一、sleep和wait的区别。
1.wait可以指定时间,也可以不指定。
而sleep必须制定。
2.在同步的时候,对于CPU的执行权和以及锁的处理不同。
wait:释放执行权,释放锁。
sleep:释放执行权,不释放锁。
二、线程是否安全?

1 class Test implements Runnable 2 { 3 public synchronized void show() 4 { 5 try 6 { 7 wait(); 8 } 9 catch (InterruptedException e) 10 { 11 } 12 } 13 public synchronized void method() 14 { 15 notifyAll(); 16 } 17 }
假设有四个线程0123,其中有三个线程012全部挂在wait上了,另外一个线3程则调用了notifyAll方法,这样在同步代码块中就有了三个线程,这和“在同步代码块中只能有一个线程”的原则相违背,线程变得不安全了。这话乍听起来没有错,事实上是有问题的。实际上,当线程3调用了notifyAll方法的时候,CPU执行权还在自己手里,而被唤醒的三个线程虽然拥有了执行资格,但是仅仅是执行资格,他们将会加入堵塞队列,等待执行权;等到线程三释放了执行权以及锁(method方法结束),在堵塞队列中的012线程中的一个将会获得执行权,任务结束后,释放锁以及执行权并交给下一个线程。。
验证代码:

1 class Test implements Runnable 2 { 3 public boolean flag=true; 4 public void run() 5 { 6 if(this.flag==true) 7 show(); 8 else 9 method(); 10 } 11 public synchronized void show() 12 { 13 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":将会等待"); 14 try 15 { 16 wait(); 17 } 18 catch (InterruptedException e) 19 { 20 } 21 for(int i=1;i<=10;i++) 22 { 23 try 24 { 25 Thread.sleep(50); 26 } 27 catch (InterruptedException e) 28 { 29 } 30 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":正在执行"+i); 31 } 32 } 33 public synchronized void method() 34 { 35 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":将会唤醒所有线程"); 36 notifyAll(); 37 for(int i=1;i<=10;i++) 38 { 39 try 40 { 41 Thread.sleep(50); 42 } 43 catch (InterruptedException e) 44 { 45 } 46 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":正在执行"+i); 47 } 48 } 49 } 50 public class Demo 51 { 52 public static void main(String args[]) 53 { 54 Test t=new Test(); 55 Thread t1=new Thread(t); 56 Thread t2=new Thread(t); 57 Thread t3=new Thread(t); 58 Thread t4=new Thread(t); 59 t1.start(); 60 t2.start(); 61 t3.start(); 62 63 try 64 { 65 Thread.sleep(20); 66 } 67 catch (InterruptedException e) 68 { 69 } 70 t.flag=false; 71 t4.start(); 72 73 } 74 }
其运行结果和预想的结果相同。
三、怎么结束线程
1.使用stop方法:已过时,不推荐使用。
2.控制run方法结束。
可以使用标志变量的方法。

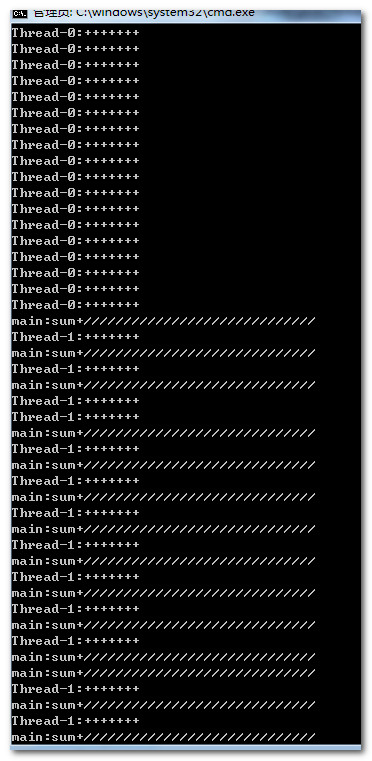
1 /* 2 能控制线程停止的情况。 3 */ 4 class Test implements Runnable 5 { 6 private boolean flag=true; 7 public void run() 8 { 9 while(flag) 10 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":+++++++++++++++++++"); 11 } 12 public void setFlag() 13 { 14 this.flag=false; 15 } 16 } 17 public class Demo 18 { 19 public static void main(String args[]) 20 { 21 Test t=new Test(); 22 Thread t1=new Thread(t); 23 Thread t2=new Thread(t); 24 t1.start(); 25 t2.start(); 26 27 int sum=0; 28 while(true) 29 { 30 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":sum+"+"/////////////////////////////"); 31 if(++sum==20) 32 { 33 t.setFlag(); 34 System.out.println("over"); 35 break; 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 }
这是在未加同步的时候。若是加上同步,有的时候就不管用了。

