本文将从 GPU-Operator 概念介绍、安装部署、深度训练测试应用部署,以及在 KubeSphere 使用自定义监控面板对接 GPU 监控,从原理到实践,逐步浅析介绍与实践 GPU-Operator。
GPU-Operator简介
众所周知,Kubernetes 平台通过设备插件框架提供对特殊硬件资源的访问,如 NVIDIA GPU、网卡、Infiniband 适配器和其他设备。然而,使用这些硬件资源配置和管理节点需要配置多个软件组件,如驱动程序、容器运行时或其他依赖库,这是困难的和容易出错的。
NVIDIA GPU Operator 由 Nvidia 公司开源,利用了 Kubernetes 平台的 Operator 控制模式,方便地自动化集成管理 GPU 所需的 NVIDIA 设备组件,有效地解决了上述GPU设备集成的痛点。这些组件包括 NVIDIA 驱动程序(用于启用 CUDA )、用于 GPU 的 Kubernetes 设备插件、NVIDIA Container 运行时、自动节点标签、基于 DCGM 的监控等。
NVIDIA GPU Operator 的不仅实现了设备和组件一体化集成,而且它管理 GPU 节点就像管理 CPU 节点一样方便,无需单独为 GPU 节点提供特殊的操作系统。值得关注的是,它将GPU各组件容器化,提供 GPU 能力,非常适合快速扩展和管理规模 GPU 节点。当然,对于已经为GPU组件构建了特殊操作系统的应用场景来说,显得并不是那么合适了。
GPU-Operator 架构原理
前文提到,NVIDIA GPU Operator 管理 GPU 节点就像管理 CPU 节点一样方便,那么它是如何实现这一能力呢?
我们一起来看看 GPU-Operator 运行时的架构图:
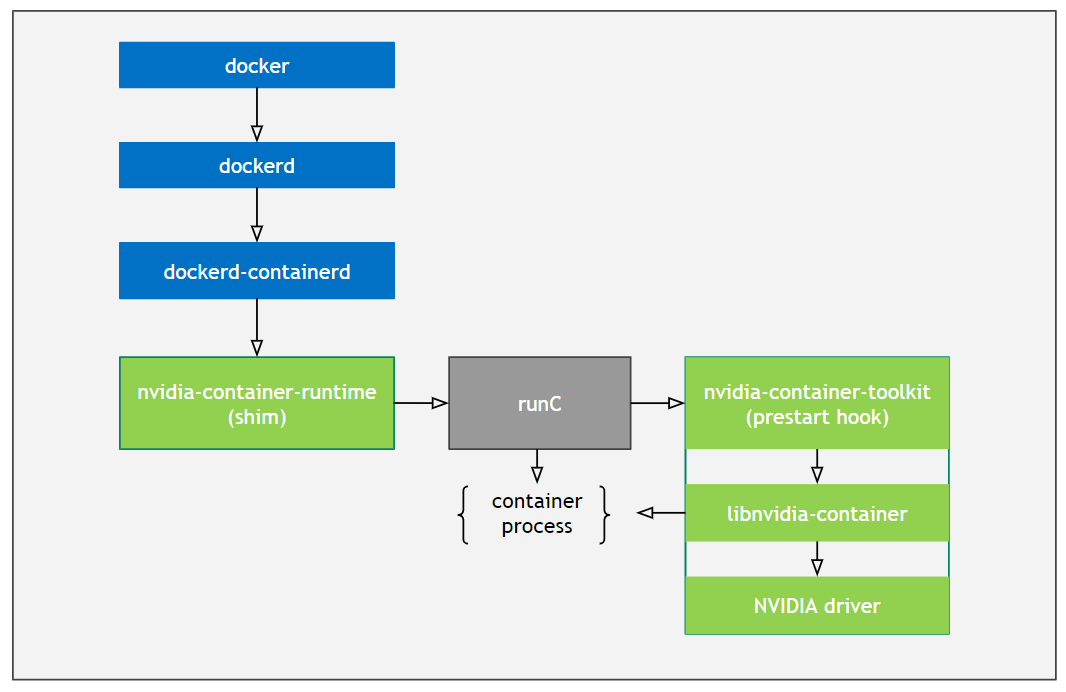
通过图中的描述,我们可以知道, GPU-Operator 是通过实现了 Nvidia 容器运行时,以runC作为输入,在runC中preStart hook中注入了一个名叫nvidia-container-toolkit的脚本,该脚本调用libnvidia-container CLI设置一系列合适的flags,使得容器运行后具有 GPU 能力。
GPU-Operator 安装说明
前提条件
在安装 GPU Operator 之前,请配置好安装环境如下:
- 所有节点不需要预先安装NVIDIA组件(
driver,container runtime,device plugin); - 所有节点必须配置
Docker,cri-o, 或者containerd.对于 docker 来说,可以参考这里; - 如果使用HWE内核(e.g. kernel 5.x) 的 Ubuntu 18.04 LTS 环境下,需要给
nouveau driver添加黑名单,需要更新initramfs;
$ sudo vim /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist.conf # 在尾部添加黑名单
blacklist nouveau
options nouveau modeset=0
$ sudo update-initramfs -u
$ reboot
$ lsmod | grep nouveau # 验证nouveau是否已禁用
$ cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep name | cut -f2 -d: | uniq -c #本文测试时处理器架构代号为Broadwell
16 Intel Core Processor (Broadwell)
- 节点发现(NFD) 需要在每个节点上配置,默认情况会直接安装,如果已经配置,请在
Helm chart变量设置nfd.enabled为false, 再安装; - 如果使用 Kubernetes 1.13和1.14, 需要激活 KubeletPodResources;
支持的linux版本
| OS Name / Version | Identifier | amd64 / x86_64 | ppc64le | arm64 / aarch64 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon Linux 1 | amzn1 | X | ||
| Amazon Linux 2 | amzn2 | X | ||
| Amazon Linux 2017.09 | amzn2017.09 | X | ||
| Amazon Linux 2018.03 | amzn2018.03 | X | ||
| Open Suse Leap 15.0 | sles15.0 | X | ||
| Open Suse Leap 15.1 | sles15.1 | X | ||
| Debian Linux 9 | debian9 | X | ||
| Debian Linux 10 | debian10 | X | ||
| Centos 7 | centos7 | X | X | |
| Centos 8 | centos8 | X | X | X |
| RHEL 7.4 | rhel7.4 | X | X | |
| RHEL 7.5 | rhel7.5 | X | X | |
| RHEL 7.6 | rhel7.6 | X | X | |
| RHEL 7.7 | rhel7.7 | X | X | |
| RHEL 8.0 | rhel8.0 | X | X | X |
| RHEL 8.1 | rhel8.1 | X | X | X |
| RHEL 8.2 | rhel8.2 | X | X | X |
| Ubuntu 16.04 | ubuntu16.04 | X | X | |
| Ubuntu 18.04 | ubuntu18.04 | X | X | X |
| Ubuntu 20.04 | ubuntu20.04 | X | X | X |
支持的容器运行时
| OS Name / Version | amd64 / x86_64 | ppc64le | arm64 / aarch64 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Docker 18.09 | X | X | X |
| Docker 19.03 | X | X | X |
| RHEL/CentOS 8 podman | X | ||
| CentOS 8 Docker | X | ||
| RHEL/CentOS 7 Docker | X |
安装doker环境
可参考 Docker 官方文档
安装NVIDIA Docker
配置 stable 仓库和 GPG key :
