谈谈 React 里面的一些类型及使用场景
- React.Component<P,S,SS>, 这个类型绝对是 react 里面的一哥,P 是 props, S: State, SS: SnapShot. 凡是 class 组件,都得继承这个基类。下面是这个类的 type.d.ts. 生命周期主要参考下面这副图 类生命周期
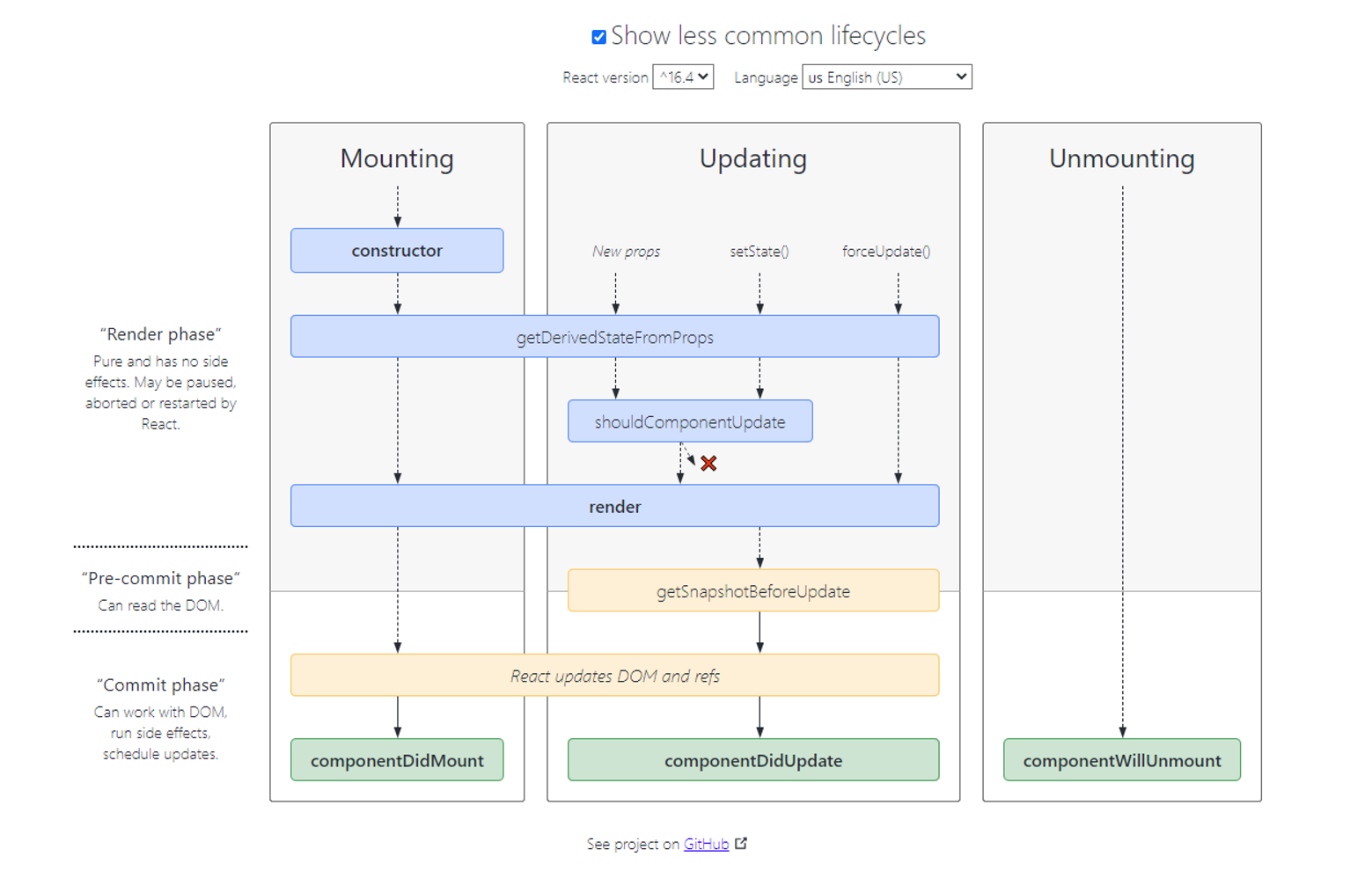 .
.
