Function Curve
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65535/65535 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 31 Accepted Submission(s): 10
Problem Description
Given sequences of k1, k2, … kn, a1, a2, …, an and b1, b2, …, bn. Consider following function:
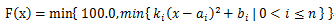
Then we draw F(x) on a xy-plane, the value of x is in the range of [0,100]. Of course, we can get a curve from that plane.
Can you calculate the length of this curve?
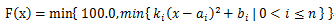
Then we draw F(x) on a xy-plane, the value of x is in the range of [0,100]. Of course, we can get a curve from that plane.
Can you calculate the length of this curve?
Input
The first line of the input contains one integer T (1<=T<=15), representing the number of test cases.
Then T blocks follow, which describe different test cases.
The first line of a block contains an integer n ( 1 <= n <= 50 ).
Then followed by n lines, each line contains three integers ki, ai, bi ( 0<=ai, bi<100, 0<ki<100 ) .
Then T blocks follow, which describe different test cases.
The first line of a block contains an integer n ( 1 <= n <= 50 ).
Then followed by n lines, each line contains three integers ki, ai, bi ( 0<=ai, bi<100, 0<ki<100 ) .
Output
For each test case, output a real number L which is rounded to 2 digits after the decimal point, means the length of the curve.
Sample Input
2
3
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
1
4 5 6
Sample Output
215.56
278.91
Hint
All test cases are generated randomly.
Source
Recommend
liuyiding



写起来太多了,希望没有写错了。,基本和代码实现对应的
1 /* *********************************************** 2 Author :kuangbin 3 Created Time :2013/8/24 13:45:56 4 File Name :F:2013ACM练习比赛练习2013通化邀请赛1006.cpp 5 ************************************************ */ 6 7 #include <stdio.h> 8 #include <string.h> 9 #include <iostream> 10 #include <algorithm> 11 #include <vector> 12 #include <queue> 13 #include <set> 14 #include <map> 15 #include <string> 16 #include <math.h> 17 #include <stdlib.h> 18 #include <time.h> 19 using namespace std; 20 double k[100],a[100],b[100]; 21 vector<double>p; 22 const double eps = 1e-8; 23 void add(double a1,double b1,double c1) 24 { 25 if(fabs(a1) < eps && fabs(b1) < eps) 26 return; 27 if(fabs(a1) < eps) 28 { 29 double x = -c1/b1; 30 if(x >= 0 && x <= 100) 31 p.push_back(x); 32 return; 33 } 34 double tmp = b1*b1 - 4*a1*c1; 35 if(fabs(tmp) < eps) 36 { 37 double x = -b1/(2*a1); 38 if(x >= 0 && x <= 100) 39 p.push_back(x); 40 return; 41 } 42 else if(tmp <=-eps) 43 { 44 return; 45 } 46 double x1 = (-b1+sqrt(tmp))/(2*a1); 47 double x2 = (-b1-sqrt(tmp))/(2*a1); 48 if(x1 >= 0 && x1 <= 100) 49 p.push_back(x1); 50 if(x2 >= 0 && x2 <= 100) 51 p.push_back(x2); 52 } 53 double calc(double x) 54 { 55 return x*sqrt(1+x*x)/2 + log(x+sqrt(1+x*x))/2; 56 } 57 int main() 58 { 59 //freopen("in.txt","r",stdin); 60 //freopen("out.txt","w",stdout); 61 int T; 62 int n; 63 scanf("%d",&T); 64 while(T--) 65 { 66 scanf("%d",&n); 67 for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) 68 scanf("%lf%lf%lf",&k[i],&a[i],&b[i]); 69 p.clear(); 70 for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) 71 add(k[i],-2*k[i]*a[i],k[i]*a[i]*a[i]+b[i]-100); 72 for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) 73 for(int j = i+1;j < n;j++) 74 { 75 add(k[i]-k[j],2*k[j]*a[j]-2*k[i]*a[i],k[i]*a[i]*a[i]+b[i]-k[j]*a[j]*a[j]-b[j]); 76 } 77 p.push_back(0); 78 p.push_back(100); 79 double ans = 0; 80 sort(p.begin(),p.end()); 81 int sz = p.size(); 82 for(int i = 1;i < sz;i++) 83 { 84 if(p[i] - p[i-1] < eps)continue; 85 double tmp = (p[i] + p[i-1])/2; 86 int tt = 0; 87 for(int j = 0;j < n;j++) 88 if( k[j]*(tmp-a[j])*(tmp-a[j])+b[j] < k[tt]*(tmp-a[tt])*(tmp-a[tt])+b[tt]) 89 tt = j; 90 if(k[tt]*(tmp-a[tt])*(tmp-a[tt])+b[tt] > 100) 91 { 92 ans += p[i] - p[i-1]; 93 continue; 94 } 95 ans += (calc(2*k[tt]*(p[i]-a[tt]))-calc(2*k[tt]*(p[i-1]-a[tt])))/(2*k[tt]); 96 97 } 98 printf("%.2lf ",ans); 99 } 100 return 0; 101 }