LinkedHahsMap的继承关系
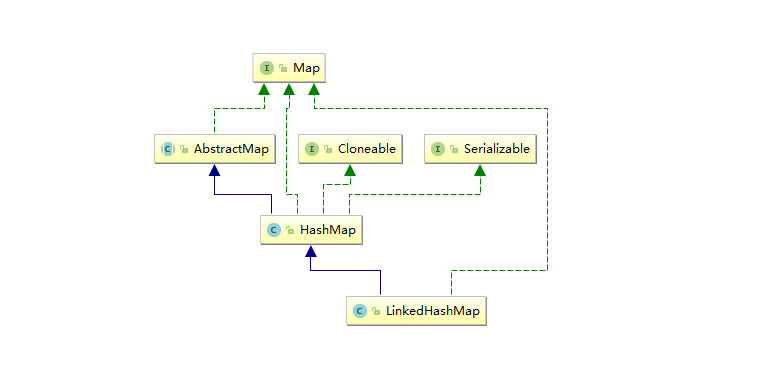
LinkedHashMap直接继承了HahsMap,而linkedHashMap和HashMap在同一个包下,因此HashMap中所有的非private的属性都能拿过来直接用。
LinkedHashMap继承HashMap原来的功能同时进行了修改。主要对原来Entry的结构进行了扩展,在继承父类Entry的基础上,有添加的两个属性Entry<K,V> before, after;和addBefore方法。同时覆盖了父类的init,addEntry,createEntry,transfer等方法,添加了header成员变量。
private transient Entry<K,V> header;
private static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Entry<K,V> { // These fields comprise the doubly linked list used for iteration. Entry<K,V> before, after; Entry(int hash, K key, V value, HashMap.Entry<K,V> next) { super(hash, key, value, next); } /** * Removes this entry from the linked list. */ private void remove() { before.after = after; after.before = before; } /** * Inserts this entry before the specified existing entry in the list. */ private void addBefore(Entry<K,V> existingEntry) { after = existingEntry; before = existingEntry.before; before.after = this; after.before = this; } /** * This method is invoked by the superclass whenever the value * of a pre-existing entry is read by Map.get or modified by Map.set. * If the enclosing Map is access-ordered, it moves the entry * to the end of the list; otherwise, it does nothing. */ void recordAccess(HashMap<K,V> m) { LinkedHashMap<K,V> lm = (LinkedHashMap<K,V>)m; if (lm.accessOrder) { lm.modCount++; remove(); addBefore(lm.header); } } void recordRemoval(HashMap<K,V> m) { remove(); } }
LinkedHashMap的初始化
linkedHashMap所有的构造方法里都调用了父类相关的构造方法,在父类构造中有调用了init方法,而linkedHashMap又覆盖了init方法,因此初始化先执行父类相关的操作,再执行自己init方法
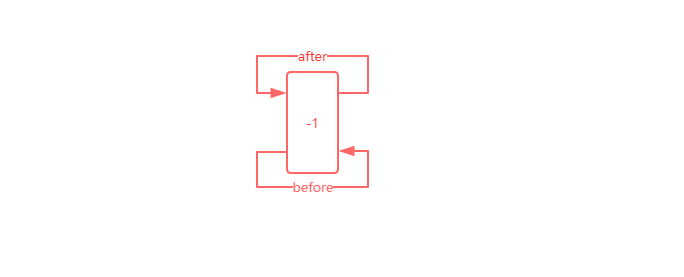
@Override void init() { header = new Entry<>(-1, null, null, null); header.before = header.after = header; }
init方法主要是将header实例化,实例化之后就会出现一个Entry类型的header的指针,其before和after都指向自己,如下图所示
LinkedHashMap put操作
linkedHashMap没有覆盖put方法,还是用父类的,因此调用父类的put会完成table属性的初始化,以及计算元素在table中的索引(调用的都是父类相关方法),然后调用addEntry方法,这时会调用自己的addEntry方法,因为linkedHashMap重写了addEntry方法
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { // 调用父类的addEntry super.addEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex); // Remove eldest entry if instructed Entry<K,V> eldest = header.after; if (removeEldestEntry(eldest)) { removeEntryForKey(eldest.key); } }
在自己的addEntry方法里面又调用了父类的方法,父类的方法如下:
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { //看是否需要扩容 if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) { resize(2 * table.length); hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0; bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length); } // 又调用createEntry createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex); }
addEntry方法里又调用createEntry,同样linkedHashMap覆盖了父类的createEntry,调用本地的
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
HashMap.Entry<K,V> old = table[bucketIndex];
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, old);
table[bucketIndex] = e;
e.addBefore(header);
size++;
}
把entry添加到数组里面后,又调用了entry对象的addBefore方法,该方法主要是将当前Entry节点的after指针指向header,before指针指向上一次put的entry,header的before指针指向
当前Entry节点,这样在下一次put新的Entry时总能通过header的before指针找到上一次put的Entry,从而维持Entry节点之间的先后顺序。
private void addBefore(Entry<K,V> existingEntry) { after = existingEntry; before = existingEntry.before; before.after = this; after.before = this; }
addBefore传进来的是header,进行如下操作
1. after = existingEntry;
把当前节点(比如是A)的after指向header(existingEntry传递的都是header), 因此A.after--->header
2. before = existingEntry.before;
当前节点的before指向 header所指向的before(header.before=B),A.before---->B
3. before.after = this;