这幅图是新旧生命周期执行的图,橘色是 deprecated, 绿色是新的,新老不能同时定义,否则会报错。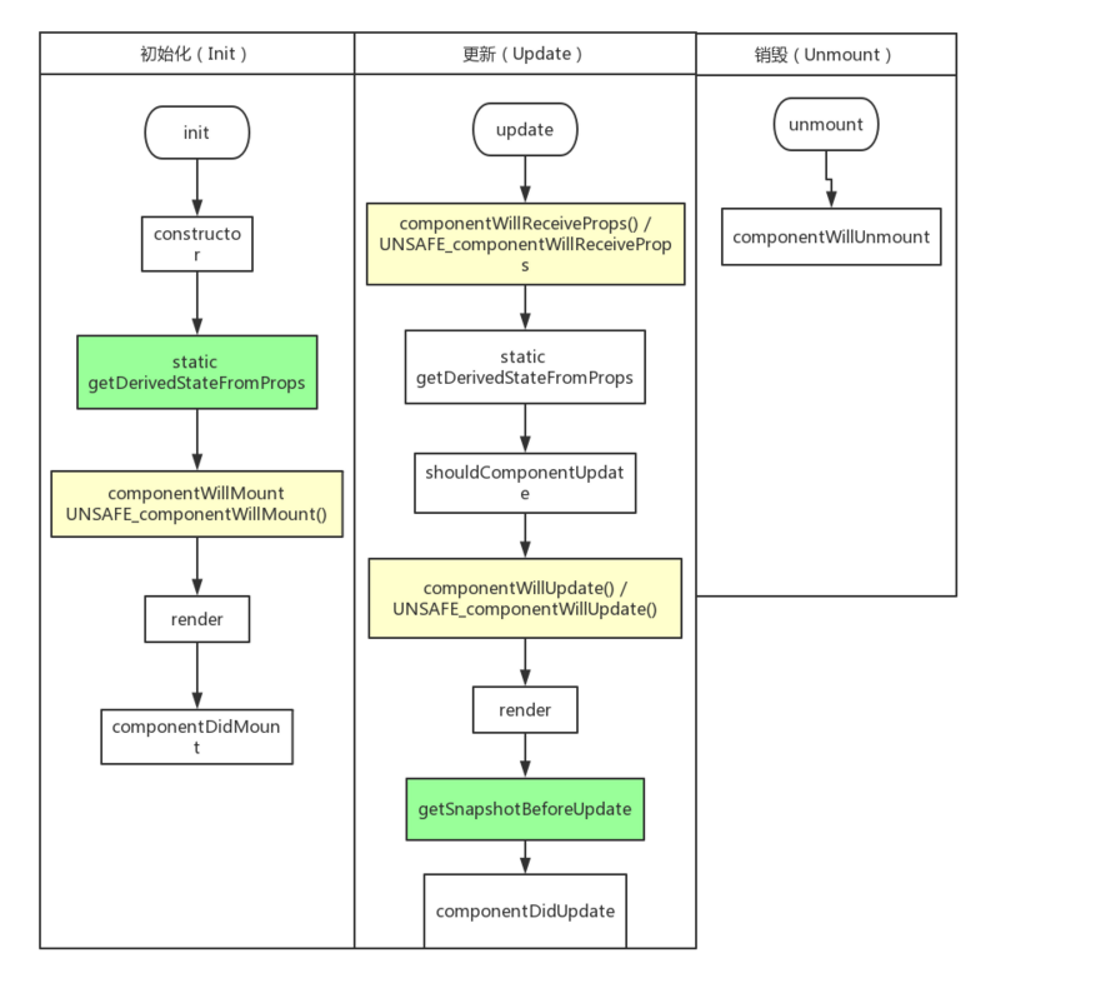
interface Component<P = {}, S = {}, SS = any>
extends ComponentLifecycle<P, S, SS> {}
ComponentLifecycle
interface ComponentLifecycle<P, S, SS = any>
extends NewLifecycle<P, S, SS>,
DeprecatedLifecycle<P, S> {
/**
* Called immediately after a component is mounted. Setting state here will trigger re-rendering.
*/
componentDidMount?(): void;
/**
* Called to determine whether the change in props and state should trigger a re-render.
*
* `Component` always returns true.
* `PureComponent` implements a shallow comparison on props and state and returns true if any
* props or states have changed.
