1.字节流 FileInputStream、FileOutputStream
①FileInputStream
1 import java.io.FileInputStream; 2 3 public class FileInputStreamDemo { 4 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 5 FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("D:\a.txt"); 6 // 构建一个字节数组作为缓冲区 7 byte[] bs = new byte[10]; 8 // 定义一个变量来记录读取的字节个数 9 int len = -1; 10 while ((len = in.read(bs)) != -1) { 11 System.out.println(new String(bs, 0, len, "utf-8")); 12 } 13 in.close(); 14 } 15 }
②FileOutputStream
1 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 2 3 public class FileOutputStreamDemo { 4 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 5 //true是追加。不加true,或者是false会新建并覆盖已有的。 6 FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("D:\a.txt", false); 7 // 字节流身上没有缓冲区 8 out.write("缓冲区".getBytes("utf-8")); //utf-8编码 9 out.write("abc".getBytes()); 10 out.close(); 11 } 12 }
关于流中的异常处理
1.将刘对象放在try之外声明并且赋值为null,放到try内初始化。
2.在关流之前需要判断流对象是否初始化成功(判断流对象是否为null)。
3.关流之后需要将流对象强制置为null,防止关流失败流对象依然占用文件。
4.需要在关流之前手动冲刷缓冲区以防关流失败导致一部分数据死在缓冲区中。
③用FileInputStream、FileOutputStream复制文件
1 import java.io.FileInputStream; 2 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 3 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 6 public class CopyFileDemo { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 FileInputStream in = null; 9 FileOutputStream out = null; 10 try { 11 in = new FileInputStream("D:\a.zip"); 12 out = new FileOutputStream("C:\a.zip"); 13 // 构建一个字节数组作为缓冲区 14 byte[] bs = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 10]; 15 // 定义一个变量来记录每次读取的字节个数 16 int len = -1; 17 while ((len = in.read(bs)) != -1) { 18 out.write(bs, 0, len); 19 } 20 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 21 e.printStackTrace(); 22 } catch (IOException e1){ 23 e1.printStackTrace(); 24 } finally{ 25 if(in != null){ 26 try { 27 in.close(); 28 } catch (IOException e) { 29 e.printStackTrace(); 30 } finally { 31 in = null; 32 } 33 } 34 if(out != null){ 35 try { 36 out.close(); 37 } catch (IOException e) { 38 e.printStackTrace(); 39 } finally { 40 out = null; 41 } 42 } 43 } 44 } 45 }
2.转换流 InputStreamReader、OutputStreamWriter
①InputStreamReader 将字节转化为字符的流
1 import java.io.FileInputStream; 2 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 3 4 public class InputStreamReaderDemo { 5 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 6 // 底层靠的是FileInputStream 7 // 读取出来的是字节,但是展现的是字符---将字节转化为字符 8 InputStreamReader in = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("D:\test.txt"), "utf-8"); 9 char[] cs = new char[3]; 10 in.read(cs); 11 in.close(); 12 System.out.println(cs); 13 } 14 }
②OutputStreamWriter 将字符转化为字节的流
1 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 2 import java.io.IOException; 3 import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; 4 5 public class OutputStreamWriterDemo { 6 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 7 // OutputStreamWriter将字符转化为字节的流 8 // 实际上是用FileOutputStream来写出数据 9 // 传入的参数是字符形式,但是最后以字节形式向外写出---字符转字节 10 OutputStreamWriter ow = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("D:\test.txt"), "utf-8"); 11 ow.write("转换流"); 12 ow.close(); 13 } 14 }
③用InputStreamReader、OutputStreamWriter改变文件的编码
