(说明:本博客中的题目、题目详细说明及参考代码均摘自 “何海涛《剑指Offer:名企面试官精讲典型编程题》2012年”)
题目
把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。输入一个递增排序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素。例如数组 {3, 4, 5, 1, 2} 为 {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} 的一个旋转,该数组的最小值为 1 。
算法设计思想
1. 暴力查找(Bruteforce Search):把旋转数组从前到后遍历一遍,其时间复杂度为 O(n)。很明显,这种思想非常直接粗暴,没有用到旋转数组的性质。
2. 二分查找(Binary Search):每次查找都把旋转数组平均分成两部分,通过比较当前旋转数组两端点和中间点的值,判断最小值在数组的哪一部分,从而达到缩小搜索范围的目的。其中,两端点为当前的旋转数组索引最小和索引最大的元素,中间点为这两部分子数组的连结元素,也可以看做为轴枢点(pivot point),这里取旋转数组的最小索引和最大索引的算术平均值(向下取整)作为索引,其对应的元素作为中间点。具体过程,如图 2.10 所示。

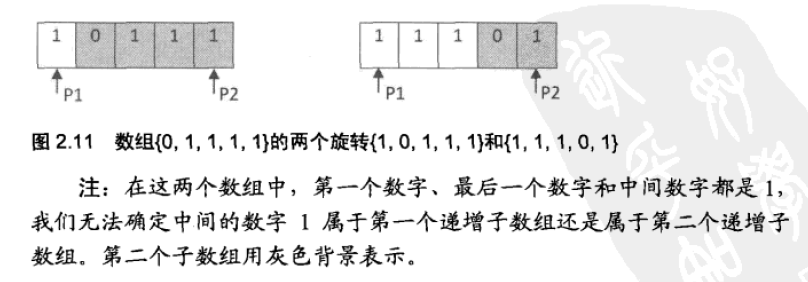
需要注意,当旋转数组的两端点的值都与中间点的值相等时,因为无法判断最小值在哪一部分,因此需要采用顺序查找方法,即暴力查找。其示例如图 2.11 所示。
C++ 实现
#include <stdio.h>
#include <exception>
#include <iostream>
// Declare a parameter exception
class ParamException: public std::exception {
virtual const char* what() const throw()
{
return "Error: input parameters exception!";
}
};
// find minimum in data[staIndex..endIndex]
int findMinInRotatedArray(int data[], int staIndex, int endIndex)
{
if (staIndex > endIndex || data == NULL)
{
throw ParamException();
}
int minimum = data[staIndex];
if (data[staIndex] >= data[endIndex] && staIndex < endIndex - 1) // 易错点
{
// Use Binary Search
int midIndex = (staIndex + endIndex) / 2;
if (data[midIndex] > data[staIndex])
minimum = findMinInRotatedArray(data, midIndex, endIndex);
else if (data[midIndex] < data[endIndex])
minimum = findMinInRotatedArray(data, staIndex, midIndex);
else
{
// Find the minimum sequentially
for (int i = staIndex+1; i <= endIndex; ++i)
if (minimum > data[i])
minimum = data[i];
}
}
else if (staIndex == (endIndex - 1))
{
minimum = data[staIndex] > data[endIndex]? data[endIndex]:data[staIndex];
}
return minimum;
}
void unitest()
{
int arr1[] = {3, 4, 5, 1, 2};
int arr2[] = {1, 0, 1, 1, 1};
int arr3[] = {1, 1, 1, 0, 1};
int arr4[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
printf("The minimum of the rotated array {3, 4, 5, 1, 2} is %d.
", findMinInRotatedArray(arr1, 0, 4));
printf("The minimum of the rotated array {1, 0, 1, 1, 1} is %d.
", findMinInRotatedArray(arr2, 0, 4));
printf("The minimum of the rotated array {1, 1, 1, 0, 1} is %d.
", findMinInRotatedArray(arr3, 0, 4));
printf("The minimum of the rotated array {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} is %d.
", findMinInRotatedArray(arr4, 0, 4));
// Test index parameter exception
try {
findMinInRotatedArray(arr3, 5, 4);
}
catch(std::exception& e) {
std::cout << e.what() << std::endl;
};
}
int main(void)
{
unitest();
return 0;
}
Python 实现
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf8 -*-
# Define ParamError Exception
class ParamError(Exception):
def __init__(self, value):
self.value = value
def __str__(self):
return repr(self.value)
# Find the minimum in rotated array
def min_in_rotated_array(data, length):
if data is None or length <= 0:
raise ParamError("Error: input parameters exception!")