*
* If false is returned, `Component#render`, `componentWillUpdate`
* and `componentDidUpdate` will not be called.
*/
shouldComponentUpdate?(
nextProps: Readonly<P>,
nextState: Readonly<S>,
nextContext: any
): boolean;
/**
* Called immediately before a component is destroyed. Perform any necessary cleanup in this method, such as
* cancelled network requests, or cleaning up any DOM elements created in `componentDidMount`.
*/
componentWillUnmount?(): void;
/**
* Catches exceptions generated in descendant components. Unhandled exceptions will cause
* the entire component tree to unmount.
*/
componentDidCatch?(error: Error, errorInfo: ErrorInfo): void;
}
NewLifecycle
interface NewLifecycle<P, S, SS> {
/**
* Runs before React applies the result of `render` to the document, and
* returns an object to be given to componentDidUpdate. Useful for saving
* things such as scroll position before `render` causes changes to it.
*
* Note: the presence of getSnapshotBeforeUpdate prevents any of the deprecated
* lifecycle events from running.
*/
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate?(
prevProps: Readonly<P>,
prevState: Readonly<S>
): SS | null;
/**
* Called immediately after updating occurs. Not called for the initial render.
*
* The snapshot is only present if getSnapshotBeforeUpdate is present and returns non-null.
*/
componentDidUpdate?(
prevProps: Readonly<P>,
prevState: Readonly<S>,
snapshot?: SS
): void;
}
DeprecatedLifecycle
interface DeprecatedLifecycle<P, S> {
/**
* Called immediately before mounting occurs, and before `Component#render`.
* Avoid introducing any side-effects or subscriptions in this method.
*
* Note: the presence of getSnapshotBeforeUpdate or getDerivedStateFromProps
* prevents this from being invoked.
*
* @deprecated 16.3, use componentDidMount or the constructor instead; will stop working in React 17
* @see https://reactjs.org/blog/2018/03/27/update-on-async-rendering.html#initializing-state
* @see https://reactjs.org/blog/2018/03/27/update-on-async-rendering.html#gradual-migration-path
*/
componentWillMount?(): void;
/**
* Called immediately before mounting occurs, and before `Component#render`.
* Avoid introducing any side-effects or subscriptions in this method.
*
* This method will not stop working in React 17.
*
* Note: the presence of getSnapshotBeforeUpdate or getDerivedStateFromProps
* prevents this from being invoked.
*
* @deprecated 16.3, use componentDidMount or the constructor instead
* @see https://reactjs.org/blog/2018/03/27/update-on-async-rendering.html#initializing-state
* @see https://reactjs.org/blog/2018/03/27/update-on-async-rendering.html#gradual-migration-path
*/
UNSAFE_componentWillMount?(): void;
/**
* Called when the component may be receiving new props.
* React may call this even if props have not changed, so be sure to compare new and existing
* props if you only want to handle changes.
*
* Calling `Component#setState` generally does not trigger this method.
*
* Note: the presence of getSnapshotBeforeUpdate or getDerivedStateFromProps
* prevents this from being invoked.
*
* @deprecated 16.3, use static getDerivedStateFromProps instead; will stop working in React 17
* @see https://reactjs.org/blog/2018/03/27/update-on-async-rendering.html#updating-state-based-on-props
* @see https://reactjs.org/blog/2018/03/27/update-on-async-rendering.html#gradual-migration-path
*/
componentWillReceiveProps?(nextProps: Readonly<P>, nextContext: any): void;
/**
* Called when the component may be receiving new props.
* React may call this even if props have not changed, so be sure to compare new and existing
* props if you only want to handle changes.
*
* Calling `Component#setState` generally does not trigger this method.
*
* This method will not stop working in React 17.
*
* Note: the presence of getSnapshotBeforeUpdate or getDerivedStateFromProps
* prevents this from being invoked.
*
* @deprecated 16.3, use static getDerivedStateFromProps instead
* @see https://reactjs.org/blog/2018/03/27/update-on-async-rendering.html#updating-state-based-on-props
* @see https://reactjs.org/blog/2018/03/27/update-on-async-rendering.html#gradual-migration-path
*/
UNSAFE_componentWillReceiveProps?(
nextProps: Readonly<P>,
nextContext: any
): void;
/**
* Called immediately before rendering when new props or state is received. Not called for the initial render.
