ucore lab2
练习0:填写已有实验
使用可视化diff/mege工具meld可以轻松完成填写代码的任务。只需要注意lab 2对lab 1中的文件进行了修改,不能把lab 1中的代码照搬过去。
练习1:实现first-fit连续物理内存分配算法
物理地址空间的探查
在实现物理内存的分配之前必须先探查出当前物理内存的布局和大小,根据这些信息计算出操作系统可操控的内存大小并将其划分为等大的物理页。
物理地址空间的探查在bootloader中完成,探查出的信息存放在物理地址0x8000,,C程序使用结构体struct e80map对这些数据进行操作。
// 定义在kern/mm/memlayout.h中
struct e820map {
int nr_map; //探查到的内存块总数
struct {
uint64_t addr; //内存块的起始物理地址
uint64_t size; //内存块的大小
uint32_t type; //内存块的类型
} __attribute__((packed)) map[E820MAX];
};
物理页的初始化
探查到的内存使用物理地址描述,ucore设置了物理内存地址到虚拟内存地址的临时映射关系:
虚拟地址 = 物理地址 + 0xC0000000
ucore支持的最大物理地址空间是KMEMSIZE(0x380000000)。
空闲块以物理页(4096字节)为为单位,空闲块中的第一个物理页代表整个空闲块,每一个物理页都对应着一个记录它的结构struct Page:
struct Page {
int ref; // page frame's reference counter
uint32_t flags; // array of flags that describe the status of the page frame
unsigned int property; // the num of free block, used in first fit pm manager
list_entry_t page_link; // free list link
};
-
当
flags设置为Reserved时,该物理页被硬件保留,操作系统无法使用 -
当
flags未被设置为Reserved且未被设置为Property时,该物理页已被操作系统分配 -
当
flags未被设置为Reserved且设置为Property时,该物理页空闲 -
当物理页是空闲块的第一个物理页时,
property生效,代表该空闲块的大小(以物理页为单位)
物理页的初始化的核心在于:将探查到的物理内存与相应的Page关联起来。
物理页的初始化由kern/mm/pmm.c中的page_init()和init_memmap()完成。page_init负责确定探查到的物理内存块与对应的struct Page之间的映射关系,Page的初始化工作由init_memmap()调用内存管理器pmm_manager的init_memmap()方法完成。
page_init()的算法为:
- 遍历
memmap指针指向的结构e820map中的元素,求出其中的最高物理地址,计算出可用地址总大小 - 计算出所需的
Page结构,并顺序存放在程序的.bss段之上,形成以物理地址的PPN为索引的Page数组 - 再次遍历
e820map结构,将所有的Page设置为Reserved,调用init_memmap初始化操作系统可用的且地址在支持范围内物理内存对应的Page结构
init_memmap的算法为:
- 将所有可用的
Page的flags设置为Property,引用计数设置为0,property设置为0,初始化page_link - 空闲块的第一个物理块的
property设置为该空闲块的大小,将其加入到空闲链表末尾
default_init_memmap(struct Page *base, size_t n) {
assert(n > 0);
struct Page *p = base;
for (; p != base + n; p ++) {
// 在查找可用内存并分配struct Page数组时就已经将将全部Page设置为Reserved
// 将Page标记为可用的:清除Reserved,设置Property,并把property设置为0( 不是空闲块的第一个物理页 )
assert(PageReserved(p));
p->flags = p->property = 0;
SetPageProperty(p);
set_page_ref(p, 0);
list_init(&(p->page_link));
}
cprintf("Page address is %x
", (uintptr_t)base);
base->property = n;
nr_free += n;
list_add(free_list.prev, &(base->page_link));
}
只有操作系统可使用的物理页使用该函数进行初始化,因此不能被使用的物理页的Page中的Reserved属性不会被修改,确保了所有的物理页都有正确的Page。
e820map结构中数组map中的内存块是从低地址从高地址排列的,设置内存块对应的Page时都是插入到链表的尾部,因此最后形成的空闲链表是从低地址到高地址的有序链表。
为了便于内存块的边界,我的实现要求空闲块中只有第一个物理页的property域不为0,其他物理页的property必须为0。
初始化完成后的物理内存布局:
+-------------+-------------+--------------+------------+------------------------+
| | e820map | | Pages | Free memory |
+-------------+-------------+--------------+------------+------------------------+
^ ^ ^ ^ ^
| | | | |