# Index initialization
sta, mid, end = 0, 0, length-1
# Ensure this requisite before binary search
while data[sta] >= data[end]:
if end - sta == 1:
mid = end
break
# Get the middle index
mid = (sta + end) / 2
# Find the minimum in order
if (data[sta] == data[mid]) and (data[mid] == data[end]):
minimum = data[sta]
for i in range(sta+1, end+1):
if minimum > data[i]:
minimum = data[i]
return minimum
if data[sta] <= data[mid]:
sta = mid
elif data[end] >= data[mid]:
end = mid
return data[mid]
def unitest():
arr1 = [3, 4, 5, 1, 2]
arr2 = [1, 0, 1, 1, 1]
arr3 = [1, 1, 1, 0, 1]
arr4 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
print("The minimum of the rotated array [3, 4, 5, 1, 2] is %d." % min_in_rotated_array(arr1, 5));
print("The minimum of the rotated array [1, 0, 1, 1, 1] is %d." % min_in_rotated_array(arr2, 5));
print("The minimum of the rotated array [1, 1, 1, 0, 1] is %d." % min_in_rotated_array(arr3, 5));
print("The minimum of the rotated array [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] is %d." % min_in_rotated_array(arr4, 5));
try:
min_in_rotated_array(arr1, -2)
except Exception, e:
print "
Function call: min_in_rotated_array(arr1, -2)"
print e
if __name__ == '__main__':
unitest()
参考代码
1. targetver.h
#pragma once
// The following macros define the minimum required platform. The minimum required platform
// is the earliest version of Windows, Internet Explorer etc. that has the necessary features to run
// your application. The macros work by enabling all features available on platform versions up to and
// including the version specified.
// Modify the following defines if you have to target a platform prior to the ones specified below.
// Refer to MSDN for the latest info on corresponding values for different platforms.
#ifndef _WIN32_WINNT // Specifies that the minimum required platform is Windows Vista.
#define _WIN32_WINNT 0x0600 // Change this to the appropriate value to target other versions of Windows.
#endif
2. stdafx.h
// stdafx.h : include file for standard system include files,
// or project specific include files that are used frequently, but
// are changed infrequently
//
#pragma once
#include "targetver.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <tchar.h>
// TODO: reference additional headers your program requires here
3. stdafx.cpp
// stdafx.cpp : source file that includes just the standard includes
// MinNumberInRotatedArray.pch will be the pre-compiled header
// stdafx.obj will contain the pre-compiled type information
#include "stdafx.h"
// TODO: reference any additional headers you need in STDAFX.H
// and not in this file
4. MinNumberInRotatedArray.cpp
// MinNumberInRotatedArray.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
// 《剑指Offer——名企面试官精讲典型编程题》代码
// 著作权所有者:何海涛
#include "stdafx.h"
#include<exception>
int MinInOrder(int* numbers, int index1, int index2);
int Min(int* numbers, int length)
{
if(numbers == NULL || length <= 0)
throw new std::exception("Invalid parameters");
int index1 = 0;
int index2 = length - 1;
int indexMid = index1;
while(numbers[index1] >= numbers[index2])
{
// 如果index1和index2指向相邻的两个数,
// 则index1指向第一个递增子数组的最后一个数字,
// index2指向第二个子数组的第一个数字,也就是数组中的最小数字
if(index2 - index1 == 1)
{
indexMid = index2;
break;
}
// 如果下标为index1、index2和indexMid指向的三个数字相等,
// 则只能顺序查找
indexMid = (index1 + index2) / 2;
if(numbers[index1] == numbers[index2] && numbers[indexMid] == numbers[index1])
return MinInOrder(numbers, index1, index2);
// 缩小查找范围
if(numbers[indexMid] >= numbers[index1])
index1 = indexMid;
else if(numbers[indexMid] <= numbers[index2])
index2 = indexMid;
}
return numbers[indexMid];
}
int MinInOrder(int* numbers, int index1, int index2)
{
int result = numbers[index1];
for(int i = index1 + 1; i <= index2; ++i)
{
if(result > numbers[i])
result = numbers[i];
}
return result;
}
// ====================测试代码====================
void Test(int* numbers, int length, int expected)
{
int result = 0;
try
{
result = Min(numbers, length);
for(int i = 0; i < length; ++i)
printf("%d ", numbers[i]);
if(result == expected)
printf(" passed
");
else
printf(" failed
");
}
catch (...)
{
if(numbers == NULL)
printf("Test passed.
");
else
printf("Test failed.
");
}
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
// 典型输入,单调升序的数组的一个旋转
int array1[] = {3, 4, 5, 1, 2};
Test(array1, sizeof(array1) / sizeof(int), 1);
// 有重复数字,并且重复的数字刚好的最小的数字
int array2[] = {3, 4, 5, 1, 1, 2};
Test(array2, sizeof(array2) / sizeof(int), 1);
// 有重复数字,但重复的数字不是第一个数字和最后一个数字
int array3[] = {3, 4, 5, 1, 2, 2};
Test(array3, sizeof(array3) / sizeof(int), 1);
// 有重复的数字,并且重复的数字刚好是第一个数字和最后一个数字
int array4[] = {1, 0, 1, 1, 1};
Test(array4, sizeof(array4) / sizeof(int), 0);
// 单调升序数组,旋转0个元素,也就是单调升序数组本身
int array5[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
Test(array5, sizeof(array5) / sizeof(int), 1);
// 数组中只有一个数字
int array6[] = {2};
Test(array6, sizeof(array6) / sizeof(int), 2);
// 输入NULL
Test(NULL, 0, 0);
return 0;
}
7. 参考代码下载
项目 08_MinNumberInRotatedArray 下载: 百度网盘
何海涛《剑指Offer:名企面试官精讲典型编程题》 所有参考代码下载:百度网盘
参考资料
[1] 何海涛. 剑指 Offer:名企面试官精讲典型编程题 [M]. 北京:电子工业出版社,2012. 63-71.