*
* Note: You cannot call `Component#setState` here.
*
* Note: the presence of getSnapshotBeforeUpdate or getDerivedStateFromProps
* prevents this from being invoked.
*
* @deprecated 16.3, use getSnapshotBeforeUpdate instead; will stop working in React 17
* @see https://reactjs.org/blog/2018/03/27/update-on-async-rendering.html#reading-dom-properties-before-an-update
* @see https://reactjs.org/blog/2018/03/27/update-on-async-rendering.html#gradual-migration-path
*/
componentWillUpdate?(
nextProps: Readonly<P>,
nextState: Readonly<S>,
nextContext: any
): void;
/**
* Called immediately before rendering when new props or state is received. Not called for the initial render.
*
* Note: You cannot call `Component#setState` here.
*
* This method will not stop working in React 17.
*
* Note: the presence of getSnapshotBeforeUpdate or getDerivedStateFromProps
* prevents this from being invoked.
*
* @deprecated 16.3, use getSnapshotBeforeUpdate instead
* @see https://reactjs.org/blog/2018/03/27/update-on-async-rendering.html#reading-dom-properties-before-an-update
* @see https://reactjs.org/blog/2018/03/27/update-on-async-rendering.html#gradual-migration-path
*/
UNSAFE_componentWillUpdate?(
nextProps: Readonly<P>,
nextState: Readonly<S>,
nextContext: any
): void;
}
- React.FC
函数组件,这个是绝对的后起之秀,react 的希望,官方推荐使用定义组件的方案。 它的相关类型比较多。例如 无状态组件,函数组件等等,它的运行过程就相对简单多了,就是函数的执行,从上往下执行,注意几个底层的 hook 函数
const [val,setVal]=React.useState<S>(initialState), 它的特点是函数第一次运行的时候,或者val !==undefine的时候才会执行,第二次以后就不会执行了,其实是内部直接返回了. 注意,它必须至于 function 内部的最顶层,不能存在于任何块作用域。否则会报错。const context = React.useContext(Context), 跟上面的类似,也是第一次执行,以后只有 Context.provider 的值变化的时候才会执行。const ref = React.useRef<r>(), 这个个人绝对可以看作是上面两个的基础,它的作用是确保 ref, 在函数内部永远唯一,不管函数执行多少次。
一句话,hook 函数的目的只有一个,就是确保函数在 React setState 多次时,有些变量能够被共享,相当于提供了一个上下文。
我们来看一下FC的类型定义。
/**
* @deprecated as of recent React versions, function components can no
* longer be considered 'stateless'. Please use `FunctionComponent` instead.
*
* @see [React Hooks](https://reactjs.org/docs/hooks-intro.html)
*/
type StatelessComponent<P = {}> = FunctionComponent<P>;
type FC<P = {}> = FunctionComponent<P>;
interface FunctionComponent<P = {}> {
(props: PropsWithChildren<P>, context?: any): ReactElement<any, any> | null;
propTypes?: WeakValidationMap<P>;
contextTypes?: ValidationMap<any>;
defaultProps?: Partial<P>;
displayName?: string;
}
React.ForwardRefRenderFunction<TRef,P>以及著名的React.forwardRef<TRef,P>()它是用来定义组件,同时将 ref 传递给内部的组件,因为一般情况下,ref 会被赋予当前组件的值,而这个方法的作用就是洞穿当前组件,将 ref 往下传递。 我们来看一下类型定义,很清楚.forwardRef() 返回的其实是一个方法,同时含有一下属性.