0 0x8000 .bss段结束位置(end) freemem 0x380000000
物理页的分配
设计目标:
- 能标识请求失败的原因,便于调试
- 每次分配的内存块都是空闲链表中的最低地址空闲块
- 正确处理空闲块分割、
static struct Page *
default_alloc_pages(size_t n) {
assert(n > 0);
/* There are not enough physical memory */
if (n > nr_free) {
warn("memory shortage");
return NULL;
}
struct Page *page = NULL;
struct Page *p = NULL;
list_entry_t *le = &free_list;
/* try to find empty space to allocate */
while ((le = list_next(le)) != &free_list) {
p = le2page(le, page_link);
if (p->property >= n) {
page = p;
break;
}
}
/* external fragmentation */
if (page == NULL) {
warn("external fragmentation: There are enough memory, but can't find continuous space to allocate");
return NULL;
}
unsigned int property = page->property;
/* modify pages in allocated block(except of first page)*/
p = page + 1;
for (; p < page + n; ++p) {
ClearPageProperty(p);
// property is zero, so we needn't modify it.
}
/* modify first page of allcoated block */
ClearPageProperty(page);
page->property = n;
nr_free -= n;
/*
* If block size is bigger than requested size, split it;
* */
if (property > n) {
p = page +
p->property = property - n;
list_add_after(&(page->page_link), &(p->page_link));
}
list_del(&(page->page_link));
return page;
}
物理页的回收
default_free_pages(struct Page *page, size_t n)设计目标:
- 能够正确地处理参数:当1
n超过已分配块的页数时,回收整个块;当n小于也分配块的页数时,回收n页,剩下的内存不回收;当base指向的内存块不是已分配块的起始地址时,从base开始回收 - 能够正确的合并空闲块(我的实现回收在
base块高地址的所有相邻空闲块) - 能够正确分割已分配块:
default_free_pages要求回收已分配块中的任意页,剩下的未回收的部分作为新的已分配块 - 在回收后,空闲链表仍然是有序的
思路:
- 根据
base和n合理分割欲回收的内存块 - 合并邻接与
base块的空闲块 - 将代表新空闲块的
page_link插入到有序空闲链表中
static void
default_free_pages(struct Page *base, size_t n) {
assert(n > 0);
/* if @base is not the beginning of the alloacted block which @base points in,
* change the #property filed of the allocated block.
*/
/* find the beginning of the allocated block.
* only begging page's #property fild is non-zero.
*/
struct Page *begin = base;
size_t count = 0;
for ( ; begin->property == 0; ++count, --begin) {
assert(!PageReserved(begin) && !PageProperty(begin));
}
/* If @base is not the beginning of the allocated block,
* split the allocated block into two part.
* One part is @begin to @base,
* other part is @base to the end of the original part.
*/
if (begin != base) {
base->property = begin->property - count;
begin->property = count;
}
/* If @n is bigger than the number of pages in the @base block,
* it is not an error, just free all pages in block.
*/
if (n > base->property) {
n = base->property;
}
/* If @n is smaller than the number of pages in @base block,
* split @base block into two block.
