输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]] 输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]
给你一个长度为 n 的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random ,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
构造这个链表的 深拷贝。 深拷贝应该正好由 n 个 全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的 next 指针和 random 指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点 。
例如,如果原链表中有 X 和 Y 两个节点,其中 X.random --> Y 。那么在复制链表中对应的两个节点 x 和 y ,同样有 x.random --> y 。
返回复制链表的头节点。
用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
- val:一个表示 Node.val 的整数。
- random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从 0 到 n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为 null 。
你的代码 只 接受原链表的头节点 head 作为传入参数。
示例 1:
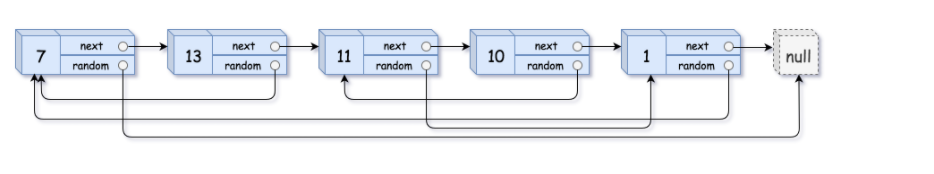
输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]] 输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
示例 2:
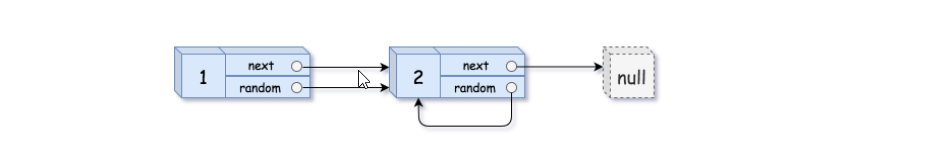
输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]] 输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]
示例 3:

输入:head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]] 输出:[[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
示例 4:
输入:head = [] 输出:[] 解释:给定的链表为空(空指针),因此返回 null。
方法一:深拷贝(投机取巧哈哈)
最直接的办法就是遍历一次这个链表,然后把每个节点本身,
以及它的next和它的random指针指向的节点都重新new一遍(为了达到深拷贝的目的),
最后返回新的头部节点就行了。在Java里面需要用到一个HashMap<Node, Node>这样的结构,
作为key的Node是老的Node,作为value的Node是新的Node。
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { int val; Node next; Node random; public Node(int val) { this.val = val; this.next = null; this.random = null; } } */ class Solution { public Node copyRandomList(Node head) { if (head == null) return null; Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>(); Node cursor = head; while(cursor != null) { Node n = map.get(cursor); if (n == null) { n = new Node(cursor.val); map.put(cursor, n); } Node next = map.get(cursor.next); if (next == null && cursor.next != null) { next = new Node(cursor.next.val); map.put(cursor.next, next); } n.next = next; Node random = map.get(cursor.random); if (random == null && cursor.random != null) { random = new Node(cursor.random.val); map.put(cursor.random, random); } n.random = random; cursor = cursor.next; } return map.get(head); } }
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { int val; Node next; Node random; public Node(int val) { this.val = val; this.next = null; this.random = null; } } */ class Solution { public Node copyRandomList(Node head) { if(head==null) return null; Node node = head; while(node!=null){ Node temp = new Node(node.val); temp.next = node.next; node.next = temp; node = temp.next; } node = head; while(node!=null){ if(node.random!=null) node.next.random = node.random.next; //注意判断是否为空 node = node.next.next; } node = head; Node res = head.next; Node temp = head.next; while(temp!=null&&temp.next!=null){ node.next = temp.next; temp.next = node.next.next; node = node.next; temp = temp.next; } node.next = null; //别忘了最后一个节点连接给null return res; } }
2回溯法:
public class Solution { // HashMap which holds old nodes as keys and new nodes as its values. HashMap<Node, Node> visitedHash = new HashMap<Node, Node>(); public Node copyRandomList(Node head) { if (head == null) { return null; } // If we have already processed the current node, then we simply return the cloned version of // it. if (this.visitedHash.containsKey(head)) { return this.visitedHash.get(head); } // Create a new node with the value same as old node. (i.e. copy the node) Node node = new Node(head.val, null, null); // Save this value in the hash map. This is needed since there might be // loops during traversal due to randomness of random pointers and this would help us avoid // them. this.visitedHash.put(head, node); // Recursively copy the remaining linked list starting once from the next pointer and then from // the random pointer. // Thus we have two independent recursive calls. // Finally we update the next and random pointers for the new node created. node.next = this.copyRandomList(head.next); node.random = this.copyRandomList(head.random); return node; } }