1. JUnit4基础
JUnit4 与 JUnit3不同的是,不需要继承测试类,而是通过JDK5提供的注解去标识测试方法。
常用的注解如下:
@Before:初始化方法 对于每一个测试方法都要执行一次(注意与BeforeClass区别,后者是对于所有方法执行一次)
@After:释放资源 对于每一个测试方法都要执行一次(注意与AfterClass区别,后者是对于所有方法执行一次)
@Test:测试方法,在这里可以测试期望异常和超时时间
--@Test(expected=ArithmeticException.class)检查被测方法是否抛出ArithmeticException异常
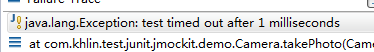
--@Test(timeout=100)检查测试方法运行耗费的时间,如果超时,则抛出异常:test timed out after xxx milliseconds
@Ignore:忽略的测试方法
@BeforeClass:针对所有测试,只执行一次,且必须为static void
@AfterClass:针对所有测试,只执行一次,且必须为static void
一个JUnit4的单元测试用例执行顺序为:
@BeforeClass -> @Before -> @Test -> @After -> @AfterClass;
一个Junit4的单元测试方法执行顺序为:
@Before -> @Test -> @After
示例代码:
package com.khlin.test.junit.jmockit.demo; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.AfterClass; import org.junit.Assert; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.BeforeClass; import org.junit.Test; public class CameraTest { private static Camera camera; //针对所有测试,只运行一次。且只能是static方法 @BeforeClass public static void init() { camera = new Camera(); System.out.println("annotation BeforeClass:"); } //每个测试方法调用前都会调用此方法 @Before public void initClass() { System.out.println("annotation Before:"); } @Test(timeout=1) public void testTakePhoto() { Assert.assertEquals(48, camera.takePhoto("abc")); System.out.println("test method"); } @After public void teardownClass() { System.out.println("annotation After:"); } @AfterClass public static void teardown() { System.out.println("annotation AfterClass:"); } }
2.JUnit4高级特性
此外,JUnit4为单元测试提供了默认的测试运行器,它的测试方法都是由它负责执行的。
开发者也可以通过继承org.junit.runner.Runner来定制自己的运行器,然后通过RunWith注解指定对应的测试运行器。
作为非专业测试人员,一般的默认运行器就可以满足需要了。当要使用一些高级特性时,就必须显式指定测试运行器。
高级特性常用的有参数化和套件测试。
1)参数化测试
构建无限组数据,对一个方法进行测试,优点是多次测试时测试方法只需要写一个,缺点是这样只能对一个方法进行测试,除非有必要大量测试,否则意义不是很大。
步骤如下:
1.在测试类上添加注解@RunWith(Parameterized.class),指定测试运行器
2.创建用于存储期望值和参数的变量
3.声明构造方法,为上述变量赋值
4.声明数据供给方法,static,返回值为Collection类型(二维数组),用@Parameters注解
示例代码:
1 package com.khlin.test.junit.jmockit.demo; 2 3 import java.util.Arrays; 4 import java.util.Collection; 5 6 import org.junit.After; 7 import org.junit.Assert; 8 import org.junit.Before; 9 import org.junit.Test; 10 import org.junit.runner.RunWith; 11 import org.junit.runners.Parameterized; 12 import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameters; 13 14 //0.注解,表示是参数化测试 15 @RunWith(Parameterized.class) 16 public class CalculatorTest { 17 18 private Calculator calculator; 19 20 //1.创建用于存储期望值和参数 21 22 private int expected; 23 24 private int i; 25 26 private int j; 27 28 //2. 构造方法赋值 29 public CalculatorTest(int expected, int i, int j) { 30 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub 31 this.expected = expected; 32 this.i = i; 33 this.j = j; 34 } 35 36 //3. 数据供给方法,static,返回值为Collection类型,用@Parameters注解 37 @Parameters 38 public static Collection initParameter() { 39 return Arrays.asList(new Object[][] { { 2, 1, 1 }, { 3, 2, 1 }, 40 { 88, 22, 66 }}); 41 } 42 43 // 每次方法前都会调用 44 @Before 45 public void init() { 46 calculator = new Calculator(); 47 } 48 49 @Test 50 public void testAdd() { 51 Assert.assertEquals(expected, calculator.add(i, j)); 52 } 53 54 @After 55 public void teardown() { 56 this.calculator = null; 57 } 58 }
2)套件测试
实际上就是将所有的测试类,集合到一个总的测试类当中,运行时将会依次去调用所有测试类的测试方法,意义。。。。好像也不是很大的样子。
步骤如下:
1.创建一个空的测试类
2.在该测试类上使用注解,@RunWith(Suite.class)指定运行器,@SuiteClasses({xxx.class, xxx.class})指定集合进来的测试类
3.保证这个空类使用public 修饰,而且存在公开的不带有任何参数的构造函数
以上面两段代码为例,套件测试类的代码如下:
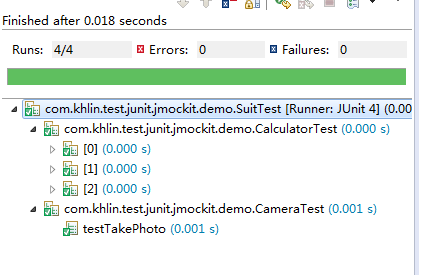
1 package com.khlin.test.junit.jmockit.demo; 2 3 import org.junit.runner.RunWith; 4 import org.junit.runners.Suite; 5 import org.junit.runners.Suite.SuiteClasses; 6 7 @RunWith(Suite.class) 8 @SuiteClasses({CalculatorTest.class, CameraTest.class}) 9 public class SuitTest { 10 11 }
运行结果,依次调用了测试方法: