这里多表,为了方便我只建了两张表,更复杂的表间也就是这些东西,就是复杂程度不一样。
数据源准备
建立一个学生表,和一个班级表


# 建立学生表 create table student( id int not null unique auto_increment, name varchar(20) not null, sex enum('male','female') not null default 'male', age int(3) unsigned not null default 28, birthday date not null, class_id int ); # 建立班级表 create table class( id int not null unique auto_increment, class_name varchar(20) not null );

# 给学生表插入数据 insert into student(name,sex,age,birthday,class_id) values ('成龙','male',48,'20101111',1), ('歪歪','female',48,'20150311',2), ('丫丫','female',38,'20101101',2), ('丁丁','female',18,'20110312',2), ('星星','female',18,'20160513',2), ('格格','female',28,'20170127',2), ('张野','male',28,'20160311',3), ('程咬金','male',18,'19970312',3), ('程咬银','female',18,'20130311',3), ('程咬铜','male',18,'20150411',3), ('程咬铁','female',18,'20140512',3); # 给班级表插入数据 insert into class (class_name) values ("一班"), ("二班");
多表连接查询
交叉连接
不适用任何匹配条件,生成笛卡儿积。
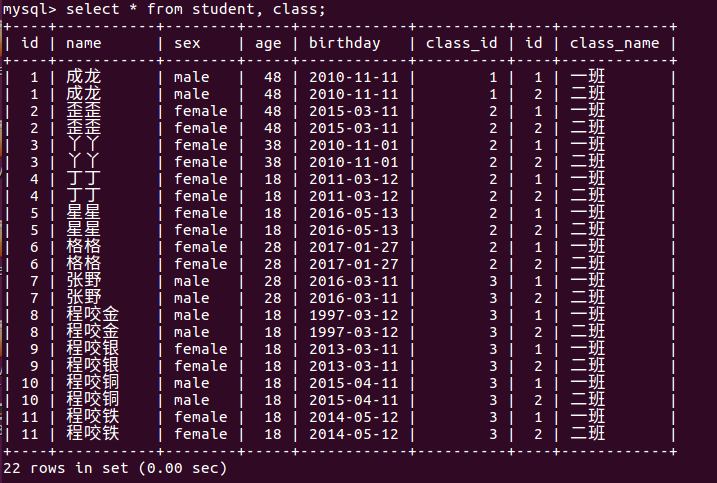
交叉连接生成的笛卡儿积是最全的数据源,但是基本无用,因为大量无用的数据充斥其中。所以我们需要加入条件,找到我们需要的数据。
内连接
只连接匹配的行
找两张表共有个部分,相当于利用条件从笛卡儿积结果中筛选正确的结果。
mysql> mysql> select * from student, class where student.class_id = class.id; +----+--------+--------+-----+------------+----------+----+------------+ | id | name | sex | age | birthday | class_id | id | class_name | +----+--------+--------+-----+------------+----------+----+------------+ | 1 | 成龙 | male | 48 | 2010-11-11 | 1 | 1 | 一班 | | 2 | 歪歪 | female | 48 | 2015-03-11 | 2 | 2 | 二班 | | 3 | 丫丫 | female | 38 | 2010-11-01 | 2 | 2 | 二班 | | 4 | 丁丁 | female | 18 | 2011-03-12 | 2 | 2 | 二班 | | 5 | 星星 | female | 18 | 2016-05-13 | 2 | 2 | 二班 | | 6 | 格格 | female | 28 | 2017-01-27 | 2 | 2 | 二班 | +----+--------+--------+-----+------------+----------+----+------------+
因为我在班级表中没有定义三班,所以筛选的查询结果中没有找到三班和三班人员的记录。
除了上面的的写法外,还有一种写法
select * from student inner join class on student.class_id=class.id;
两个语句查找的内容是一致的。
外连接
外连接之左连接:优先显示左表的全部记录
本质上就是在内连接的基础上增加左边有,右边没有的结果
mysql> select * from student left join class on student.class_id=class.id;
+----+-----------+--------+-----+------------+----------+------+------------+ | id | name | sex | age | birthday | class_id | id | class_name | +----+-----------+--------+-----+------------+----------+------+------------+ | 1 | 成龙 | male | 48 | 2010-11-11 | 1 | 1 | 一班 | | 2 | 歪歪 | female | 48 | 2015-03-11 | 2 | 2 | 二班 | | 3 | 丫丫 | female | 38 | 2010-11-01 | 2 | 2 | 二班 | | 4 | 丁丁 | female | 18 | 2011-03-12 | 2 | 2 | 二班 | | 5 | 星星 | female | 18 | 2016-05-13 | 2 | 2 | 二班 | | 6 | 格格 | female | 28 | 2017-01-27 | 2 | 2 | 二班 | | 7 | 张野 | male | 28 | 2016-03-11 | 3 | NULL | NULL | | 8 | 程咬金 | male | 18 | 1997-03-12 | 3 | NULL | NULL | | 9 | 程咬银 | female | 18 | 2013-03-11 | 3 | NULL | NULL | | 10 | 程咬铜 | male | 18 | 2015-04-11 | 3 | NULL | NULL | | 11 | 程咬铁 | female | 18 | 2014-05-12 | 3 | NULL | NULL | +----+-----------+--------+-----+------------+----------+------+------------+ 11 rows in set (0.00 sec)
外连接之右连接,优先显示右表的全部记录
本质上就是在内连接的基础上加上右边有,左边没有的结果