*/
else if (n < base->property) {
(base + n)->property = base->property - n;
base->property = n;
}
/* modify status information */
struct Page *p = base;
for (; p != base + n; ++p) {
assert(!PageReserved(p) && !PageProperty(p));
p->flags = 0;
SetPageProperty(p);
}
// extern struct Page *pages;
// struct Page *pages_end = pages + npage;
// unsigned int property, old_base_property = base->property;
// list_entry_t *pos = NULL; //insert new free block after @pos
// /* merge free blocks next to current freeing block */
// p = base + base->property;
// while ((p < pages_end) && PageProperty(p)) {
// property = p->property;
// pos = (p->page_link).prev;
// base->property += p->property;
// p->property = 0;
// list_del(&p->page_link);
// p += property;
// }
// /* merge free blocks before current freeing block */
// p = base - 1;
// while ((p >= pages)) {
// while (p->property == 0) {
// --p;
// if ((p < pages) || (p->property != 0)) break;
// }
// if ((p >= pages) && (p->property != 0)) {
// p->property += base->property;
// base->property = 0;
// base = p;
// pos = (p->page_link).prev;
// list_del(&p->page_link);
// }
// }
// /* There is no free blocks adjcent to @base block. */
// if (base->property == old_base_property) {
// list_entry_t *le = &free_list;
// while ((le = list_next(le)) != &free_list) {
// if (le2page(le, page_link) > base) {
// pos = le->prev;
// break;
// }
// }
// /* free list is empty or @base points to the upmost free block */
// if (le == &free_list)
// pos = free_list.prev;
// }
// list_add(pos, &base->page_link);
// nr_free += n;
/* merge adjcent free blocks */
list_entry_t *le = list_next(&free_list), *pos = free_list.prev, *merge_before_ptr = NULL;
unsigned int old_base_property = base->property;
/* merge free blocks */
while (le != &free_list) {
p = le2page(le, page_link);
/* free_list is ascending sorted, only one free block before @base block will be merged */
if ((p + p->property == base)) {
p->property += base->property;
base->property = 0;
base = p;
pos = le->prev;
merge_before_ptr = le;
list_del(le);
}
if ((base + base->property) == p) {
base->property += p->property;
p->property = 0;
pos = le->prev;
list_del(le);
}
le = list_next(le);
}
