1. System.out.println(true && false || true && true);

true // false||true // &&优先级高于||
2. System.out.println(1 + 2 + "3");

33 //数字转化为字符串
3. a. System.out.println('b');
b. System.out.println('b' + 'c');
c. System.out.println((char) ('a' + 4));

b 197 //b的ASCII码为98,c的为99。记住a是97 e
4.编写一段代码,打印出一个二维布尔数组的内容。其中,使用 * 表示真,/表示假。打印出行号和列号。

/* * 格式化打印字符串 * */ public class TwoDArray { private static void printout(boolean[][] a1) { for (int i = 0; i < a1.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < a1[i].length; j++) { if (a1[i][j]) { System.out.println(String.format(Locale.CHINA, "%d %d *", i + 1, j + 1)); } else { System.out.println(String.format(Locale.CHINA, "%d %d /", i + 1, j + 1)); } } } } public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub boolean[][] arr = new boolean[3][4]; arr[0][0] = true; arr[0][1] = true; arr[0][2] = false; arr[0][3] = true; printout(arr); } }
5.编写一个静态方法lg(),接受一个整型参数N,返回不大于log2(N)的最大整数。不要使用 Math 库。

1 public class Log { 2 /* 3 * 返回不大于log2N的最大整数, 4 * 利用逼近的思想逆向思维,找到N下面第一个以log2为底的数M就可以了,log2M的值就是我们要找的数。 5 * 6 */ 7 private static int lg(int N) { 8 int product = 1; 9 int x = -1;// 注意这里为什么是-1 10 while (product <= N) { 11 product *= 2; 12 x++; 13 } 14 return x; 15 } 16 17 public static void main(String[] args) { 18 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 19 System.out.println(lg(1)); 20 System.out.println(lg(5)); 21 System.out.println(lg(8)); 22 System.out.println(lg(9)); 23 System.out.println(lg(18)); 24 25 } 26 27 }
6.编写一个递归的静态方法计算 ln(N!) 的值。
思想:通过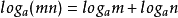 来进行递归,最简单的递归应用(求阶乘)。
来进行递归,最简单的递归应用(求阶乘)。

1 public class Product { 2 public static long logarithmic(int N) { 3 if (N == 0) return 0; 4 if (N == 1) return 1;//基础条件可能有两个 5 return N * logarithmic(N-1); 6 } 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 result = logarithmic(100); 10 double a = Math.log(result) / Math.log(e); //记得公式 11 System.out.println(a); 12 } 13 }
7.输出什么
String string1 = "hello";
String string2 = string1;
string1 = "world";
StdOut.println(string1);
StdOut.println(string2);

world
hello
8.输出什么
String s = "Hello World";
s.toUpperCase();
s.substring(6, 11);
StdOut.println(s);

Hello World //String对象是不可变的——所有字符串方法都会返回一个新的String对象 //string 类型中的 Uppercase() 以及 Substring() 都不会改变原有字符串,而是新建一个字符串。因此输出仍然为 Hello World。 //若要打印“WORLD”,请使用s=s.toUpperCase();和s=s.subSring(6,11)
***9.输出什么
String s1 = new String("hello"); // 新对象不同堆空间
String s2 = new String("hello");
String ss1 = "hello"; // 指向同一常量池
String ss2 = "hello";
System.out.println(s1 == ss1); // false
System.out.println(s1 == s2); // false
System.out.println(ss1 == ss2); // true
String t1 = "a";
String t2 = t1 + "b";
String t3 = "a" + "b";
System.out.println(t2 == "ab"); // false,t1是final类型字符串,不能改变,如要改变要创建新对象,t2是新对象。
final String tt1 = "a";
String tt2 = tt1 + "b";
System.out.println(tt2 == "ab"); // true,编译器优化把能确定的对象tt1当成了常量"a",所以tt2=tt1+"b" 成了tt2="ab"。
System.out.println(t3 == "ab"); // true 编译器把String t3= "a" + "b"; 优化成String t3="ab";
String s = "a" + "b" + "c" + "d";
System.out.println(s == "abcd");// true 只生成一个对象"abcd"