mysql> select * from student right join class on student.class_id=class.id; +------+--------+--------+------+------------+----------+----+------------+ | id | name | sex | age | birthday | class_id | id | class_name | +------+--------+--------+------+------------+----------+----+------------+ | 1 | 成龙 | male | 48 | 2010-11-11 | 1 | 1 | 一班 | | 2 | 歪歪 | female | 48 | 2015-03-11 | 2 | 2 | 二班 | | 3 | 丫丫 | female | 38 | 2010-11-01 | 2 | 2 | 二班 | | 4 | 丁丁 | female | 18 | 2011-03-12 | 2 | 2 | 二班 | | 5 | 星星 | female | 18 | 2016-05-13 | 2 | 2 | 二班 | | 6 | 格格 | female | 28 | 2017-01-27 | 2 | 2 | 二班 | +------+--------+--------+------+------------+----------+----+------------+ 6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
全外连接,显示左右两个表中全部记录
全连接本质上就是在内连接的基础上增加左边有,右边没有的,和右边没有,左边没有的结果。
然而在mysql中是没有full join的,所以,我们需要用union。
mysql> select * from student left join class on student.class_id=class.id -> union -> select * from student right join class on student.class_id=class.id; +------+-----------+--------+------+------------+----------+------+------------+ | id | name | sex | age | birthday | class_id | id | class_name | +------+-----------+--------+------+------------+----------+------+------------+ | 1 | 成龙 | male | 48 | 2010-11-11 | 1 | 1 | 一班 | | 2 | 歪歪 | female | 48 | 2015-03-11 | 2 | 2 | 二班 | | 3 | 丫丫 | female | 38 | 2010-11-01 | 2 | 2 | 二班 | | 4 | 丁丁 | female | 18 | 2011-03-12 | 2 | 2 | 二班 | | 5 | 星星 | female | 18 | 2016-05-13 | 2 | 2 | 二班 | | 6 | 格格 | female | 28 | 2017-01-27 | 2 | 2 | 二班 | | 7 | 张野 | male | 28 | 2016-03-11 | 3 | NULL | NULL | | 8 | 程咬金 | male | 18 | 1997-03-12 | 3 | NULL | NULL | | 9 | 程咬银 | female | 18 | 2013-03-11 | 3 | NULL | NULL | | 10 | 程咬铜 | male | 18 | 2015-04-11 | 3 | NULL | NULL | | 11 | 程咬铁 | female | 18 | 2014-05-12 | 3 | NULL | NULL | +------+-----------+--------+------+------------+----------+------+------------+ 11 rows in set (0.00 sec)
子查询
子查询是将一个查询语句嵌套在另一个查询语句中。
内层查询语句的结果可以为外层查询语句提供查询条件
子查询中可以包含:in, not in, any, all, exists , not exists,union, union all等关键字。还可以包含:=,!=, >, <等。
# any 关键字 select ...from ... where a > any(...); 相当于 select ...from ... where a > result1 or a > result2 or a > result3; # all关键字 与any关键字类似,只不过上面的or改成and。即: select ...from ... where a > all(...); 相当于 select ...from ... where a > result1 and a > result2 and a > result3; # some关键字 some关键字和any关键字是一样的功能。所以: select ...from ... where a > some(...); 相当于 select ...from ... where a > result1 or a > result2 or a > result3; # in关键字 in运算符用于where语句中,以列表项的形式支持多个选择。 select * from student where class_id in (1,3); select * from student where class_id not in (1,3); select * from student where class_id in (select id from class); 最后的这个查询语句等价于:select * from student where class_id=any (select id from class); not in 和in作用相反 # exists关键字 exists只返回True或者False。 select * from student where exists (select * from class); # exists返回True,外层查询会执行。 select * from student where exists (select * ); # exists返回True,外层查询会执行。 select * from student where exists (select 1); # exists返回True,外层查询会执行。 select * from student where exists (select * from class where class_id =4); # exists返回True,外层查询不会执行。 select * from student where sex="male" and exists(select * from class); # 可以配合其他查询条件一起使用。 not exists和exists作用相反 # union关键字 用来将多个select语句的结果组合到一个结果集中,前面说全外间连接有相应的例子。 在多个select语句中,对应的列应该有相同的字段属性,且第一个select语句中被使用的字段名称也被用于结果的字段名称。 union和union all的区别:当使用union时,MySQL会把结果集中重复的记录删除掉,而使用union all后,mysql会把所有记录返回,而且效率要比union高。