/* if there may be free blocks before @base block, try to merge them */
if (merge_before_ptr != NULL) {
le = merge_before_ptr->prev;
while (le != &free_list) {
p = le2page(le, page_link);
if (p + p->property == base) {
p->property += base->property;
base->property = 0;
base = p;
pos = le->prev;
list_del(le);
}
le = list_prev(le);
}
}
/* @pos indicate position in whith @base's page_link should insert;
* only when there are no adjcent free blocks, should we try to find insertion position
*/
if (base->property == old_base_property) {
le = list_next(&free_list);
while (le != &free_list) {
if (le2page(le, page_link) > base) {
assert((base + base->property) < le2page(le, page_link));
pos = le->prev;
break;
}
le = list_next(le);
}
}
list_add(pos, &base->page_link);
nr_free += n;
}
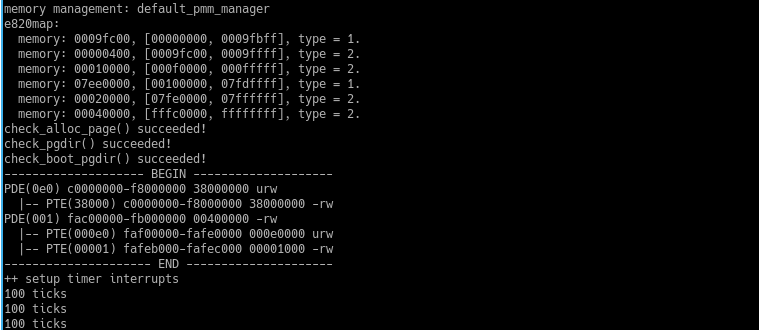
运行结果:
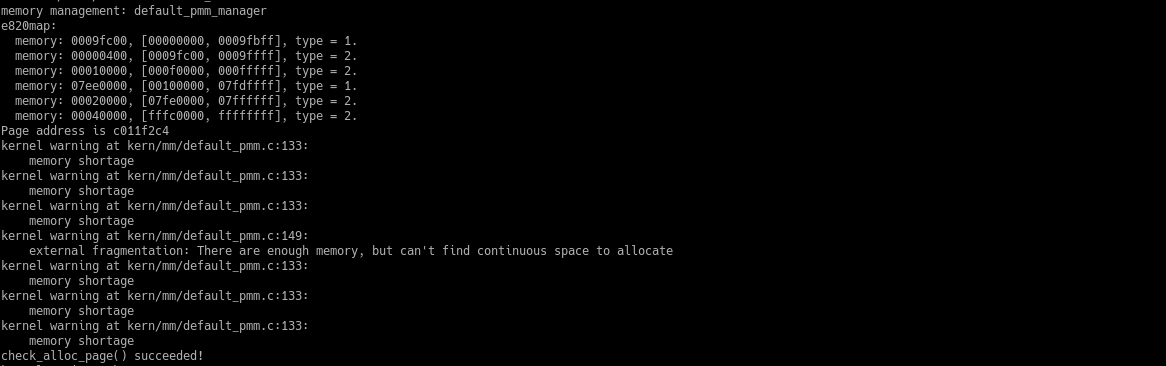
缺陷
- 空闲链表是升序的,从合并空闲块时从链表头开始遍历,最多只能够合并一个在
base块之前(低地址)的空闲块。为了将base块之前的空闲块全部合并,不得不在第一次合并后,从base块之前的空闲块向链表头遍历。 - 使用链表,分配、合并都要遍历链表,时间复杂度为O(n)。可以使用平衡二叉树替代链表,将时间复杂度降低到O(n*logn)。
default_check有bug
//风格的注释中的代码功能和下面未加注释的代码功能相同,但是注释中的代码通过查找欲回收的块相邻的Page的flags域来查找、合并空闲块。这段代码是正确的,却无法通过default_check测试。
default_check无法修改内存布局,只能临时篡改空闲链表,制造出没有可用内存或只有特定数目的可用内存的假象。当实现不通过空闲链表查找邻接空闲块时,就会“看穿”测试代码制造的假象,发现并合并空闲块、修改怕property域,测试检查对应的property时就会出错。
这个实现应该是正确的,但是因为default_check自身的缺陷,无法通过完整地通过default_check,只能通过basic_check及之前的检查。
无法通过的default_check代码如下(之后的代码进行的是相同的检查):
struct Page *p0 = alloc_pages(5), *p1, *p2;
assert(p0 != NULL);
assert(!PageProperty(p0));
list_entry_t free_list_store = free_list; //制造没有可用内存的假象,但是邻接空闲块仍然存在
list_init(&free_list);
assert(list_empty(&free_list));
assert(alloc_page() == NULL);
unsigned int nr_free_store = nr_free;
nr_free = 0;
free_pages(p0 + 2, 3); //只回收一部分内存。该内存块高地址处有相邻的空闲块
assert(alloc_pages(4) == NULL);
assert(PageProperty(p0 + 2) && p0[2].property == 3);
assert((p1 = alloc_pages(3)) != NULL);
assert(alloc_page() == NULL);
assert(p0 + 2 == p1);
测试用例分配了大小为5页的内存,但只回收其中第3页及之后的内存。
回收时,注释中的代码发现在欲回收的块之上(更高地址)的Page的flags被设置为PG_Property,这表明存在邻接空闲块,所以将这三页和其上的空闲块合并成了一个空闲块,p0[2]是这个新空闲块的第一页,property域被修改成新空闲块的页数。因此PageProperty(p0+2)为真,但p0[2].property == 3为假,测试失败。
练习2:实现寻找虚拟地址对应的页表项
页目录项和页表项中每个组成部分的含义及对ucore而言的潜在用处(还有很多不清楚的地方!!!)