$ distribution=$(. /etc/os-release;echo $ID$VERSION_ID) \
&& curl -s -L https://nvidia.github.io/nvidia-docker/gpgkey | sudo apt-key add - \
&& curl -s -L https://nvidia.github.io/nvidia-docker/$distribution/nvidia-docker.list | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nvidia-docker.list
更新软件仓库后安装nvidia-docker2并添加运行时配置:
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install -y nvidia-docker2
-----
What would you like to do about it ? Your options are:
Y or I : install the package maintainer's version
N or O : keep your currently-installed version
D : show the differences between the versions
Z : start a shell to examine the situation
-----
# 初次安装,遇到以上交互式问题可选择N
# 如果选择Y会覆盖你的一些默认配置
# 选择N后,将以下配置添加到etc/docker/daemon.json
{
"runtimes": {
"nvidia": {
"path": "/usr/bin/nvidia-container-runtime",
"runtimeArgs": []
}
}
}
重启docker:
$ sudo systemctl restart docker
安装Helm
$ curl -fsSL -o get_helm.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/master/scripts/get-helm-3 \
&& chmod 700 get_helm.sh \
&& ./get_helm.sh
添加helm仓库
$ helm repo add nvidia https://nvidia.github.io/gpu-operator \
&& helm repo update
安装 NVIDIA GPU Operator
docker as runtime
$ kubectl create ns gpu-operator-resources
$ helm install gpu-operator nvidia/gpu-operator -n gpu-operator-resources --wait
如果需要指定驱动版本,可参考如下:
$ helm install gpu-operator nvidia/gpu-operator -n gpu-operator-resources \
--set driver.version="450.80.02"
crio as runtime
helm install gpu-operator nvidia/gpu-operator -n gpu-operator-resources\
--set operator.defaultRuntime=crio
containerd as runtime
helm install gpu-operator nvidia/gpu-operator -n gpu-operator-resources\
--set operator.defaultRuntime=containerd
Furthermore, when setting containerd as the defaultRuntime the following options are also available:
toolkit:
env:
- name: CONTAINERD_CONFIG
value: /etc/containerd/config.toml
- name: CONTAINERD_SOCKET
value: /run/containerd/containerd.sock
- name: CONTAINERD_RUNTIME_CLASS
value: nvidia
- name: CONTAINERD_SET_AS_DEFAULT
value: true
由于安装的镜像比较大,所以初次安装过程中可能会出现超时的情形,请检查你的镜像是否在拉取中!可以考虑使用离线安装解决该类问题,参考离线安装的链接。
使用 values.yaml 安装
$ helm install gpu-operator nvidia/gpu-operator -n gpu-operator-resources -f values.yaml
考虑离线安装
应用部署
检查已部署 operator 服务状态
检查 pods 状态
$ kubectl get pods -n gpu-operator-resources
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
gpu-feature-discovery-4gk78 1/1 Running 0 35s
gpu-operator-858fc55fdb-jv488 1/1 Running 0 2m52s
gpu-operator-node-feature-discovery-master-7f9ccc4c7b-2sg6r 1/1 Running 0 2m52s
gpu-operator-node-feature-discovery-worker-cbkhn 1/1 Running 0 2m52s
gpu-operator-node-feature-discovery-worker-m8jcm 1/1 Running 0 2m52s
nvidia-container-toolkit-daemonset-tfwqt 1/1 Running 0 2m42s
nvidia-dcgm-exporter-mqns5 1/1 Running 0 38s
nvidia-device-plugin-daemonset-7npbs 1/1 Running 0 53s
nvidia-device-plugin-validation 0/1 Completed 0 49s
nvidia-driver-daemonset-hgv6s 1/1 Running 0 2m47s
检查节点资源是否处于可分配
$ kubectl describe node worker-gpu-001