也就是 B.after---->A
4. after.before = this;
相当于header.before--->A
如果是第一次添加,上面的B就是header对应如下图

linkedHashMap的Entry之间按照元素的put的先后顺序形成了双向循环链表,hashMap中元素与元素没有先后顺序,没法知道元素的put先后顺序,而linkedHashMap每次添加元素时都能通过header找到上一次添加的元素,通过after,和before记录当前元素前面的entry与后面的entry的联系。
LinkedHashMap和HashMap的结构的比较
linkedHashMap
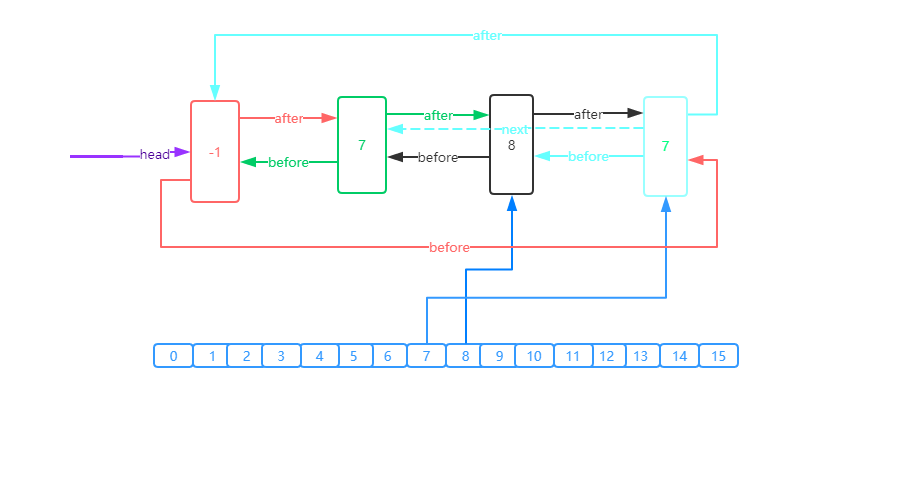
HashMap

LinkedHashMap的迭代
public static void main(String[]args){ LinkedHashMap<String,String> lm = new LinkedHashMap(); lm.put("1","python"); lm.put("2","java"); lm.put("3","c++"); //变量linkdeHashMap //方式一:迭代器迭代 Iterator<Map.Entry<String,String>> i = lm.entrySet().iterator(); while(i.hasNext()){ Map.Entry<String,String> entry = i.next(); System.out.println(entry.getKey()+":"+entry.getValue()); } //方式二:for循环 迭代entrySet,keySet,values,这里只写了entrySet for(Map.Entry<String,String> e:lm.entrySet()){ System.out.println(e.getKey()+":"+e.getValue()); } //方式一和方式二,本质上是一样的只不过方式一是手动获取迭代器,手动调用迭代器的next方法,方式二jvm自动帮你调用iterator获取迭代器和执行迭代器的next方法 //只不过方式一可以对迭代器进行操作,比如迭代的时候删除元素,方式二不能显示的获取迭代器,也就没法对迭代器操作,写法简单一点 }
1:python
2:java
3:c++
1:python
2:java
3:c++
输出的顺序和元素添加的顺序是一样的,因为linkedHashMap自己重写了父类的迭代器,从header.after开始迭代
private abstract class LinkedHashIterator<T> implements Iterator<T> { Entry<K,V> nextEntry = header.after; Entry<K,V> lastReturned = null; /** * The modCount value that the iterator believes that the backing * List should have. If this expectation is violated, the iterator * has detected concurrent modification. */ int expectedModCount = modCount; public boolean hasNext() { return nextEntry != header; } public void remove() { if (lastReturned == null) throw new IllegalStateException(); if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); LinkedHashMap.this.remove(lastReturned.key); lastReturned = null; expectedModCount = modCount; } //每次调用迭代器的next方法,都会执行该方法 Entry<K,V> nextEntry() { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); if (nextEntry == header) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Entry<K,V> e = lastReturned = nextEntry;//初始状态为header.after, nextEntry = e.after;//一次迭代之后,nextEntry指向到当前元素的after return e; } }
HashMap遍历通过table的索引遍历,从table的索引0开始,之后遍历0索引处形成的链表,再从1开始......,而添加元素时散列的位置具有不确定性,第一个添加的
可能散列到最后一个位置了,因此不能确保按照元素添加时的顺序输出。
private abstract class HashIterator<E> implements Iterator<E> { Entry<K,V> next; // next entry to return int expectedModCount; // For fast-fail int index; // current slot index从0开始 Entry<K,V> current; // current entry HashIterator() { expectedModCount = modCount; if (size > 0) { // advance to first entry Entry[] t = table;
//从table中找到第一个不为空的索引位置,比如索引为0的位置没有元素为null,index++继续循环,到索引为1的位置,判断该位置是否有entry,直到找到第一个不为空的索引位置 while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null) ; } } public final boolean hasNext() { return next != null; } //调用迭代器的next方法,会执行该方法 final Entry<K,V> nextEntry() { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); Entry<K,V> e = next; if (e == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); if ((next = e.next) == null) {
//当前索引形成的链没有下一entry,index++到下一个索引位置 Entry[] t = table; while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null)//迭代时按照索引 ; } current = e; return e; } public void remove() { if (current == null) throw new IllegalStateException(); if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); Object k = current.key; current = null; HashMap.this.removeEntryForKey(k); expectedModCount = modCount; } }
linkedHashMap的应用
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/beiyeqingteng/article/details/7010411