1 import java.io.FileInputStream; 2 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 5 import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; 6 7 public class ChangeEncode { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 changeEncode("srcTest.txt", "destTest.txt", "gbk", "utf-8"); 10 System.out.println("over"); 11 12 } 13 public static void changeEncode(String srcFile, String destFile, String srcEncodeType, String dstEncodeType){ 14 InputStreamReader isr = null; 15 OutputStreamWriter osw = null; 16 17 try { 18 isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(srcFile),srcEncodeType); 19 osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(destFile),dstEncodeType); 20 char[] cs = new char[1024]; 21 int len = 0; 22 while((len = isr.read(cs)) != -1){ 23 osw.write(cs, 0, len); 24 osw.flush(); 25 } 26 } catch (Exception e) { 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 } finally { 29 if(isr != null){ 30 try { 31 isr.close(); 32 } catch (IOException e) { 33 e.printStackTrace(); 34 } finally { 35 isr = null; 36 } 37 } 38 if(osw != null){ 39 try { 40 osw.close(); 41 } catch (IOException e) { 42 e.printStackTrace(); 43 } finally { 44 osw = null; 45 } 46 } 47 } 48 } 49 }
效果:
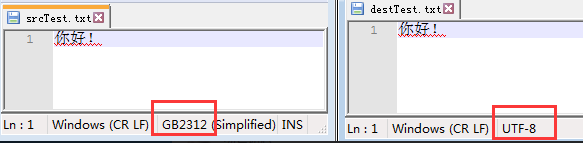
3.字符流 FileReader,FileWriter
①FileReader
Demo1:单个字符读取
1 import java.io.FileReader; 2 3 public class FileReaderDemo1 { 4 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 5 // 创建了一个输入流对象指向了要读取的文件 6 FileReader reader = new FileReader("D:\a.txt"); 7 // 返回的是这字符所对应的编码 8 // int i = reader.read(); 9 // 定义一个变量来存储读取的字符 10 int i = -1; 11 // 如果读取到文件的末尾,则返回一个-1 12 while ((i = reader.read()) != -1) { 13 System.out.println((char)i); 14 } 15 reader.close(); 16 } 17 }
Demo2:多个字符读取
1 import java.io.FileReader; 2 3 public class FileReaderDemo2 { 4 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 5 FileReader reader = new FileReader("D:\a.docx"); 6 // 提供一个字符数组作为缓冲区 7 char[] cs = new char[20]; 8 // 定义一个变量来记录每次读取到的字符个数 9 int i = -1; 10 // 如果读取到了末尾同样返回一个-1 11 // 返回本次读取到的字符个数 12 while ((i = reader.read(cs)) != -1) { 13 System.out.println(new String(cs, 0, i)); 14 } 15 reader.close(); 16 } 17 }
②FileWriter
import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; public class FileWriterDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileWriter writer = new FileWriter("D:\a.txt"); writer.write("def"); writer.flush(); writer.close(); writer = null; System.out.println(writer); } }
③用FileReader,FileWriter复制文件

1 import java.io.FileReader; 2 import java.io.FileWriter; 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 5 public class CopyFile { 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 FileReader reader = null; 8 FileWriter writer = null; 9 try { 10 reader = new FileReader("D:\a.txt"); 11 writer = new FileWriter("D:\b.txt"); 12 char[] cs = new char[10]; 13 int i = -1; 14 while ((i = reader.read(cs)) != -1) { 15 writer.write(cs, 0, i); 16 } 17 writer.flush(); 18 } catch (Exception e) { 19 e.printStackTrace(); 20 } finally { 21 if (reader != null) { 22 try { 23 reader.close(); 24 } catch (IOException e) { 25 e.printStackTrace(); 26 } finally { 27 reader = null; 28 } 29 } 30 if (writer != null) { 31 try { 32 writer.close(); 33 } catch (IOException e) { 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } finally { 36 writer = null; 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 }
4.缓冲流 BufferedReader、BufferedWriter
①BufferedReader
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.FileReader; public class BufferedReaderDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 实际上读取文件的是FileReader,BufferedReader的作用是在FileReader的基础上来提供一个缓冲区 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\aaa.txt")); // BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("D:\a.txt"))); // 每次读取一行数据 String str = null; while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) { System.out.println(str); } // 关流: 要么只关外层的流,要么从里向外关 br.close(); } }