---
Allocatable:
cpu: 15600m
ephemeral-storage: 82435528Ki
hugepages-2Mi: 0
memory: 63649242267
nvidia.com/gpu: 1 #check here
pods: 110
---
部署官方文档中的两个实例
实例一
$ cat cuda-load-generator.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: dcgmproftester
spec:
restartPolicy: OnFailure
containers:
- name: dcgmproftester11
image: nvidia/samples:dcgmproftester-2.0.10-cuda11.0-ubuntu18.04
args: ["--no-dcgm-validation", "-t 1004", "-d 120"]
resources:
limits:
nvidia.com/gpu: 1
securityContext:
capabilities:
add: ["SYS_ADMIN"]
EOF
实例二
$ curl -LO https://nvidia.github.io/gpu-operator/notebook-example.yml
$ cat notebook-example.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: tf-notebook
labels:
app: tf-notebook
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 80
name: http
targetPort: 8888
nodePort: 30001
selector:
app: tf-notebook
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: tf-notebook
labels:
app: tf-notebook
spec:
securityContext:
fsGroup: 0
containers:
- name: tf-notebook
image: tensorflow/tensorflow:latest-gpu-jupyter
resources:
limits:
nvidia.com/gpu: 1
ports:
- containerPort: 8
基于 Jupyter Notebook 应用运行深度学习训练任务
部署应用
$ kubectl apply -f cuda-load-generator.yaml
pod/dcgmproftester created
$ kubectl apply -f notebook-example.yml
service/tf-notebook created
pod/tf-notebook created
查看 GPU 处于已分配状态:
$ kubectl describe node worker-gpu-001
---
Allocated resources:
(Total limits may be over 100 percent, i.e., overcommitted.)
Resource Requests Limits
-------- -------- ------
cpu 1087m (6%) 1680m (10%)
memory 1440Mi (2%) 1510Mi (2%)
ephemeral-storage 0 (0%) 0 (0%)
nvidia.com/gpu 1 1 #check this
Events: <none>
当有 GPU 任务发布给平台时,GPU 资源从可分配状态转变为已分配状态,安装任务发布的先后顺序,第二个任务在第一个任务运行结束后开始运行:
$ kubectl get pods --watch
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
dcgmproftester 1/1 Running 0 76s
tf-notebook 0/1 Pending 0 58s
------
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
dcgmproftester 0/1 Completed 0 4m22s
tf-notebook 1/1 Running 0 4m4s
获取应用端口信息:
$ kubectl get svc # get the nodeport of the svc, 30001
gpu-operator-1611672791-node-feature-discovery ClusterIP 10.233.10.222 <none> 8080/TCP 12h
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.233.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 12h
tf-notebook NodePort 10.233.53.116 <none> 80:30001/TCP 7m52s
查看日志,获取登录口令:
$ kubectl logs tf-notebook
[I 21:50:23.188 NotebookApp] Writing notebook server cookie secret to /root/.local/share/jupyter/runtime/notebook_cookie_secret
[I 21:50:23.390 NotebookApp] Serving notebooks from local directory: /tf
[I 21:50:23.391 NotebookApp] The Jupyter Notebook is running at:
[I 21:50:23.391 NotebookApp] http://tf-notebook:8888/?token=3660c9ee9b225458faaf853200bc512ff2206f635ab2b1d9
[I 21:50:23.391 NotebookApp] or http://127.0.0.1:8888/?token=3660c9ee9b225458faaf853200bc512ff2206f635ab2b1d9
[I 21:50:23.391 NotebookApp] Use Control-C to stop this server and shut down all kernels (twice to skip confirmation).