1 /* 2 不能控制线程停止的情况。 3 */ 4 class Test implements Runnable 5 { 6 private boolean flag=true; 7 public void run() 8 { 9 while(flag) 10 { 11 synchronized(this) 12 { 13 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正在执行"); 14 try 15 { 16 this.wait(); 17 } 18 catch(InterruptedException e) 19 { 20 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":+++++++++++++++++++"); 21 } 22 } 23 } 24 } 25 public void setFlag() 26 { 27 this.flag=false; 28 } 29 } 30 public class Demo 31 { 32 public static void main(String args[]) 33 { 34 Test t=new Test(); 35 Thread t1=new Thread(t); 36 Thread t2=new Thread(t); 37 t1.start(); 38 t2.start(); 39 40 int sum=0; 41 while(true) 42 { 43 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":sum+"+"/////////////////////////////"); 44 if(++sum==20) 45 { 46 t.setFlag(); 47 System.out.println("over"); 48 break; 49 } 50 } 51 } 52 }
由于线程0、1均进入了冻结状态,所以不再判断flag标记,线程也就不会结束了。
3.使用interrupt方法结束线程。
此方法带有强制性,因此会抛出异常,需要捕获。
interrupt方法的功能是将处于冻结状态的线程强制性唤醒,使其具有CPU执行资格。

1 /* 2 使用interrupt方法控制线程停止的情况。 3 */ 4 class Test implements Runnable 5 { 6 private boolean flag=true; 7 public void run() 8 { 9 while(flag) 10 { 11 synchronized(this) 12 { 13 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正在执行"); 14 try 15 { 16 this.wait(); 17 } 18 catch(InterruptedException e) 19 { 20 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":+++++++++++++++++++"); 21 } 22 } 23 } 24 } 25 public void setFlag() 26 { 27 this.flag=false; 28 } 29 } 30 public class Demo 31 { 32 public static void main(String args[]) 33 { 34 Test t=new Test(); 35 Thread t1=new Thread(t); 36 Thread t2=new Thread(t); 37 t1.start(); 38 t2.start(); 39 40 int sum=0; 41 while(true) 42 { 43 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":sum+"+"/////////////////////////////"); 44 if(++sum==20) 45 { 46 t.setFlag(); 47 t1.interrupt(); 48 t2.interrupt(); 49 System.out.println("over"); 50 break; 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 }
4、使用守护线程
setDaemon方法:设置线程为守护线程或者用户线程、后台线程。
守护线程具有依附性,一旦所依附的线程结束,自己也将会消失,所以要“守护”,所以叫“用户线程”(这是和系统线程相对应的叫法)。
JAVA中规定,一旦程序中线程全部为守护线程,则JAVA虚拟机将会自动退出,所有线程都将会结束。
将t2设置成守护线程,一旦t1线程和main线程全部结束,t2线程将成为唯一一个线程而且是守护线程,JAVA虚拟机将会自动退出,t2线程也会跟着结束。

1 /* 2 守护线程举例。 3 */ 4 class Test implements Runnable 5 { 6 private boolean flag=true; 7 public void run() 8 { 9 while(flag) 10 { 11 synchronized(this) 12 { 13 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正在执行"); 14 try 15 { 16 this.wait(); 17 } 18 catch(InterruptedException e) 19 { 20 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":+++++++++++++++++++"); 21 } 22 } 23 } 24 } 25 public void setFlag() 26 { 27 this.flag=false; 28 } 29 } 30 public class Demo 31 { 32 public static void main(String args[]) 33 { 34 Test t=new Test(); 35 Thread t1=new Thread(t); 36 Thread t2=new Thread(t); 37 t1.start(); 38 //要在t2线程开启之前设置。 39 t2.setDaemon(true); 40 41 t2.start(); 42 43 44 int sum=0; 45 while(true) 46 { 47 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":sum+"+"/////////////////////////////"); 48 if(++sum==20) 49 { 50 t.setFlag(); 51 t1.interrupt(); 52 //t2.interrupt(); 53 System.out.println("over"); 54 break; 55 } 56 } 57 } 58 }
设置守护线程要在线程启动之前设置。
四.join方法。
join方法的功能:加入当前线程,当前线程会释放执行权,一直等到新加入的线程执行完任务之后才执行自己的任务。