②BufferedWriter
1 import java.io.BufferedWriter; 2 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 3 import java.io.FileWriter; 4 import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; 5 6 public class BufferedWriterDemo { 7 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 8 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("D:\aaa.txt")); 9 // BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("D:\a.txt"))); 10 bw.write("123"); 11 bw.flush(); 12 bw.close(); 13 } 14 }
③用BufferedReader、BufferedWriter改变文件的编码

1 import java.io.BufferedReader; 2 import java.io.BufferedWriter; 3 import java.io.FileInputStream; 4 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 7 import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; 8 9 10 public class ChangeEncode { 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 changeEncode("srcTest.txt", "destTest.txt", "gbk", "utf-8"); 13 System.out.println("over"); 14 15 } 16 public static void changeEncode(String srcFile, String destFile, String srcEncodeType, String dstEncodeType){ 17 InputStreamReader isr = null; 18 BufferedReader br = null; 19 OutputStreamWriter osw = null; 20 BufferedWriter bw = null; 21 22 try { 23 isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(srcFile),srcEncodeType); 24 br = new BufferedReader(isr); 25 osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(destFile),dstEncodeType); 26 bw = new BufferedWriter(osw); 27 String line = null; 28 while((line = br.readLine()) != null){ 29 bw.write(line); 30 bw.newLine(); 31 } 32 } catch (Exception e) { 33 e.printStackTrace(); 34 } finally{ 35 if(br != null){ 36 try { 37 br.close(); 38 } catch (IOException e) { 39 e.printStackTrace(); 40 } finally { 41 br = null; 42 } 43 } 44 if(bw != null){ 45 try { 46 bw.close(); 47 } catch (IOException e) { 48 e.printStackTrace(); 49 } finally { 50 bw = null; 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 } 55 }
5.合并流 SequenceInputStream
将多个流放入一个Vector集合中,利用Vector的elements方法来获取一个Enumeration对象,再利用Enumeration对象来构建SequenceInputStream对象。
1 import java.io.FileInputStream; 2 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 3 import java.io.InputStream; 4 import java.io.SequenceInputStream; 5 import java.util.Enumeration; 6 import java.util.Vector; 7 8 public class SequenceInputStreamDemo { 9 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 10 FileInputStream in1 = new FileInputStream("D:\a.txt"); 11 FileInputStream in2 = new FileInputStream("D:\b.txt"); 12 FileInputStream in3 = new FileInputStream("D:\c.txt"); 13 14 Vector<InputStream> v = new Vector<>(); 15 v.add(in1); 16 v.add(in2); 17 v.add(in3); 18 // 将v转化为一个Enumeration对象 19 Enumeration<InputStream> e = v.elements(); 20 // 构建合并流对象 21 SequenceInputStream sis = new SequenceInputStream(e); 22 // 创建一个输出流对象指向合并后的文件 23 FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("D:\test.txt"); 24 25 byte[] bs = new byte[5]; 26 int len = -1; 27 while ((len = sis.read(bs)) != -1) { 28 out.write(bs, 0, len); 29 } 30 sis.close(); 31 out.close(); 32 } 33 }
其它文件读写练习:
1.统计目录中java代码的行数