[C 21:50:23.394 NotebookApp]
To access the notebook, open this file in a browser:
file:///root/.local/share/jupyter/runtime/nbserver-1-open.html
Or copy and paste one of these URLs:
http://tf-notebook:8888/?token=3660c9ee9b225458faaf853200bc512ff2206f635ab2b1d9
or http://127.0.0.1:8888/?token=3660c9ee9b225458faaf853200bc512ff2206f635ab2b1d9
运行深度学习任务
进入jupyter notebook 环境后,尝试进入终端,运行深度学习任务:
进入terminal后拉取tersorflow测试代码并运行:
与此同时,开启另外一个终端运行nvidia-smi查看 GPU 监控使用情况:

利用 KubeSphere 自定义监控功能监控 GPU
部署 ServiceMonitor
gpu-operator帮我们提供了nvidia-dcgm-exporter这个exportor, 只需要将它集成到Prometheus的可采集对象中,也就是ServiceMonitor中,我们就能获取GPU监控数据了:
$ kubectl get pods -n gpu-operator-resources
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
gpu-feature-discovery-ff4ng 1/1 Running 2 15h
nvidia-container-toolkit-daemonset-2vxjz 1/1 Running 0 15h
nvidia-dcgm-exporter-pqwfv 1/1 Running 0 5h27m #here
nvidia-device-plugin-daemonset-42n74 1/1 Running 0 5h27m
nvidia-device-plugin-validation 0/1 Completed 0 5h27m
nvidia-driver-daemonset-dvd9r 1/1 Running 3 15h
可以构建一个busybox查看该exporter暴露的指标:
$ kubectl get svc -n gpu-operator-resources
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
gpu-operator-node-feature-discovery ClusterIP 10.233.54.111 <none> 8080/TCP 56m
nvidia-dcgm-exporter ClusterIP 10.233.53.196 <none> 9400/TCP 54m
$ kubectl exec -it busybox-sleep -- sh
$ wget http://nvidia-dcgm-exporter.gpu-operator-resources:9400/metrics
$ cat metrics
----
DCGM_FI_DEV_SM_CLOCK{gpu="0",UUID="GPU-eeff7856-475a-2eb7-6408-48d023d9dd28",device="nvidia0",container="tf-notebook",namespace="default",pod="tf-notebook"} 405
DCGM_FI_DEV_MEM_CLOCK{gpu="0",UUID="GPU-eeff7856-475a-2eb7-6408-48d023d9dd28",device="nvidia0",container="tf-notebook",namespace="default",pod="tf-notebook"} 715
DCGM_FI_DEV_GPU_TEMP{gpu="0",UUID="GPU-eeff7856-475a-2eb7-6408-48d023d9dd28",device="nvidia0",container="tf-notebook",namespace="default",pod="tf-notebook"} 30
----
查看nvidia-dcgm-exporter暴露的svc和ep:
$ kubectl describe svc nvidia-dcgm-exporter -n gpu-operator-resources
Name: nvidia-dcgm-exporter
Namespace: gpu-operator-resources
Labels: app=nvidia-dcgm-exporter
Annotations: prometheus.io/scrape: true
Selector: app=nvidia-dcgm-exporter
Type: NodePort
