锐化概念
图像平滑过程是去除噪声的过程。图像的主要能量在低频部分,而噪声主要集中在高频部分。图像的边缘信息主要也在高频部分,在平滑处理后,将会丢不部分边缘信息。因此需要使用锐化技术来增强边缘。
平滑处理的本质是图像经过平均或积分运算,锐化进行逆运算(如微分)即可。微分运算是求信号变化频率,可以增强高频分量的作用。在对图像进行锐化处理前要确定图像有较高的信噪比,否则处理后的图像增加的噪声比信号多。
常用的微分运算有一阶微分和二阶微分。一阶微分
二阶微分
一阶微分特点:
1、平坦段为0
2、灰度阶梯和斜坡起始点为非0
3、斜坡面为非0
二阶微分特点:
1、平坦段为0
2、灰度阶梯和斜坡起始、终止处为非0
3、沿着常数斜率斜坡段为0
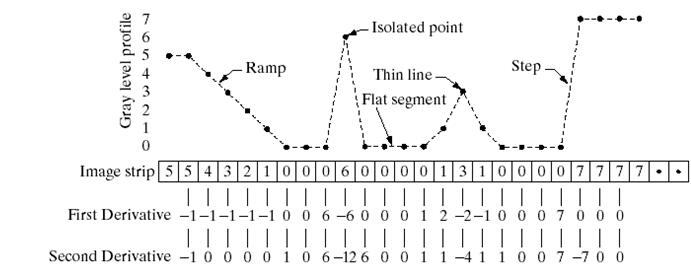
可以看出:
1、一阶微分能产生比较宽的边缘(沿斜坡很长一段为非0),而二阶微对细节更敏感(如细线、孤立点、斜坡起始点不为0)。
2、一阶微分都灰度阶跃反应强烈;二阶微分对灰度阶梯变换产生双相应(阶跃点两边都不为0)。
3、在大多数图像增强应用中,二阶微分效果好过一阶微分。
图像微分定义
图像数据是离散数据,用差分代替微分
x方向
y方向
其模和方向
同理,可以得到二阶微分(差分公式)
x方向
y方向
其模和方向
单方向一阶微分锐化
单方向一阶微分锐化是指锐化某一方向的边缘。最简单的就是锐化水平方向和垂直方向。
锐化水平方向
锐化垂直方向
锐化后可能出现像素值为负,这处理方法有:
(1):所有像素值统一加上一个值。这样处理效果类似浮雕。
(2):所有像素取绝对值,这样可以有效提取边缘。
实验:
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
const char* path = "";
Mat img = imread(path);
if (img.empty())
{
cout << "error";
return -1;
}
imshow("原图像", img);
//水平方向边缘提取
Mat h_kern = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 1, 1, 1,
0, 0, 0,
-1, -1, -1);
Mat h_mat;
filter2D(img, h_mat, img.depth(), h_kern);
imshow("水平方向边缘提取", h_mat);
Mat v_kern = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 1, 0, -1,
1, 0, -1,
1, 0, -1);
Mat v_mat;
filter2D(img, v_mat, img.depth(), v_kern);
imshow("线性非均值滤波2", v_mat);
waitKey();
return 0;
}
无方向一阶微分锐化
对于有规则的物体,单方向锐化有比较好的效果,但是对于不规则物体,常常需要无方向一节锐化。
交叉微分(Roberts算法)
Sobel锐化
OpenCV函数
void Sobel(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int ddepth, int dx, int dy, int ksize=3, double scale=1, double delta=0, int borderType=BORDER_DEFAULT )
Priwitt锐化
实验
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
const char* path = "";
Mat img = imread(path);
if (img.empty())
{
cout << "error";
return -1;
}
imshow("原图像", img);
/****************************Roberts**************************/
Mat Roberts_kern_x = (Mat_<float>(2, 2) << -1, 0,
0, 1);
Mat Roberts_kern_y = (Mat_<float>(2, 2) << 0, 1,
- 1, 0);
Mat Roberts_Mat_x, Roberts_Mat_y, Roberts_Mat;
filter2D(img, Roberts_Mat_x, img.depth(), Roberts_kern_x);
filter2D(img, Roberts_Mat_y, img.depth(), Roberts_kern_y);
Mat Roberts_abs_x, Roberts_abs_y;
convertScaleAbs(Roberts_Mat_x, Roberts_abs_x);
convertScaleAbs(Roberts_Mat_y, Roberts_abs_y);
addWeighted(Roberts_abs_x, 0.5, Roberts_abs_y, 0.5, 0, Roberts_Mat);
imshow("Roberts", Roberts_Mat);
/****************************Roberts**************************/
/****************************Sobel**************************/
Mat Sobel_Mat_x, Sobel_Mat_y, Sobel_Mat;
Sobel(img, Sobel_Mat_x, img.depth(), 1, 0);
Sobel(img, Sobel_Mat_y, img.depth(), 0, 1);
convertScaleAbs(Sobel_Mat_x, Sobel_Mat_x);
convertScaleAbs(Sobel_Mat_y, Sobel_Mat_y);
addWeighted(Sobel_Mat_x, 0.5, Sobel_Mat_y, 0.5, 0, Sobel_Mat);
imshow("Sobel", Sobel_Mat);
/****************************Sobel**************************/
/****************************Priwitt**************************/
Mat Priwitt_kern_x = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << -1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1);
Mat Priwitt_kern_y = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << -1, 0, 1, -1, 0, 1, -1, 0, 1);
Mat Priwitt_Mat_x, Priwitt_Mat_y, Priwitt_Mat;
filter2D(img, Priwitt_Mat_x, img.depth(), Priwitt_kern_x);
filter2D(img, Priwitt_Mat_y, img.depth(), Priwitt_kern_y);
convertScaleAbs(Priwitt_Mat_x, Priwitt_Mat_x);
convertScaleAbs(Priwitt_Mat_y, Priwitt_Mat_y);
addWeighted(Priwitt_Mat_x, 0.5, Priwitt_Mat_y, 0.5, 0, Priwitt_Mat);
imshow("Peiwitt", Priwitt_Mat);
waitKey();
return 0;
}
结论:
Roberts算法的模板为2 * 2,提取边缘能力较弱。
Sobel算法与Priwitt算法的模板大小相同,属于同一类型,因此处理效果基本相同。
二阶微分锐化
有些灰度特性,一阶微分并不能有效提取,这时需要二阶微分
对应矩阵
上面矩阵即为Laplacian算子。Laplacian算子还有变形
Laplacian算子
上面几个算子,(H_1)和(H_2)效果接近,(H_3)效果比较差,(H_4)相加后为1,接近原图。
Wallis算子
在处理时,加入对数处理过程。
在前面的算法公式中注意以下几点:
1)为了防止对0取对数,计算时实际上是用log(f(i, j) + 1);
2)因为对数值很小log(256) = 5.45, 所以计算
时用46*log(f(i, j) + 1)。
(46 = 255 / log(256))
高斯-拉普拉斯算子
Laplacian算子对噪声很敏感,所以在进行锐化之前,需要先对图像进行平滑,减小噪声影响。高斯拉普拉斯算子将平滑和锐化结合在一起,适应了上面的需求。