intel手册还没读到详细介绍,有很多不清楚的地方,等读到了再补。
ucore使用的是页大小为 4K 的 32-bit paging,页目录项和页表项结构如下如下:
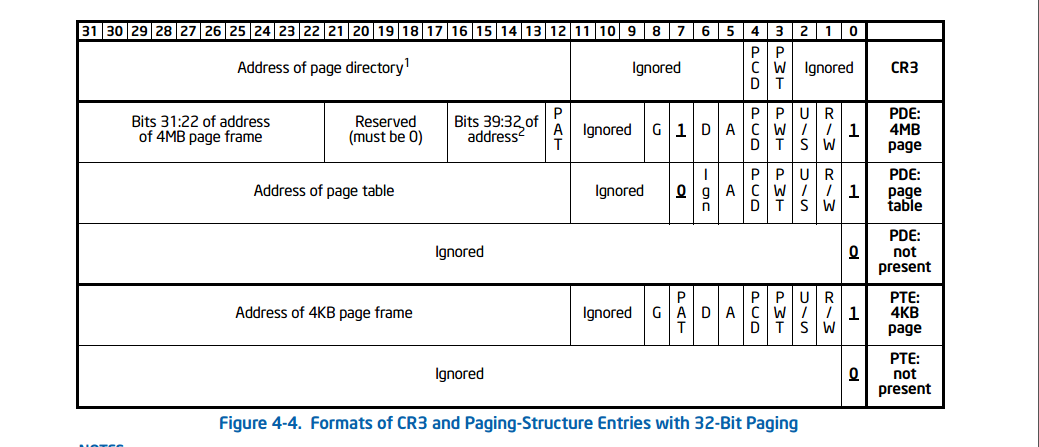
页目录项:
- bit 0(P): resent 位,若该位为 1 ,则 PDE 存在,否则不存在。
- bit 1(R/W): read/write 位,若该位为 0 ,则只读,否则可写。
- bit 2(U/S): user/supervisor位。
- bit 3(PWT): page-level write-through,若该位为1则开启页层次的写回机制。
- bit 4(PCD): page-level cache disable,若该位为1,则禁止页层次的缓存。
- bit 5(A): accessed 位,若该位为1,表示这项曾在地址翻译的过程中被访问。
- bit 6: 该位忽略。
- bit 7(PS): 这个位用来确定 32 位分页的页大小,当该位为 1 且 CR4 的 PSE 位为 1 时,页大小为4M,否则为4K。
- bit 11:8: 这几位忽略。
- bit 32:12: 页表的PPN(页对齐的物理地址)。
页表项:
页表项除了第 7 , 8 位与 PDE 不同,其余位作用均相同。
- bit 7(PAT): 如果支持 PAT 分页,间接决定这项访问的 4 K 页的内存类型;如果不支持,这位保留(必须为 0 )。
- bit 8(G): global 位。当 CR4 的 PGE 位为 1 时,若该位为 1 ,翻译是全局的;否则,忽略该位。
其中被忽略的位可以被操作系统用于实现各种功能;和权限相关的位可以用来增强ucore的内存保护机制;access 位可以用来实现内存页交换算法。
出现页访问异常时,硬件执行的工作(待续...)
intel手册还没读到这部分内容,等读到了再补。
get_pte函数的实现
get_pte函数的语义为:根据页目录pgdir来获取或创建指向线性地址la的 PTE ,是否创建页表取决于create。
步骤:
- 计算
la1对应的 PDE 地址。 - 若该 PDE 不存在(PTE 所在的页表不存在)且
create为 不为 0 ,创建页表并设置 PTE。 - 若该 PDE 不存在且
create为 0 ,返回NULL。 - 若该 PDE 存在,直接返回 PTE 虚拟地址。
PTE 内容的设置是调用者的职责,get_pte只需要给调用者一个可访问的 PTE即可。
pte_t *
get_pte(pde_t *pgdir, uintptr_t la, bool create) {
assert(pgdir != NULL);
struct Page *struct_page_vp; // virtual address of struct page
uint32_t pdx = PDX(la), ptx = PTX(la); // index of PDE, PTE
pde_t *pdep, *ptep;
pte_t *page_pa; // physical address of page
pdep = pgdir + pdx;
ptep = (pte_t *)KADDR(PDE_ADDR(*pdep)) + ptx;
// if PDE exists
if (test_bit(0, pdep)) {
return ptep;
}
/* if PDE not exsits, allocate one page for PT and create corresponding PDE */
if ((!test_bit(0, pdep)) && create) {
struct_page_vp = alloc_page(); // allocate page for PT
assert(struct_page_vp != NULL); // allocate successfully
set_page_ref(struct_page_vp, 1); // set reference count
page_pa = (pte_t *)page2pa(struct_page_vp); // convert virtual address to physical address
ptep = KADDR(page_pa + ptx); // virtual address of PTE
*pdep = (PADDR(ptep)) | PTE_P | PTE_U | PTE_W; // set PDE
memset(ptep, 0, PGSIZE); // clear PTE content
return ptep;
}
return NULL;
练习3:释放某虚地址所在的页并取消对应二级页表项的映射