1 /* 2 join方法使用 3 */ 4 class Test implements Runnable 5 { 6 private boolean flag=true; 7 public void run() 8 { 9 int sum=1; 10 while(++sum<21) 11 { 12 13 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":+++++++"); 14 } 15 } 16 public void setFlag() 17 { 18 this.flag=false; 19 } 20 } 21 public class Demo 22 { 23 public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception 24 { 25 Test t=new Test(); 26 Thread t1=new Thread(t); 27 Thread t2=new Thread(t); 28 t1.start(); 29 t1.join(); 30 31 t2.start(); 32 33 34 35 int sum=0; 36 while(true) 37 { 38 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":sum+"+"/////////////////////////////"); 39 if(++sum==20) 40 { 41 t.setFlag(); 42 t1.interrupt(); 43 t2.interrupt(); 44 System.out.println("over"); 45 break; 46 } 47 } 48 } 49 }
五、线程优先级
toString方法:返回字符串包括线程名称、线程优先级、线程所属的线程组。
线程有10个优先级1-10,且数字越大,优先级越大。为了便于使用,将优先级划分为三级:
Thread.MAX_PRIORITY:最大优先级,相当于10
Thread.MIN_PRIORITY:最小优先级,相当于1
Thread.MAX_PRIORITY:默认优先级,相当于5
设置优先级的方法是setPriority();

1 /* 2 验证优先级,其实没什么效果 3 */ 4 class Test implements Runnable 5 { 6 private boolean flag=true; 7 public void run() 8 { 9 int sum=1; 10 while(++sum<21) 11 { 12 13 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()); 14 } 15 } 16 public void setFlag() 17 { 18 this.flag=false; 19 } 20 } 21 public class Demo 22 { 23 public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception 24 { 25 Test t=new Test(); 26 Thread t1=new Thread(t); 27 Thread t2=new Thread(t); 28 29 t1.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); 30 Thread.currentThread().setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); 31 t2.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY); 32 33 t1.start(); 34 t2.start(); 35 36 int sum=0; 37 while(true) 38 { 39 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()); 40 if(++sum==20) 41 { 42 t.setFlag(); 43 t1.interrupt(); 44 t2.interrupt(); 45 System.out.println("over"); 46 break; 47 } 48 } 49 } 50 }
应当注意的是,设置优先级的高低只是增加或者减小CPU切换到的概率,实际上仍然要争夺CPU执行权。
六、yied方法
yield方法是静态方法,使用Thread类名直接调用,作用是释放当前线程的执行权。给别的线程更多的机会执行任务。

1 /* 2 验证yield方法,是Thread类的静态方法。 3 */ 4 class Test implements Runnable 5 { 6 private boolean flag=true; 7 public void run() 8 { 9 int sum=1; 10 while(sum<20) 11 { 12 try 13 { 14 Thread.sleep(10); 15 } 16 catch(InterruptedException e){} 17 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+":"+sum); 18 Thread.yield(); 19 sum++; 20 } 21 } 22 public void setFlag() 23 { 24 this.flag=false; 25 } 26 } 27 public class Demo 28 { 29 public static void main(String args[]) 30 { 31 Test t=new Test(); 32 Thread t1=new Thread(t); 33 Thread t2=new Thread(t); 34 t1.start(); 35 t2.start(); 36 37 } 38 }
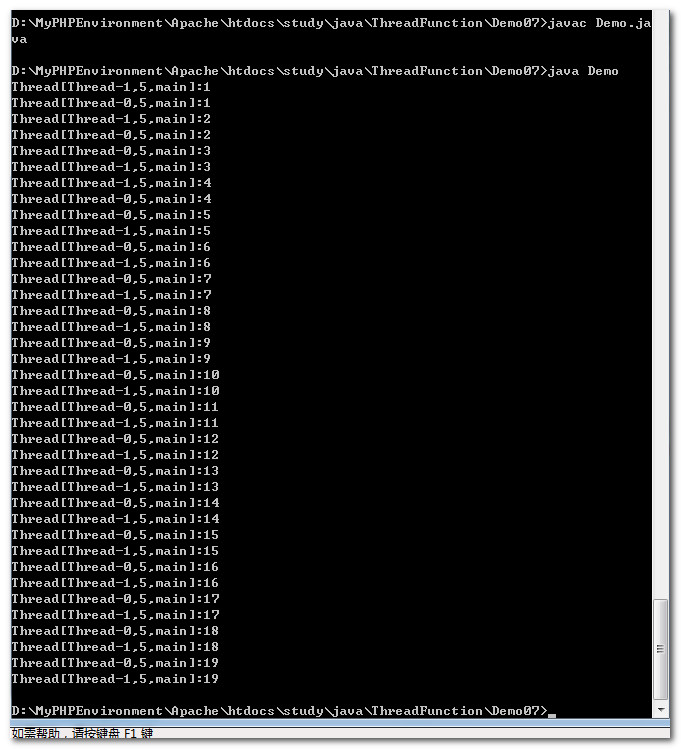
我们可以观察到两个线程任务的执行进度高度同步,这是由于yied方法强制放弃CPU执行权造成的。
