
三、LinkedList的操作
基本操作
LinkedList是一个双向链表。因此可以方便的对元素进行插入删除操作
插入元素,调用add方法
public boolean add(E e) { linkLast(e); return true; } void linkLast(E e) { final Node<E> l = last; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); last = newNode; if (l == null) first = newNode; else l.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
在插入元素时会往链表的尾部插入元素,过程如下:
1、先用一个变量l指向尾结点,
2、创建新结点
3、尾结点指向新的结点
4、判断原来的尾结点(变量l指向的结点)是否为空,
5 、如果为空说明是个空链表,将头结点指向新的结点;
6 、原来的尾结点不为空,将原来尾结点(l指向的结点)的prev指向新的结点
链表不为空的情况对应如下图

链表为空对应如下

在指定位置前插入元素
public void add(int index, E element) { checkPositionIndex(index); if (index == size) linkLast(element); else linkBefore(element, node(index)); }
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) { // assert succ != null; final Node<E> pred = succ.prev; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ); succ.prev = newNode; if (pred == null) first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
从头部插入元素
public void addFirst(E e) { linkFirst(e); }
private void linkFirst(E e) { final Node<E> f = first; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f); first = newNode; if (f == null) last = newNode; else f.prev = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
从尾部插入元素
public void addLast(E e) { linkLast(e); }
获取元素
由于linkedlist是一个链表,内部没有维护数组,因此获取元素的时候需要循环来获取,代码如下
public E get(int index) { checkElementIndex(index);//比较index是否大于等于0并且小于size,否则抛出异常 return node(index).item; } Node<E> node(int index) { // 判断要找的元素的位置是在左半部分还是右半部分 if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; //从左边开始找 for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { // 从右开始 Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } }
获取头结点
public E getFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return f.item; }
获取尾结点
public E getLast() { final Node<E> l = last; if (l == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return l.item; }
移除指定元素
移除元素,也要遍历查找然后删除
E unlink(Node<E> x) { // assert x != null; final E element = x.item; final Node<E> next = x.next; final Node<E> prev = x.prev; if (prev == null) { first = next; } else { prev.next = next; x.prev = null; } if (next == null) { last = prev; } else { next.prev = prev; x.next = null; } x.item = null; size--; modCount++; return element; } public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) { unlink(x); return true; } } } else { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (o.equals(x.item)) { unlink(x); return true; } } } return false; }
根据位置移除元素
public E remove(int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return unlink(node(index)); }
移除头元素
public E removeFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return unlinkFirst(f); }
移除尾元素
public E removeLast() { final Node<E> l = last; if (l == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return unlinkLast(l); }
清空链表
public void clear() { // Clearing all of the links between nodes is "unnecessary", but: // - helps a generational GC if the discarded nodes inhabit // more than one generation // - is sure to free memory even if there is a reachable Iterator for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; ) { Node<E> next = x.next; x.item = null; x.next = null; x.prev = null; x = next; } first = last = null; size = 0; modCount++; }
检查元素是否存在链表中
public boolean contains(Object o) { return indexOf(o) != -1; } public int indexOf(Object o) { int index = 0; if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) return index; index++; } } else { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (o.equals(x.item)) return index; index++; } } return -1; }
添加其他集合中的元素
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { return addAll(size, c); }
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { checkPositionIndex(index); Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; if (numNew == 0) return false; Node<E> pred, succ; if (index == size) { succ = null; pred = last; } else { succ = node(index); pred = succ.prev; } for (Object o : a) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o; Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null); if (pred == null) first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; pred = newNode; } if (succ == null) { last = pred; } else { pred.next = succ; succ.prev = pred; } size += numNew; modCount++; return true; }
改变指定位置的元素
public E set(int index, E element) { checkElementIndex(index); Node<E> x = node(index); E oldVal = x.item; x.item = element; return oldVal; }
迭代器操作
LinkedList的iterator()方法内部调用了其listIterator()方法,所以可以只分析listIterator()方法。listIterator()提供了两个重载方法。iterator()方法和listIterator()方法的关系如下:
public Iterator<E> iterator() { return listIterator(); } public ListIterator<E> listIterator() { return listIterator(0); } public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) { checkPositionIndex(index); return new ListItr(index); }
从上面可以看到三者的关系是iterator()——>listIterator(0)——>listIterator(int index)。最终都会调用listIterator(int index)方法,其中参数表示迭代器开始的位置。在ArrayList源码分析中提到过ListIterator是一个可以指定任意位置开始迭代,并且有两个遍历方法。下面直接看ListItr的实现:
private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> { private Node<E> lastReturned; private Node<E> next; private int nextIndex; private int expectedModCount = modCount;//保存当前modCount,确保fail-fast机制 ListItr(int index) { // assert isPositionIndex(index); next = (index == size) ? null : node(index);//得到当前索引指向的next节点 nextIndex = index; } public boolean hasNext() { return nextIndex < size; } //获取下一个节点 public E next() { checkForComodification(); if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); lastReturned = next; next = next.next; nextIndex++; return lastReturned.item; } public boolean hasPrevious() { return nextIndex > 0; } //获取前一个节点,将next节点向前移 public E previous() { checkForComodification(); if (!hasPrevious()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); lastReturned = next = (next == null) ? last : next.prev; nextIndex--; return lastReturned.item; } public int nextIndex() { return nextIndex; } public int previousIndex() { return nextIndex - 1; } public void remove() { checkForComodification(); if (lastReturned == null) throw new IllegalStateException(); Node<E> lastNext = lastReturned.next; unlink(lastReturned); if (next == lastReturned) next = lastNext; else nextIndex--; lastReturned = null; expectedModCount++; } public void set(E e) { if (lastReturned == null) throw new IllegalStateException(); checkForComodification(); lastReturned.item = e; } public void add(E e) { checkForComodification(); lastReturned = null; if (next == null) linkLast(e); else linkBefore(e, next); nextIndex++; expectedModCount++; } public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) { Objects.requireNonNull(action); while (modCount == expectedModCount && nextIndex < size) { action.accept(next.item); lastReturned = next; next = next.next; nextIndex++; } checkForComodification(); } final void checkForComodification() { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } }
用linkedList实现一个栈的结构
栈是先进后出的结构,而linkedlist中有往头结点插入元素,从头结点取出元素的方法,因此可以将linkedlist的头结点作为栈顶,每一次都往头部添加元素,取元素的时候往头部取,实现与先进先出,也可以把尾结点作为栈顶,每一次都往尾部添加,往尾部取数据也可以实现,下面的代码使用尾结点作为栈顶
public class LinkStack<E> { private LinkedList<E> stack; public LinkStack(){ stack = new LinkedList<E>(); } //压入数据 public void push(E e) { stack.add(e); } //弹出数据,在Stack为空时将抛出异常 public E pop() { return stack.removeLast(); } //检索栈顶数据,但是不删除 public E peek() { return stack.getLast(); } public static void main(String[] args){ LinkStack<Integer> stack = new LinkStack<>(); stack.push(1); stack.push(2); System.out.println(stack.pop()); } }
LinkedList是基于双端链表的List,其内部的实现源于对链表的操作,所以适用于频繁增加、删除的情况;该类不是线程安全的;另外,由于LinkedList实现了Queue接口,所以LinkedList不止有队列的接口,还有栈的接口,可以使用LinkedList作为队列和栈的实现。