Page数组元素与页目录项、页表项的对应关系
直到现在,ucore还没有实现进程,所以暂时认为只有一个页目录。页目录定义在kern/mm/entry.s中,不是通过alloc_page()创建的,所以
Page数组元素与页目录项、页表项存在对应关系。所有的物理页都有一个描述它的Page结构。所有的页表都是通过alloc_page()分配的,每个页表项都存放在一个Page结构描述的物理页中;如果 PTE 指向某物理页,同时也有一个Page结构描述这个物理页。
(1)可以通过 PTE 的地址计算其所在的页表的Page结构,(2)可以通过 PTE 指向的物理地址计算出该物理页对应的Page结构。
- (1): 将虚拟地址向下对齐到页大小,换算成物理地址(减
KERNBASE), 再将其右移PGSHIFT(12)位获得在pages数组中的索引PPN,&pages[PPN]就是所求的Page结构地址。 - (2): PTE 按位与
0xFFF获得其指向页的物理地址,再右移PGSHIFT(12)位获得在pages数组中的索引PPN,&pages[PPN]就 PTE 指向的地址对应的Page结构。
C代码如下:
// (1) this function don't exist in ucore
struct Page* page_for_pte(pde_t *ptep) {
return &pages[PPN(PADDR(ROUNDDOWN(ptep, PGSIZE))))
}
// (2) this function exists in ucore
static inline struct Page *
pte2page(pte_t pte) {
if (!(pte & PTE_P)) {
panic("pte2page called with invalid pte");
}
return pa2page(PTE_ADDR(pte));
}
让虚拟地址等于物理地址的方法
ucore 设置虚拟地址到物理地址的映射分为两步:
- lab 2 中 ucore的入口点
kern_entry()(定义在 kern/init/entry.s)中,设置了一个临时页表,将虚拟地址 KERNBASE ~ KERNBASE + 4M 映射到物理地址 0 ~ 4M ,并将 eip 修改到对应的虚拟地址。ucore 所有代码和本实验操作的所有数据结构(Page数组)都在这个虚拟地址范围内。 - 在确保程序可以正常运行后,调用
boot_map_segment(boot_pgdir, KERNBASE, KMEMSIZE, 0, PTE_W);将虚拟地址KERNBASE ~ KERNBASE + KMEMSIZE。
因为在编译链接时 ld 脚本 kern/tools/kernel.ld设置链接地址(虚拟地址),代码段基地址为0xC0100000(对应物理地址0x00100000),必须将该地址修改为0x00100000以确保内核加载正确。
/* Load the kernel at this address: "." means the current address */
/* . = 0xC0100000; */
. = 0x00100000;
.text : {
*(.text .stub .text.* .gnu.linkonce.t.*)
}
在第1步中,ucore 设置了虚拟地址 0 ~ 4M 到物理地址 0 ~ 4M 的映射以确保开启页表后kern_entry能够正常执行,在将 eip 修改为对应的虚拟地址(加KERNBASE)后就取消了这个临时映射。因为我们要让物理地址等于虚拟地址,所以保留这个映射不变(将清除映射的代码注释掉)。
next:
# unmap va 0 ~ 4M, it's temporary mapping
#xorl %eax, %eax
#movl %eax, __boot_pgdir
ucore的代码大量使用了KERNBASE+物理地址等于虚拟地址的映射,为了尽可能降低修改的代码数,仍使用宏KERNBASE和VPT(lab2中没有用到,为了避免bug仍然修改它),但是将他们减去0x38000000。
// #define KERNBASE 0xC0000000
#define KERNBASE 0x00000000
// #define VPT 0xFAC00000
#define VPT 0xC2C00000
修改了KERNBASE后,虚拟地址和物理地址的关系就变成了:
physical address + 0 == virtual address
接下来ucore的虚拟地址应该会等于物理地址,但是事情并没有这么顺利。如果仅做了这些修改,ucore会在boot_map_segment设置“好”页表后异常终止或跳转到别的地方执行。阅读源代码无法发现错误。