interface ForwardRefRenderFunction<T, P = {}> {
(props: PropsWithChildren<P>, ref: ForwardedRef<T>): ReactElement | null;
displayName?: string;
// explicit rejected with `never` required due to
// https://github.com/microsoft/TypeScript/issues/36826
/**
* defaultProps are not supported on render functions
*/
defaultProps?: never;
/**
* propTypes are not supported on render functions
*/
propTypes?: never;
}
function forwardRef<T, P = {}>(
render: ForwardRefRenderFunction<T, P>
): ForwardRefExoticComponent<PropsWithoutRef<P> & RefAttributes<T>>;
// will show `ForwardRef(${Component.displayName || Component.name})` in devtools by default,
// but can be given its own specific name
interface ForwardRefExoticComponent<P> extends NamedExoticComponent<P> {
defaultProps?: Partial<P>;
propTypes?: WeakValidationMap<P>;
}
interface NamedExoticComponent<P = {}> extends ExoticComponent<P> {
displayName?: string;
}
// TODO: similar to how Fragment is actually a symbol, the values returned from createContext,
// forwardRef and memo are actually objects that are treated specially by the renderer; see:
// https://github.com/facebook/react/blob/v16.6.0/packages/react/src/ReactContext.js#L35-L48
// https://github.com/facebook/react/blob/v16.6.0/packages/react/src/forwardRef.js#L42-L45
// https://github.com/facebook/react/blob/v16.6.0/packages/react/src/memo.js#L27-L31
// However, we have no way of telling the JSX parser that it's a JSX element type or its props other than
// by pretending to be a normal component.
//
// We don't just use ComponentType or SFC types because you are not supposed to attach statics to this
// object, but rather to the original function.
interface ExoticComponent<P = {}> {
/**
* **NOTE**: Exotic components are not callable.
*/
(props: P): ReactElement | null;
readonly $$typeof: symbol;
}
memo() vs React.useMemo() vs React.PureComponentReact.memo() 它是一个 HOC,只有当内部组件的输入参数变化了,或者内部组件使用了 useState,useReducer,useContext 这些 hook 函数,它才会触发 render. 否则就直接返回上次 render 的内部组件.
简单的说,memo()函数执行后返回的是内部组件,跟内部组件几乎一模一样,只是,它的更新规则变了。同时它的比较还是浅比较。它属于 HOC。
useMemo() 它是 hook 函数,它将返回的值进行缓存,除非以来项发生变化,否则值不变。它本身是一个函数。
这里还要提到 useCallback(), 跟 useMemo() 的唯一差别是它缓存的是函数。通常用于事件响应函数的缓存等。
PureComponent, 它跟普通的 Component 的差别是默认实现了 componentshouldupdate() 方法,跟 memo() 类似。
function memo<T extends ComponentType<any>>(
Component: T,
propsAreEqual?: (
prevProps: Readonly<ComponentProps<T>>,
nextProps: Readonly<ComponentProps<T>>
) => boolean
): MemoExoticComponent<T>;
// will show `Memo(${Component.displayName || Component.name})` in devtools by default,
// but can be given its own specific name
type MemoExoticComponent<T extends ComponentType<any>> = NamedExoticComponent<
ComponentPropsWithRef<T>
> & {
readonly type: T;
};
// I made 'inputs' required here and in useMemo as there's no point to memoizing without the memoization key
// useCallback(X) is identical to just using X, useMemo(() => Y) is identical to just using Y.
/**
* `useCallback` will return a memoized version of the callback that only changes if one of the `inputs`
* has changed.
*
* @version 16.8.0
* @see https://reactjs.org/docs/hooks-reference.html#usecallback
*/
// TODO (TypeScript 3.0): <T extends (...args: never[]) => unknown>
function useCallback<T extends (...args: any[]) => any>(
callback: T,
deps: DependencyList
): T;
/**
* `useMemo` will only recompute the memoized value when one of the `deps` has changed.
*
* Usage note: if calling `useMemo` with a referentially stable function, also give it as the input in
* the second argument.
*
* ```ts
* function expensive () { ... }
*
* function Component () {
* const expensiveResult = useMemo(expensive, [expensive])
* return ...
* }
* ```
*
* @version 16.8.0
* @see https://reactjs.org/docs/hooks-reference.html#usememo
*/
// allow undefined, but don't make it optional as that is very likely a mistake
function useMemo<T>(factory: () => T, deps: DependencyList | undefined): T;
class PureComponent<P = {}, S = {}, SS = any> extends Component<P, S, SS> {}
- React.cloneElement() 一般,我们如果希望改变一个组件变量的输入参数或者 ref,我们就会调用它。因为我们不知道它内容是什么,所以需要这个方法,特别是写一个同样组件时,希望给传进来的组件添加一些额外功能的时候,类似与 Angular 里面的
TemplateRef<any>. - ReactDom.render(), 这个方法是将一个 React 组件插入到 React Virtual Dom 树上,类似与 Angular 里面的
AppRef.AttachRef()。这个很厉害的,可以通过编程的方式动态添加组件。