IP: 10.233.28.200
Port: gpu-metrics 9400/TCP
TargetPort: 9400/TCP
NodePort: gpu-metrics 31129/TCP
Endpoints: 10.233.84.54:9400
Session Affinity: None
External Traffic Policy: Cluster
Events: <none>
配置ServiceMonitor定义清单:
$ cat custom/gpu-servicemonitor.yaml
apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1
kind: ServiceMonitor
metadata:
name: nvidia-dcgm-exporter
namespace: gpu-operator-resources
labels:
app: nvidia-dcgm-exporter
spec:
jobLabel: nvidia-gpu
endpoints:
- port: gpu-metrics
interval: 15s
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nvidia-dcgm-exporter
namespaceSelector:
matchNames:
- gpu-operator-resources
$ kubectl apply -f custom/gpu-servicemonitor.yaml
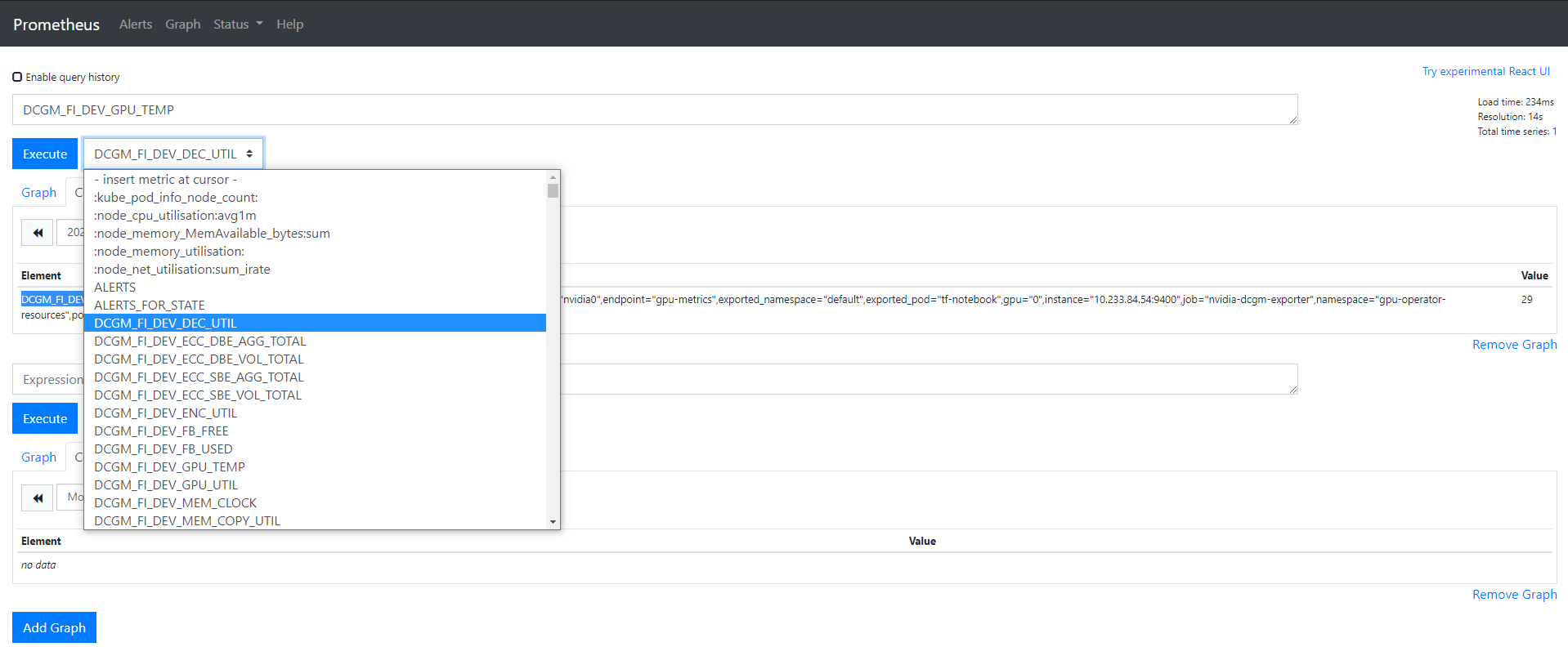
检查 GPU 指标是否被采集到(可选)
将servicemonitor提交给kubesphere平台后,通过暴露prometheus-k8s为NodePort,我们可以在Prometheus的UI上验证一下是否采集到的相关指标:
创建 KubeSphere GPU 自定义监控面板
KubeSphere 3.0
如果部署的 KubeSphere 版本是KubeSphere 3.0,需要简单地配置以下几个步骤,便可顺利完成可观察性监控。
首先, 登录kubsphere console后,创建一个企业空间名称为ks-monitoring-demo, 名称可按需创建;
其次,需要将ServiceMonitor所在的目标名称空间gpu-operator-resources分配为已存在的企业空间中,以便纳入监控。