GDB调试发现boot_map_setment()在设置好boot_pgdir[0](0 ~ 4M)后,设置boot_pgdir[1]时get_pte会取得目录项boot_pgdir[0]指向的页表。也就是说,页目录项 PDE 0 和 PDE 1共同指向同一个页表__boot_pt1,在设置虚拟地址4 ~ 8M 到物理地址 4 ~ 8M 的映射时,同时将虚拟地址地址0 ~ 4M 映射到了 4 ~ 8M ,导致ucore运行异常。
查看页表可以发现boot_pgdir[0]和boot_pgdir[1]的内容相同!这导致了调用get_pte()时,0 ~ 8M的虚拟地址会返回同一个 PTE __boot_pt1,出现上述现象。
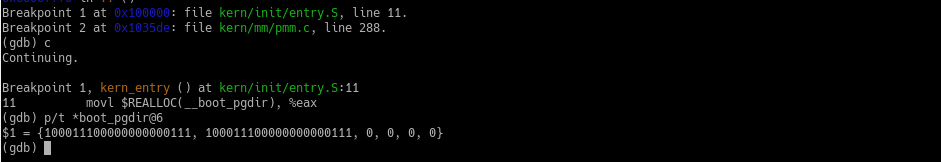
奇怪的是,kern_entry中将boot_pgdir[1]设置为0(.space指令),而不是boot_pgdir[0]。
.section .data.pgdir
.align PGSIZE
__boot_pgdir:
.globl __boot_pgdir
# map va 0 ~ 4M to pa 0 ~ 4M (temporary)
.long REALLOC(__boot_pt1) + (PTE_P | PTE_U | PTE_W)
.space (KERNBASE >> PGSHIFT >> 10 << 2) - (. - __boot_pgdir) # pad to PDE of KERNBASE
# map va KERNBASE + (0 ~ 4M) to pa 0 ~ 4M
.long REALLOC(__boot_pt1) + (PTE_P | PTE_U | PTE_W)
.space PGSIZE - (. - __boot_pgdir) # pad to PGSIZE
为了修复这个问题,在boot_map_segment()中,先清除boot_pgdir[1]的 present 位,再进行其他操作。这是get_pte会分配一个物理页作为boot_pgdir[1]指向的页表。
static void
boot_map_segment(pde_t *pgdir, uintptr_t la, size_t size, uintptr_t pa, uint32_t perm)
{
boot_pgdir[1] &= ~PTE_P;
...
}
虚拟地址到物理地址的映射改变了,不可能通过check_pgdir()和check_boot_pgdir()的测试,所以要注释掉这两行调用。
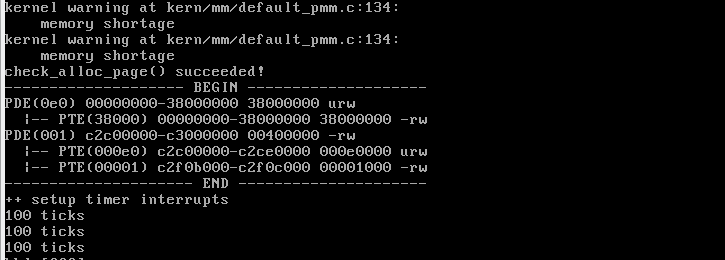
最终运行结果如下:
page_remove_pte函数的实现
page_remove_pte语义为:清除 PTE 指向的内存对应的 PTE 和 Page结构。
步骤:
- 判断
ptep指向的 PTE 是否存在,若不存在,不需要进行处理。 - 若
ptep指向的 PTE 存在,计算其指向的内存对应的Page结构,递减引用计数,若已无虚拟地址指向该页,将其释放。 - 清除 PTE 并刷新 TLB。
static inline void
page_remove_pte(pde_t *pgdir, uintptr_t la, pte_t *ptep) {
assert(pgdir != NULL);
assert(ptep != NULL);
pde_t *pdep = pgdir + PDX(la); // virtual address of PDE
// PTE pointed by ptep must reside in page pointed by PDE
assert(PDE_ADDR(*pdep) == PADDR(ROUNDDOWN(ptep, PGSIZE)));
// if PDE exists
if (test_bit(0, ptep)) {
// Page struct related with la pointed by PTE
struct Page *page = pte2page(*ptep);
// decrease page reference and free this page when page reference reachs 0
page_ref_dec(page);
if (page_ref(page) == 0)
free_page(page);
// clear PTE pointed by ptep
clear_bit(PTE_P, ptep);
// flush TLB
tlb_invalidate(pgdir, la);
}
// for debug
else
cprintf("test_bit(PTE_P, ptep) error
");
}
运行结果: