一、什么是Hystrix

Hystrix是Netflix的一个开源框架,地址如下:https://github.com/Netflix/Hystrix
中文名为“豪猪”,即平时很温顺,在感受到危险的时候,用刺保护自己;在危险过去后,还是一个温顺的肉球。
所以,整个框架的核心业务也就是这2点:
- 何时需要保护
- 如何保护
二、何时需要保护
对于一个系统而言,它往往承担着2层角色,服务提供者与服务消费者。对于服务消费者而言最大的痛苦就是如何“明哲保身”,做过网关项目的同学肯定感同身受。
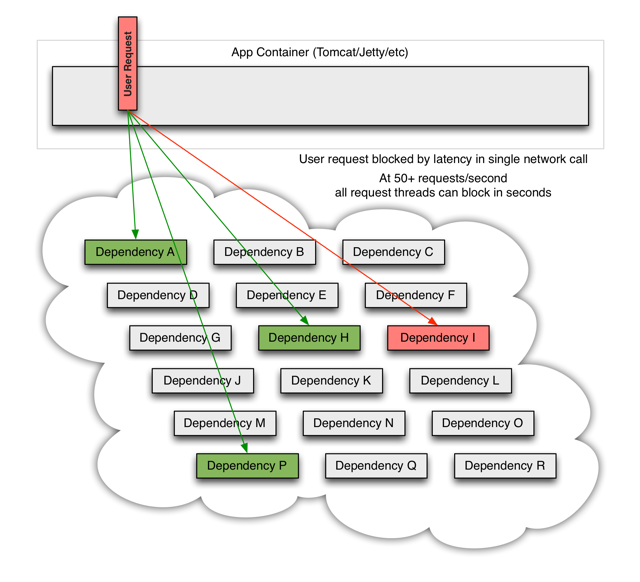
上面是一个常见的系统依赖关系,底层的依赖往往很多,通信协议包括socket、HTTP、Dubbo、webservice等等。当通信层发生网络抖动以及所依赖的系统发生业务响应异常时,我们业务本身所提供的服务能力也直接会受到影响。
这种效果传递下去就很有可能造成雪崩效应,即整个业务联调发生异常,比如业务整体超时,或者订单数据不一致。
那么核心问题就来了,如何检测业务处于异常状态?
成功率!成功率直接反映了业务的数据流转状态,是最直接的业务表现。
当然,也可以根据超时时间做判断,比如Sentinel的实现。其实这里概念上可以做一个转化,用时间做超时控制,超时=失败,这依然是一个成功率的概念。
三、如何保护
如同豪猪一样,“刺”就是他的保护工具,所有的攻击都会被刺无情的怼回去。
在Hystrix的实现中,这就出现了“熔断器”的概念,即当前的系统是否处于需要保护的状态。
当熔断器处于开启的状态时,所有的请求都不会真正的走之前的业务逻辑,而是直接返回一个约定的信息,即fallBack。通过这种快速失败原则保护我们的系统。
但是,系统不应该永远处于“有刺”的状态,当危险过后需要恢复正常。
于是对熔断器的核心操作就是如下几个功能:
- 如果成功率过低,就打开熔断器,阻止正常业务
- 随着时间的流动,熔断器处于半打开状态,尝试性放入一笔请求
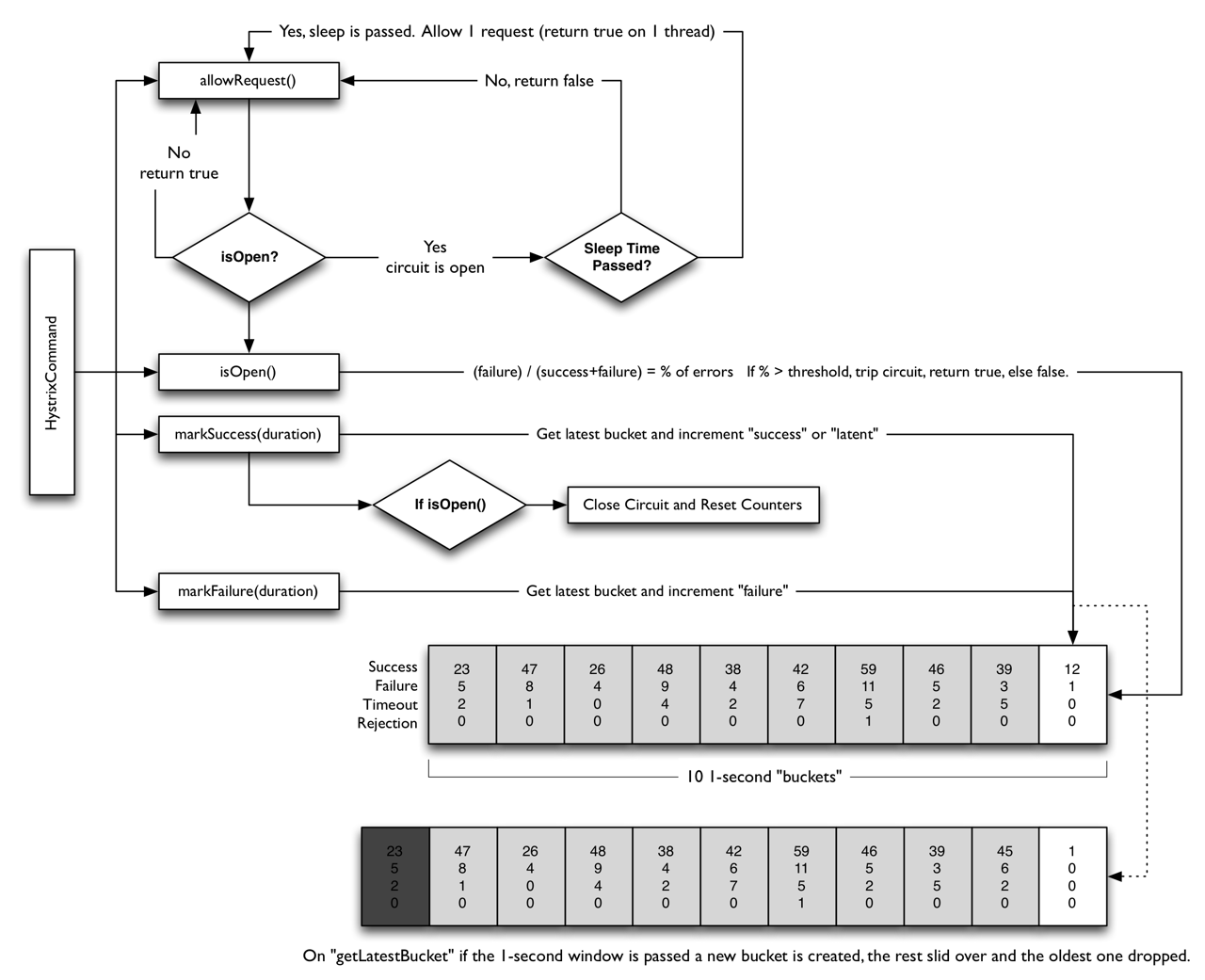
熔断器的核心API如下图:
四、限流、熔断、隔离、降级
这四个概念是我们谈起微服务会经常谈到的概念,这里我们讨论的是Hystrix的实现方式。
- 限流
- 这里的限流与guava的RateLimiter的限流差异比较大,一个是为了“保护自我”,一个是“保护下游”。
- 当对服务进行限流时,超过的流量将直接fallback,即熔断。而RateLimiter关心的其实是“流量整形”,将不规整流量在一定速度内规整。
- 熔断
- 当我的应用无法提供服务时,我要对上游请求熔断,避免上游把我压垮。
- 当我的下游依赖成功率过低时,我要对下游请求熔断,避免下游把我拖垮。
- 降级
- 降级与熔断紧密相关,熔断后业务如何表现,约定一个快速失败的fallback,即为服务降级。
- 隔离
- 业务之间不可互相影响,不同业务需要有独立的运行空间。
- 最彻底的,可以采用物理隔离,不同的机器部署。
- 次之,采用进程隔离,一个机器多个tomcat。
- 次之,请求隔离。
- 由于Hystrix框架所属的层级为代码层,所以实现的是请求隔离,线程池或信号量。
五、源码分析
先上一个Hystrix的业务流程图
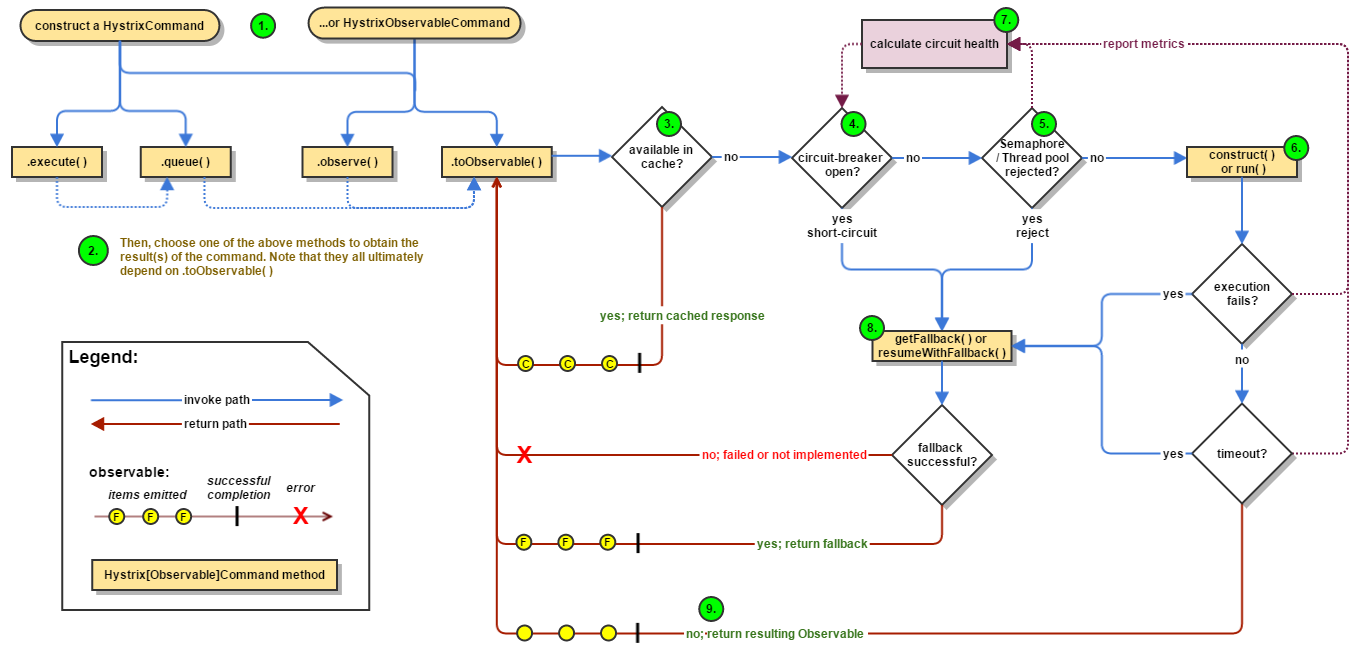
可以看到Hystrix的请求都要经过HystrixCommand的包装,其核心逻辑在AbstractComman.java类中。
下面的源码是基于RxJava的,看之前最好先了解下RxJava的常见用法与逻辑,否则看起来会很迷惑。
简单的说,RxJava就是基于回调的函数式编程。
通俗的说,就等同于策略模式的匿名内部类实现。
5.1 熔断器
首先看信号量是如何影响我们的请求的:
private Observable<R> applyHystrixSemantics(final AbstractCommand<R> _cmd) { // 自定义扩展 executionHook.onStart(_cmd); //判断熔断器是否允许请求过来 if (circuitBreaker.attemptExecution()) {
//获得分组信号量,如果没有采用信号量分组,返回默认通过的信号量实现 final TryableSemaphore executionSemaphore = getExecutionSemaphore(); final AtomicBoolean semaphoreHasBeenReleased = new AtomicBoolean(false);
//调用终止的回调函数 final Action0 singleSemaphoreRelease = new Action0() { @Override public void call() { if (semaphoreHasBeenReleased.compareAndSet(false, true)) { executionSemaphore.release(); } } }; //调用异常的回调函数 final Action1<Throwable> markExceptionThrown = new Action1<Throwable>() { @Override public void call(Throwable t) { eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.EXCEPTION_THROWN, commandKey); } }; //根据信号量尝试竞争信号量 if (executionSemaphore.tryAcquire()) { try { //竞争成功,注册执行参数 executionResult = executionResult.setInvocationStartTime(System.currentTimeMillis()); return executeCommandAndObserve(_cmd) .doOnError(markExceptionThrown) .doOnTerminate(singleSemaphoreRelease) .doOnUnsubscribe(singleSemaphoreRelease); } catch (RuntimeException e) { return Observable.error(e); } } else {
//竞争失败,进入fallback return handleSemaphoreRejectionViaFallback(); } } else {
//熔断器已打开,进入fallback return handleShortCircuitViaFallback(); } }
什么时候熔断器可以放请求进来:
@Override public boolean attemptExecution() {
//动态属性判断,熔断器是否强制开着,如果强制开着,就不允许请求 if (properties.circuitBreakerForceOpen().get()) { return false; }
//如果强制关闭,就允许请求 if (properties.circuitBreakerForceClosed().get()) { return true; }
//如果当前是关闭,就允许请求 if (circuitOpened.get() == -1) { return true; } else {
//如果当前开着,就看是否已经过了"滑动窗口",过了就可以请求,不过就不可以 if (isAfterSleepWindow()) { //only the first request after sleep window should execute //if the executing command succeeds, the status will transition to CLOSED //if the executing command fails, the status will transition to OPEN //if the executing command gets unsubscribed, the status will transition to OPEN
//这里使用CAS的方式,只有一个请求能过来,即"半关闭"状态 if (status.compareAndSet(Status.OPEN, Status.HALF_OPEN)) { return true; } else { return false; } } else { return false; } } } }
这里有个重要概念就是"滑动窗口":
private boolean isAfterSleepWindow() { final long circuitOpenTime = circuitOpened.get(); final long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); final long sleepWindowTime = properties.circuitBreakerSleepWindowInMilliseconds().get();
//滑动窗口的判断就是看看熔断器打开的时间与现在相比是否超过了配置的滑动窗口 return currentTime > circuitOpenTime + sleepWindowTime; }
5.2 隔离
如果将业务请求进行隔离?
private Observable<R> executeCommandWithSpecifiedIsolation(final AbstractCommand<R> _cmd) {
//判断隔离策略是什么,是线程池隔离还是信号量隔离 if (properties.executionIsolationStrategy().get() == ExecutionIsolationStrategy.THREAD) { // mark that we are executing in a thread (even if we end up being rejected we still were a THREAD execution and not SEMAPHORE)
//线程池隔离的运行逻辑如下 return Observable.defer(new Func0<Observable<R>>() { @Override public Observable<R> call() { executionResult = executionResult.setExecutionOccurred(); if (!commandState.compareAndSet(CommandState.OBSERVABLE_CHAIN_CREATED, CommandState.USER_CODE_EXECUTED)) { return Observable.error(new IllegalStateException("execution attempted while in state : " + commandState.get().name())); } //按照配置生成监控数据 metrics.markCommandStart(commandKey, threadPoolKey, ExecutionIsolationStrategy.THREAD); if (isCommandTimedOut.get() == TimedOutStatus.TIMED_OUT) { // the command timed out in the wrapping thread so we will return immediately // and not increment any of the counters below or other such logic return Observable.error(new RuntimeException("timed out before executing run()")); } if (threadState.compareAndSet(ThreadState.NOT_USING_THREAD, ThreadState.STARTED)) { //we have not been unsubscribed, so should proceed HystrixCounters.incrementGlobalConcurrentThreads(); threadPool.markThreadExecution(); // store the command that is being run endCurrentThreadExecutingCommand = Hystrix.startCurrentThreadExecutingCommand(getCommandKey()); executionResult = executionResult.setExecutedInThread(); /** * If any of these hooks throw an exception, then it appears as if the actual execution threw an error */ try {
//执行扩展点逻辑 executionHook.onThreadStart(_cmd); executionHook.onRunStart(_cmd); executionHook.onExecutionStart(_cmd); return getUserExecutionObservable(_cmd); } catch (Throwable ex) { return Observable.error(ex); } } else { //command has already been unsubscribed, so return immediately return Observable.empty(); } }
//注册各种场景的回调函数 }).doOnTerminate(new Action0() { @Override public void call() { if (threadState.compareAndSet(ThreadState.STARTED, ThreadState.TERMINAL)) { handleThreadEnd(_cmd); } if (threadState.compareAndSet(ThreadState.NOT_USING_THREAD, ThreadState.TERMINAL)) { //if it was never started and received terminal, then no need to clean up (I don't think this is possible) } //if it was unsubscribed, then other cleanup handled it } }).doOnUnsubscribe(new Action0() { @Override public void call() { if (threadState.compareAndSet(ThreadState.STARTED, ThreadState.UNSUBSCRIBED)) { handleThreadEnd(_cmd); } if (threadState.compareAndSet(ThreadState.NOT_USING_THREAD, ThreadState.UNSUBSCRIBED)) { //if it was never started and was cancelled, then no need to clean up } //if it was terminal, then other cleanup handled it }
//将逻辑放在线程池的调度器上执行,即将上述逻辑放入线程池中 }).subscribeOn(threadPool.getScheduler(new Func0<Boolean>() { @Override public Boolean call() { return properties.executionIsolationThreadInterruptOnTimeout().get() && _cmd.isCommandTimedOut.get() == TimedOutStatus.TIMED_OUT; } })); } else {
//走到这里就是信号量隔离,在当前线程中执行,没有调度器 return Observable.defer(new Func0<Observable<R>>() { @Override public Observable<R> call() { executionResult = executionResult.setExecutionOccurred(); if (!commandState.compareAndSet(CommandState.OBSERVABLE_CHAIN_CREATED, CommandState.USER_CODE_EXECUTED)) { return Observable.error(new IllegalStateException("execution attempted while in state : " + commandState.get().name())); } metrics.markCommandStart(commandKey, threadPoolKey, ExecutionIsolationStrategy.SEMAPHORE); // semaphore isolated // store the command that is being run endCurrentThreadExecutingCommand = Hystrix.startCurrentThreadExecutingCommand(getCommandKey()); try { executionHook.onRunStart(_cmd); executionHook.onExecutionStart(_cmd); return getUserExecutionObservable(_cmd); //the getUserExecutionObservable method already wraps sync exceptions, so this shouldn't throw } catch (Throwable ex) { //If the above hooks throw, then use that as the result of the run method return Observable.error(ex); } } }); } }
