文件的打开与关闭
打开文件
在python,使用open函数,可以打开一个已经存在的文件,或者创建一个新文件
open(文件名,访问模式)
f = open('test.txt', 'w')
关闭文件
close( )
# 新建一个文件,文件名为:test.txt f = open('test.txt', 'w') # 关闭这个文件 f.close()
文件的读写
写数据
使用write()可以完成向文件写入数据
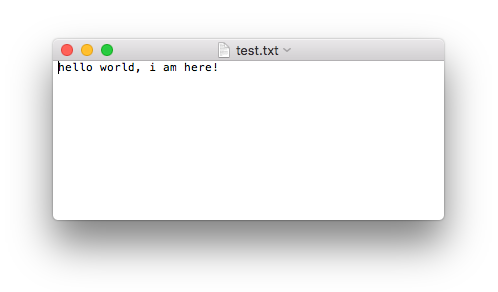
f = open('test.txt', 'w') f.write('hello world, i am here!') f.close()
运行现象:
注意:
- 如果文件不存在那么创建,如果存在那么就先清空,然后写入数据
读数据
使用read(num)可以从文件中读取数据,num表示要从文件中读取的数据的长度(单位是字节),如果没有传入num,那么就表示读取文件中所有的数据
f = open('test.txt', 'r') content = f.read(5) print(content) print("-"*30) content = f.read() print(content) f.close()
运行现象:

注意:
- 如果open是打开一个文件,那么可以不用谢打开的模式,即只写
open('test.txt') - 如果使用读了多次,那么后面读取的数据是从上次读完后的位置开始的
读数据(readlines)
就像read没有参数时一样,readlines可以按照行的方式把整个文件中的内容进行一次性读取,并且返回的是一个列表,其中每一行的数据为一个元素
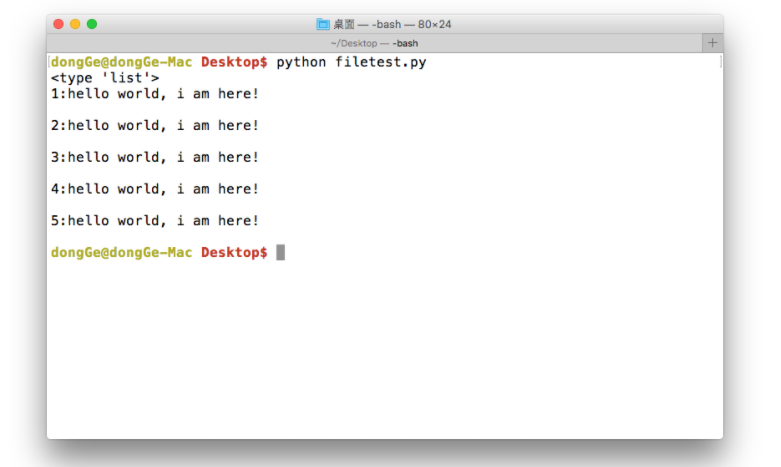
#coding=utf-8 f = open('test.txt', 'r') content = f.readlines() print(type(content)) i=1 for temp in content: print("%d:%s"%(i, temp)) i+=1 f.close()
运行现象:
读数据(readline)
一次读一行,如果多次读,读上次读的下一行。
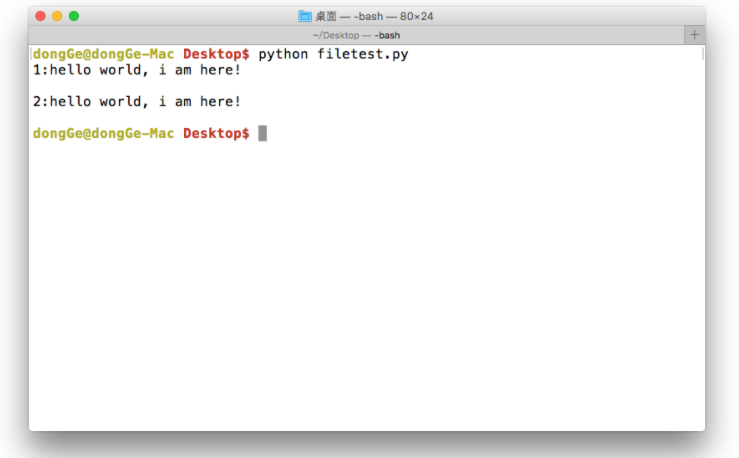
f = open('test.txt', 'r') content = f.readline() print("1:%s"%content) content = f.readline() print("2:%s"%content) f.close()
文件的定位读写
文件test.txt
0123456789
012345678
获取当前读写的位置
在读写文件的过程中,如果想知道当前的位置,可以使用tell()来获取
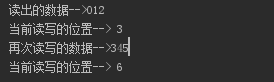
f = open("test.txt") one_read = f.read(3) print("读出的数据-->"+ one_read) print( "当前读写的位置-->", f.tell()) print("再次读写的数据-->" + f.read(3)) print( "当前读写的位置-->", f.tell()) f.close()
定位到某个位置
如果在读写文件的过程中,需要从另外一个位置进行操作的话,可以使用seek()
seek(offset, from)有2个参数
- offset:偏移量
- from:方向
- 0:表示文件开头
- 1:表示当前位置
- 2:表示文件末尾
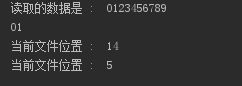
#从文件开头,偏移5个字节
str = f.read(13) print("读取的数据是 : ", str) # 查找当前位置 position = f.tell() print("当前文件位置 : ", position) # 重新设置位置 f.seek(5, 0) # 查找当前位置 position = f.tell() print("当前文件位置 : ", position)
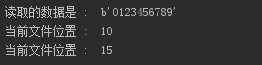
#从当前位置,偏移5个字节
注意:需要已“rb+”模式打开文件否则报错。
f = open("test.txt","rb+") str = f.read(13) print("读取的数据是 : ", str) # 查找当前位置 position = f.tell() print("当前文件位置 : ", position) # 重新设置位置 f.seek(5, 1) # 查找当前位置` position = f.tell() print("当前文件位置 : ", position) f.close()
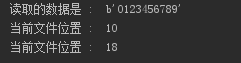
#离文件末尾,3字节处
注意:需要已“rb+”模式打开文件否则报错。
f = open("test.txt","rb+") str = f.read(10) print("读取的数据是 : ", str) # 查找当前位置 position = f.tell() print("当前文件位置 : ", position) # 重新设置位置 f.seek(-3, 2) # 查找当前位置` position = f.tell() print("当前文件位置 : ", position) f.close()
其他文件相关操作
#文件重命名。 # os.rename('test[复件].txt','rename.txt') #删除文件 # os.remove('rename.txt') #创建文件夹 # os.mkdir('k') #获取当前目录 # v = os.getcwd() #改变默认目录 # os.chdir("../") # v = os.getcwd() #获取当前目录列表 # print(os.listdir('../')) #删除文件夹 # os.rmdir('./k')