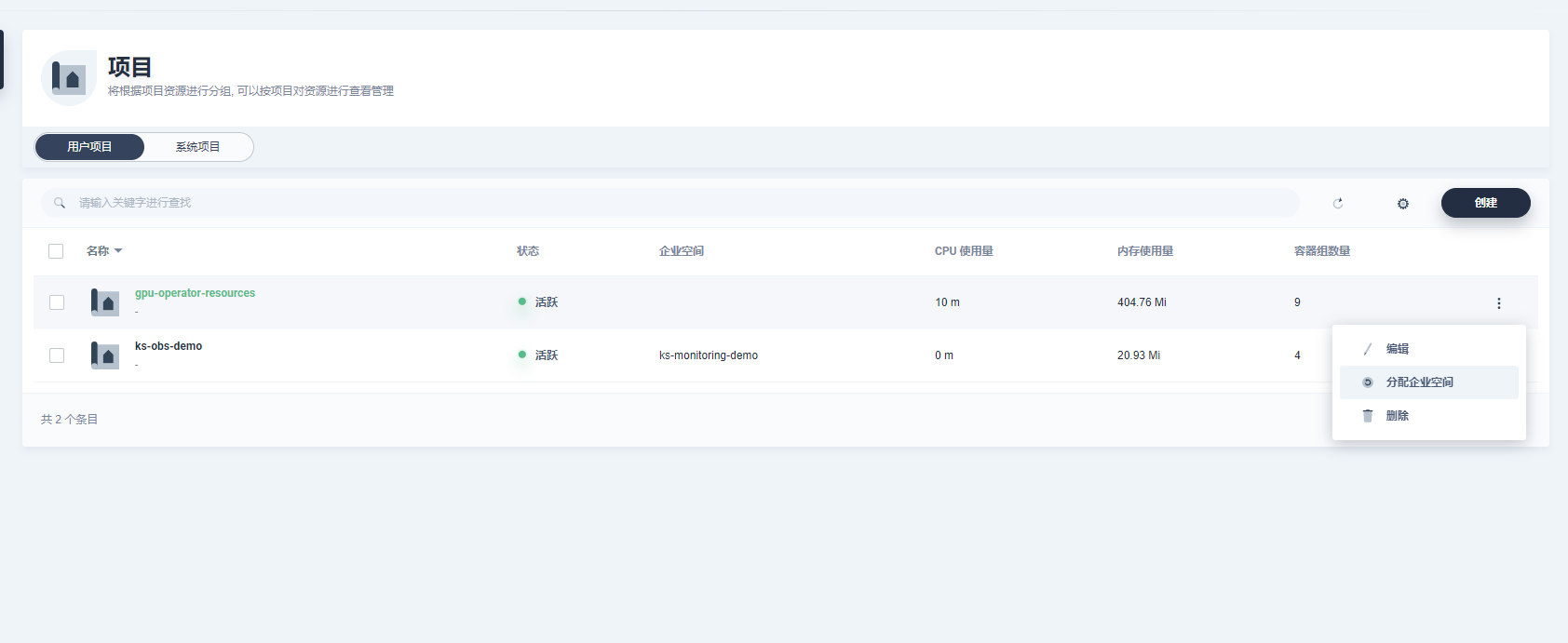
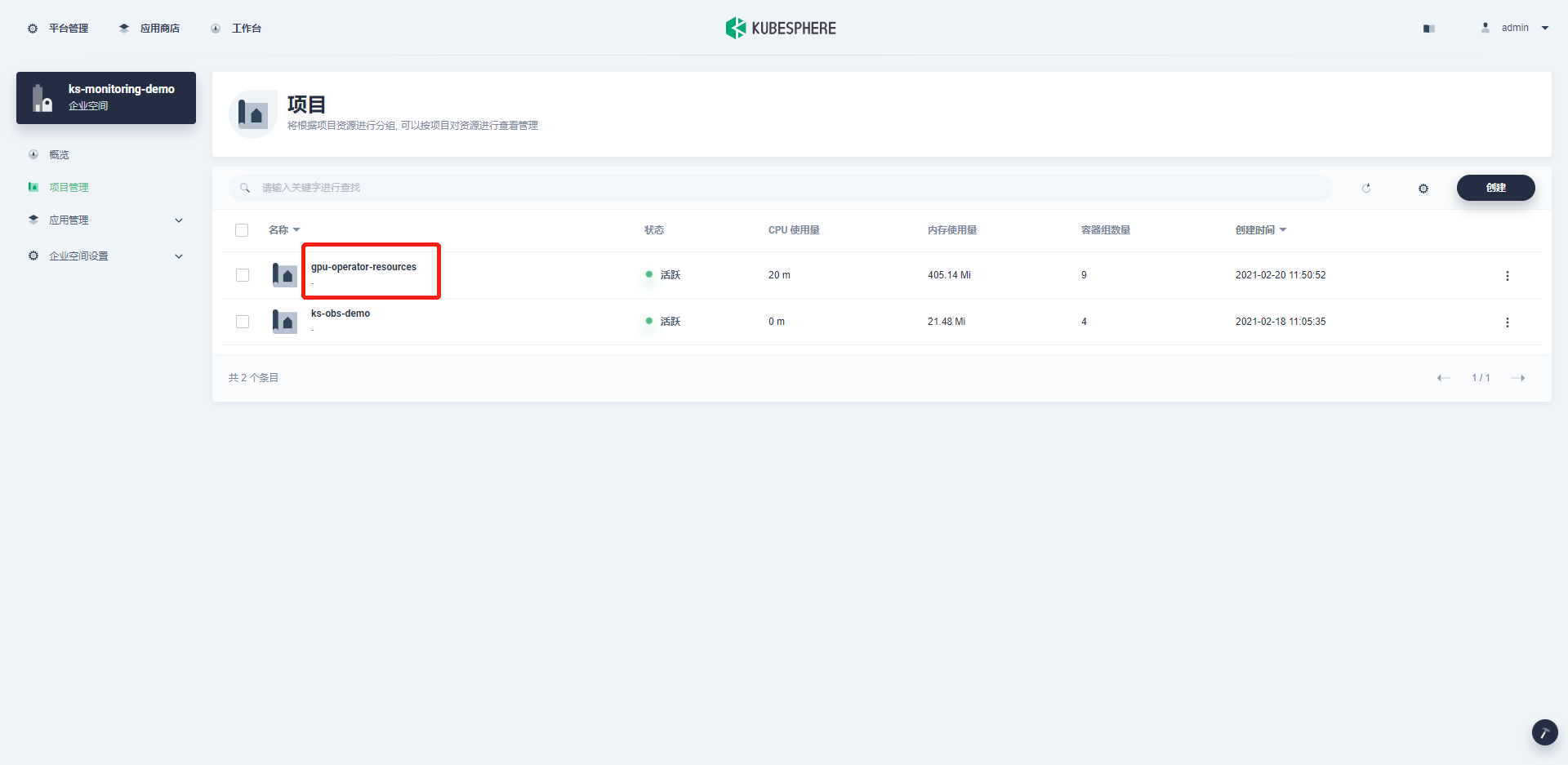
最后,进入目标企业空间,在纳管的项目找到gpu-operator-resources, 点击后找到可自定义监控界面, 即可添加自定义监控。

后续版本
后续版本可选择添加集群监控
创建自定义监控
下载dashboard以及配置namespace:
$ curl -LO https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubesphere/monitoring-dashboard/master/contrib/gallery/nvidia-gpu-dcgm-exporter-dashboard.yaml
$ cat nvidia-gpu-dcgm-exporter-dashboard.yaml
----
apiVersion: monitoring.kubesphere.io/v1alpha1
kind: Dashboard
metadata:
name: nvidia-dcgm-exporter-dashboard-rev1
namespace: gpu-operator-resources # check here
spec:
-----
可以直接命令行apply或者在自定义监控面板中选择编辑模式进行导入:

正确导入后:

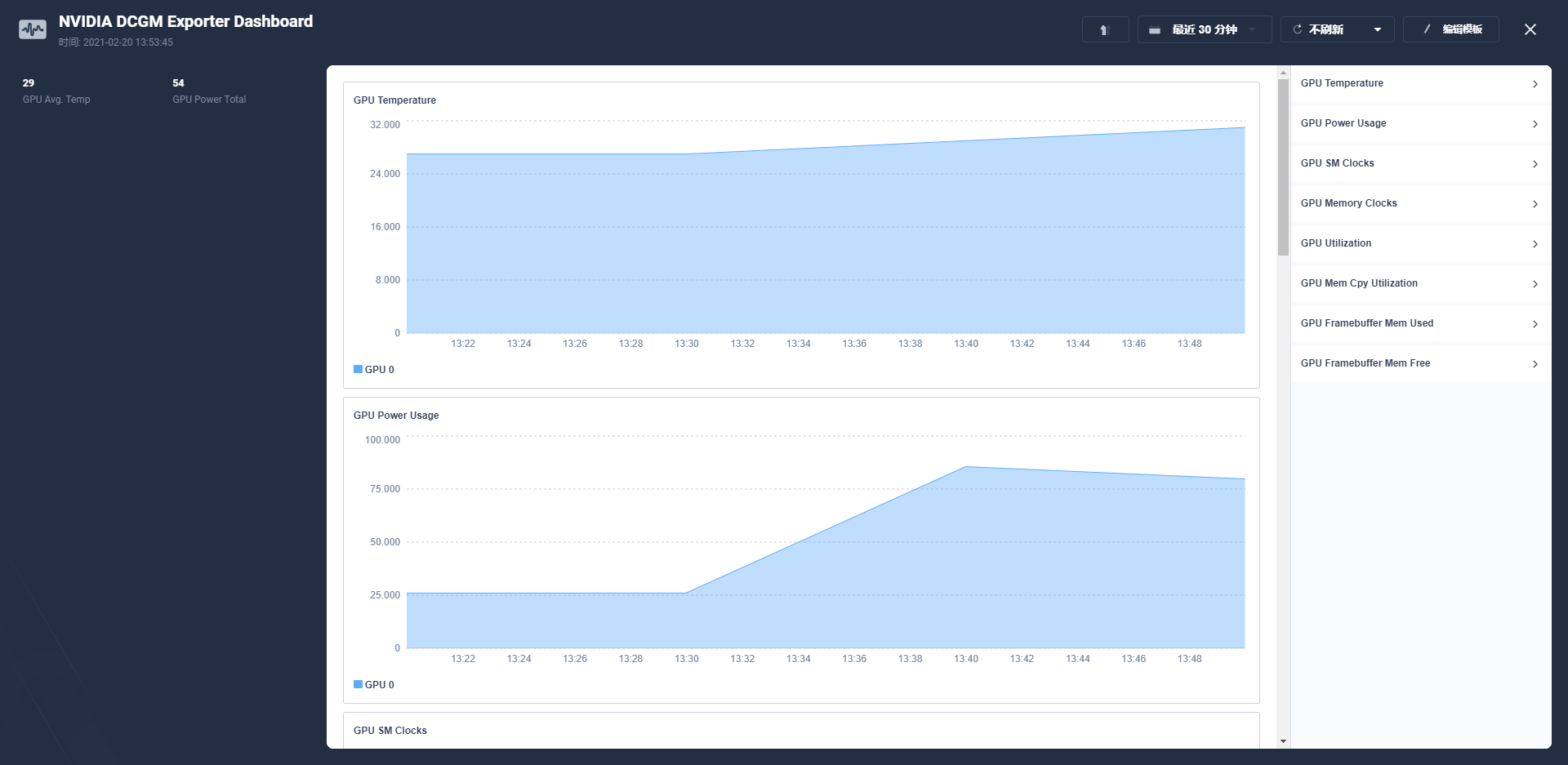
在上面创建的jupyter notebook运行深度学习测试任务后,可以明显地观察到相关GPU指标变化:
卸载
$ helm list -n gpu-operator-resources
NAME NAMESPACE REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION
gpu-operator gpu-operator-resources 1 2021-02-20 11:50:56.162559286 +0800 CST deployed gpu-operator-1.5.2 1.5.2
$ helm uninstall gpu-operator -n gpu-operator-resources
重启无法使用 GPU
关于已部署正常运行的gpu-operator和AI应用的集群,重启GPU主机后会出现没法用上 GPU 的情况,极有可能是因为插件还没加载,应用优先进行了载入,就会导致这种问题。这时,只需要优先保证插件运行正常,然后重新部署应用即可。
