说明
后台开发需要对对象的传进来的参数进行校验,有专门的校验工具,validation bean 是基于JSR-303标准开发出来的,使用注解方式实现,及其方便,但是这只是一个接口,没有具体实现。
依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.validation</groupId>
<artifactId>validation-api</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.Final</version>
</dependency>
注解类型
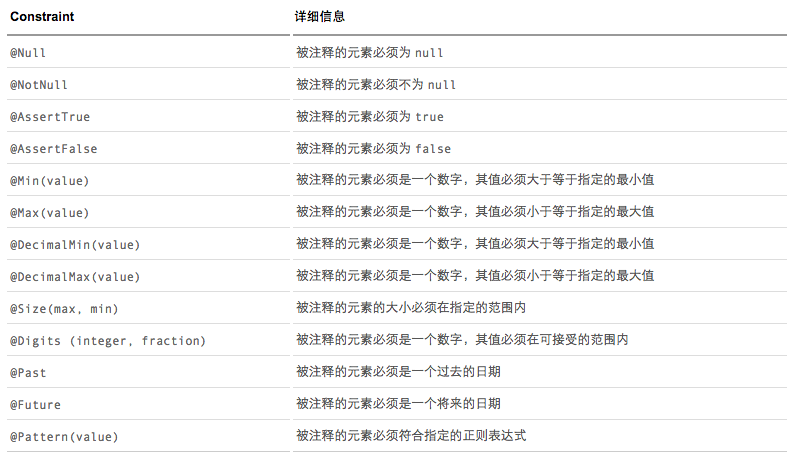
实现方式一:实体父类
一个用于VO继承的父对象,实现了一个Validate方法,可以抛出自定义异常,然后把违背约束的属性给输出出来
package com.suixingpay.dim.producersdk.entity;
import com.suixingpay.dim.producersdk.exception.ParamErrorExcaption;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.validation.ConstraintViolation;
import javax.validation.Validation;
import javax.validation.Validator;
import javax.validation.groups.Default;
public class BaseEntity implements Serializable, Cloneable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/** 得到一个验证器实例 **/
private static Validator validator = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory().getValidator();
/** 验证方法,抛出自定义异常 **/
public void validate() throws ParamErrorExcaption {
//用Map保存错误
Map<String, StringBuffer> errorMap = null;
//把对象放到验证器的验证方法中,用Set存储违背约束的对象
Set<ConstraintViolation<BaseEntity>> set = validator.validate(this, Default.class);
//当有违背约束的对象时
if (set != null && set.size() > 0) {
//初始化map
errorMap = new HashMap<String, StringBuffer>();
//保存错误属性
String property = null;
for (ConstraintViolation<BaseEntity> cv : set) {
// 这里循环获取错误信息,可以自定义格式
property = cv.getPropertyPath().toString();
if (errorMap.get(property) != null) {
errorMap.get(property).append("," + cv.getMessage());
} else {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
sb.append(cv.getMessage());
errorMap.put(property, sb);
}
}
if (errorMap != null) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
for (Map.Entry<String, StringBuffer> m : errorMap.entrySet()) {
sb.append(