1 import java.io.BufferedReader; 2 import java.io.File; 3 import java.io.FileReader; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 6 public class CountCodeLine { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 File dir = new File(".\src\lianxi"); 10 System.out.println(countCodeLine(dir)); 11 } 12 //java中代码行数 13 public static int countCodeLine(File file){ 14 if(file == null){ 15 return 0; 16 } 17 if(!file.isDirectory()){ 18 if(file.getName().endsWith(".java")){ 19 return javaLine(file); 20 } 21 else 22 return 0; 23 }else{ 24 int sum = 0; 25 File[] fs = file.listFiles(); 26 for(File f : fs){ 27 sum += countCodeLine(f); 28 } 29 return sum; 30 } 31 } 32 private static int javaLine(File file){ 33 BufferedReader br = null; 34 int countLine = 0; 35 try { 36 br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file.getAbsolutePath())); 37 while ((br.readLine()) != null) { 38 countLine++; 39 } 40 41 } catch (IOException e) { 42 e.printStackTrace(); 43 }finally{ 44 if(br != null){ 45 try { 46 br.close(); 47 } catch (IOException e) { 48 e.printStackTrace(); 49 }finally{ 50 br = null; 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 return countLine; 55 } 56 }
2.将文件切块保存
1 import java.io.File; 2 import java.io.FileInputStream; 3 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 4 import java.util.Properties; 5 import java.util.UUID; 6 7 8 public class FileSplit { 9 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 10 // 使用Properties来记录文件的切块 11 Properties p = new Properties(); 12 13 File file = new File("D:\a.avi"); 14 FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(file); 15 16 // 定义一个变量来记录文件快的个数 17 int count = 0; 18 byte[] bs = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 5]; 19 int len = -1; 20 while ((len = in.read(bs)) != -1) { 21 // 获取一个统一的值 22 int hash = UUID.randomUUID().toString().hashCode(); 23 String h = Integer.toHexString(hash); 24 // 补足8位 25 int rest = 8 - h.length(); 26 for (int i = 0; i < rest; i++) { 27 h = "0" + h; 28 } 29 // 产生对应的路径 30 String path = "D:\split"; 31 for (char c : h.toCharArray()) { 32 path = path + "\" + c; 33 } 34 System.out.println(path); 35 // 产生目录 36 new File(path).mkdirs(); 37 // 文件块的路径 38 path = path + "\" + UUID.randomUUID().toString(); 39 // 记录文件块的路径 40 p.setProperty("" + count, path); 41 count++; 42 // 将文件块放到目录里面 43 FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(path); 44 out.write(bs, 0, len); 45 out.close(); 46 } 47 p.setProperty("count", "" + count); 48 p.store(new FileOutputStream("a.properties"), null); 49 in.close(); 50 } 51 }
拆分效果:
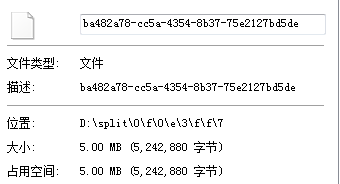
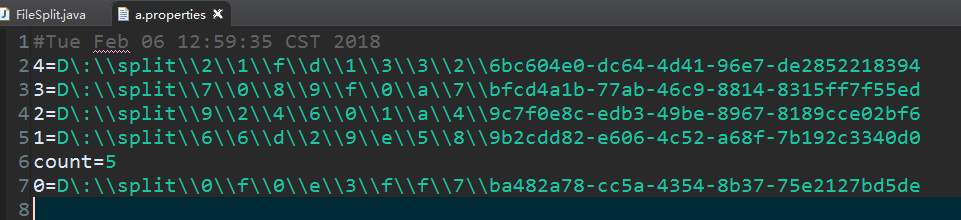
3.将切块的文件整合
1 import java.io.FileInputStream; 2 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 3 import java.io.InputStream; 4 import java.io.SequenceInputStream; 5 import java.util.Properties; 6 import java.util.Vector; 7 8 public class FileUnion { 9 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 10 Properties p = new Properties(); 11 p.load(new FileInputStream("a.properties")); 12 // 文件切得块数 13 int count = Integer.parseInt(p.getProperty("count")); 14 Vector<InputStream> v = new Vector<>(); 15 // 创建输入流指向对应的文件快 16 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { 17 v.addElement(new FileInputStream(p.getProperty(i + ""))); 18 } 19 // 创建一个输出流来指向新文件 20 FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("C:\a.avi"); 21 SequenceInputStream sis = new SequenceInputStream(v.elements()); 22 // 读取数据 23 byte[] bs = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 1]; 24 int len = -1; 25 while((len = sis.read(bs)) != -1){ 26 out.write(bs, 0, len); 27 } 28 out.close(); 29 sis.close(); 30 } 31 }
