引用的符号是&,指针的符号是*
先来看看一段测试代码,
1: #include "stdafx.h"
2: #include <iostream>
3: using namespace std;
4: int globalJ =999;
5: 6: //返回值
7: int test1()
8: {9: int j =1;
10: cout<<"in test1(),[return value] the varaible j's address :"<<&j<<endl;
11: 12: return j;
13: } 14: 15: //使用局部变量,返回引用
16: int& test2()
17: {18: int j =998;
19: cout<<"in test2(),[use field variable and return reference] the local varaible J's address :"<<&j<<endl;
20: cout<<"in test2(),[use field variable and return reference] the local varaible J's value :"<<j<<endl;
21: 22: return j;
23: } 24: 25: //使用全局变量,返回引用
26: int& test3()
27: { 28: 29: cout<<"in test3(),[use global variable and return reference] the varaible globalJ's address :"<<&globalJ<<endl;
30: 31: return globalJ;
32: } 33: 34: 35: //返回指针
36: int* test4()
37: {38: int j =998;
39: cout<<"in test4(),[use field variable and return pointer] the local varaible J's address :"<<&j<<endl;
40: cout<<"in test4(),[use field variable and return pointer] the local varaible J's value :"<<j<<endl;
41: 42: 43: return &j;
44: }45: //返回指针
46: int* test5()
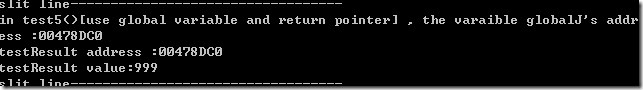
47: {48: cout<<"in test5()[use global variable and return pointer] , the varaible globalJ's address :"<<&globalJ<<endl;
49: return &globalJ;
50: } 51: 52: 53: int main(int argc, char* argv[])
54: {55: printf("Hello functions!\n");
56: 57: int testresultvalue =0;
58: testresultvalue = test1();59: cout<<"testResultValue address :"<<&testresultvalue <<endl;
60: cout<<"testResultValue value:"<<testresultvalue<<endl;
61: cout<<"slit line----------------------------------"<<endl;
62: 63: 64: int & testResultReference = test2();
65: cout<<"testResultReference address :"<<&testResultReference <<endl;
66: cout<<"testResultReference value:"<<testResultReference<<endl;
67: cout<<"slit line----------------------------------"<<endl;
68: 69: testResultReference = test3();70: cout<<"testResultReference address :"<<&testResultReference <<endl;
71: cout<<"testResultReference value:"<<testResultReference<<endl;
72: testResultReference = 4;73: cout<<"reset to 4"<<endl;
74: cout<<"testResultReference address :"<<&testResultReference <<endl;
75: cout<<"testResultReference value:"<<testResultReference<<endl;
76: 77: cout<<"slit line----------------------------------"<<endl;
78: 79: int & testResultReference2 = test3();
80: cout<<"testResultReference2 address :"<<&testResultReference2 <<endl;
81: cout<<"testResultReference2 value:"<<testResultReference2<<endl;
82: cout<<"slit line----------------------------------"<<endl;
83: 84: int* testResultPtr;
85: testResultPtr = test4();86: cout<<"testResult address :"<<testResultPtr <<endl;
87: cout<<"testResult value:"<<*testResultPtr<<endl;
88: cout<<"slit line----------------------------------"<<endl;
89: 90: testResultPtr = test5();91: cout<<"testResult address :"<<testResultPtr <<endl;
92: cout<<"testResult value:"<<*testResultPtr<<endl;
93: cout<<"slit line----------------------------------"<<endl;
94: 95: 96: 97: int temp;
98: cin>>temp; 99: 100: return 0;
101: } 102: 然后我们来分析结果,
test1 是返回值,没有什么好说的。
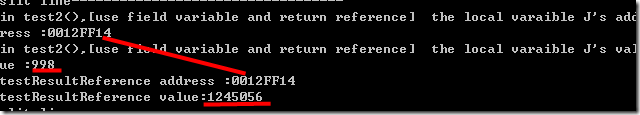
test2
本地变量的J的值是998,引用后得到的值是1245056. 因为在function作用域以外这块内存的东西就被释放掉了,所以值就不一致了。实际上,应该用全局变量(或类变量)。
注意:J的内存地址和引用变量的地址是一样的。
在编译中会报警告信息:
warning C4172: returning address of local variable or temporary
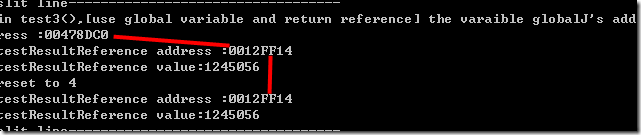
test3
globalJ全局变量的地址是00478DC0,但引用变量testresultreference的内存地址仍然是0012FF14。
结论:引用变量一次赋值后即为只读,即使再次赋值,其引用对象不变。
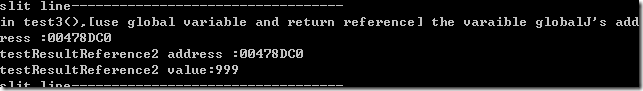
根据上面的情况我们新定义一个引用变量testresultreference2, globalJ的地址和引用变量地址是一致的。
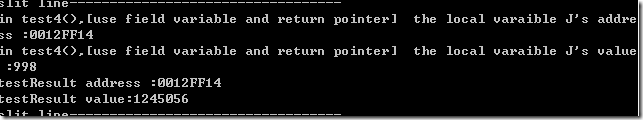
test4
这个例子跟引用有点相似。虽然指针指向的仍是本地变量的地址,但值发生了改变。
结论:指针指向局部变量,一旦超出变量域,值就有问题了。
test5
结论:请注意指针变量可以多次赋值,这样就改变了指向的对象。这点跟引用对象的使用方式不同。