5.3 核心运行流程
private Observable<R> executeCommandAndObserve(final AbstractCommand<R> _cmd) { final HystrixRequestContext currentRequestContext = HystrixRequestContext.getContextForCurrentThread(); //执行发生的回调 final Action1<R> markEmits = new Action1<R>() { @Override public void call(R r) { if (shouldOutputOnNextEvents()) { executionResult = executionResult.addEvent(HystrixEventType.EMIT); eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.EMIT, commandKey); } if (commandIsScalar()) { long latency = System.currentTimeMillis() - executionResult.getStartTimestamp(); eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.SUCCESS, commandKey); executionResult = executionResult.addEvent((int) latency, HystrixEventType.SUCCESS); eventNotifier.markCommandExecution(getCommandKey(), properties.executionIsolationStrategy().get(), (int) latency, executionResult.getOrderedList()); circuitBreaker.markSuccess(); } } }; //执行成功的回调,标记下状态,熔断器根据这个状态维护熔断逻辑 final Action0 markOnCompleted = new Action0() { @Override public void call() { if (!commandIsScalar()) { long latency = System.currentTimeMillis() - executionResult.getStartTimestamp(); eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.SUCCESS, commandKey); executionResult = executionResult.addEvent((int) latency, HystrixEventType.SUCCESS); eventNotifier.markCommandExecution(getCommandKey(), properties.executionIsolationStrategy().get(), (int) latency, executionResult.getOrderedList()); circuitBreaker.markSuccess(); } } }; //执行失败的回调 final Func1<Throwable, Observable<R>> handleFallback = new Func1<Throwable, Observable<R>>() { @Override public Observable<R> call(Throwable t) { circuitBreaker.markNonSuccess(); Exception e = getExceptionFromThrowable(t); executionResult = executionResult.setExecutionException(e);
//各种回调进行各种fallback if (e instanceof RejectedExecutionException) { return handleThreadPoolRejectionViaFallback(e); } else if (t instanceof HystrixTimeoutException) { return handleTimeoutViaFallback(); } else if (t instanceof HystrixBadRequestException) { return handleBadRequestByEmittingError(e); } else { /* * Treat HystrixBadRequestException from ExecutionHook like a plain HystrixBadRequestException. */ if (e instanceof HystrixBadRequestException) { eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.BAD_REQUEST, commandKey); return Observable.error(e); } return handleFailureViaFallback(e); } } }; final Action1<Notification<? super R>> setRequestContext = new Action1<Notification<? super R>>() { @Override public void call(Notification<? super R> rNotification) { setRequestContextIfNeeded(currentRequestContext); } }; Observable<R> execution; if (properties.executionTimeoutEnabled().get()) { execution = executeCommandWithSpecifiedIsolation(_cmd) .lift(new HystrixObservableTimeoutOperator<R>(_cmd)); } else { execution = executeCommandWithSpecifiedIsolation(_cmd); } //注册各种回调函数 return execution.doOnNext(markEmits) .doOnCompleted(markOnCompleted) .onErrorResumeNext(handleFallback) .doOnEach(setRequestContext); }
六、小结
- Hystrix是基于单机应用的熔断限流框架
- 根据熔断器的滑动窗口判断当前请求是否可以执行
- 线程竞争实现“半关闭”状态,拿一个请求试试是否可以关闭熔断器
- 线程池隔离将请求丢到线程池中运行,限流依靠线程池拒绝策略
- 信号量隔离在当前线程中运行,限流依靠并发请求数
- 当信号量竞争失败/线程池队列满,就进入限流模式,执行fallback
- 当熔断器开启,就熔断请求,执行fallback
- 整个框架采用的RxJava的编程模式,回调函数满天飞