GPU-Operator 常见问题
GPU-Operator 重启后无法使用
答:关于已部署正常运行的gpu-operator和 AI 应用的集群,重启 GPU 主机后会出现没法用上 GPU 的情况,极有可能是因为插件还没加载,应用优先进行了载入,就会导致这种问题。这时,只需要优先保证插件运行正常,然后重新部署应用即可。
Nvidia k8s-device-plugin 与 GPU-Operator 方案对比?
我之前针对GPU使用的是 https://github.com/NVIDIA/k8s-device-plugin 和 https://github.com/NVIDIA/gpu-monitoring-tools 相结合的方案来监控 GPU,请问这个方案与 GPU-Operator的方案相比,孰优孰劣一些?
答:个人认为 GPU-Operator 更简单易用,其自带 GPU 注入能力不需要构建专用的 OS,并且支持节点发现与可插拔,能够自动化集成管理 GPU 所需的 NVIDIA 设备组件,相对来说还是很省事的。
有没有 KubeSphere 自定义监控的详细使用教程?
答:可以参考 KubeSphere 官方文档来使用自定义监控。
参考资料
官方代码仓库
- GitHub: https://github.com/NVIDIA/gpu-operator
- GitLab: https://gitlab.com/nvidia/kubernetes/gpu-operator
官方文档
- GPU-Operator 快速入门:https://docs.nvidia.com/datacenter/cloud-native/gpu-operator/getting-started.html#install-nvidia-gpu-operator
- GPU-Operator 离线安装指南:https://docs.nvidia.com/datacenter/cloud-native/gpu-operator/getting-started.html#considerations-to-install-in-air-gapped-clusters
- KubeSphere 自定义监控使用文档:https://kubesphere.com.cn/docs/project-user-guide/custom-application-monitoring/examples/monitor-mysql/
本文由博客一文多发平台 OpenWrite 发布!