窗函数的设计思想就是选择一个理想的频率选择滤波器(通常其脉冲响应函数是
非因果、无限长的),然后截断(取窗)这个无限长脉冲响应,得到一个线性相位、因果的
FIR滤波器。频率域示意图如下:
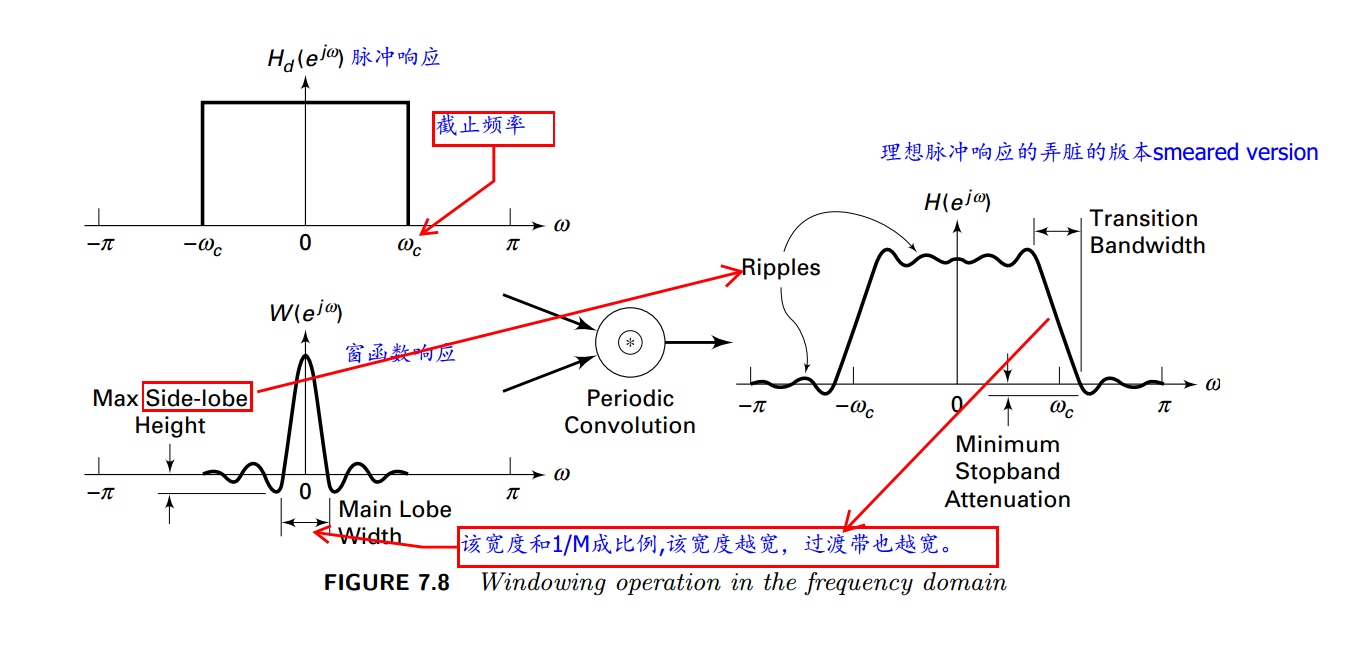
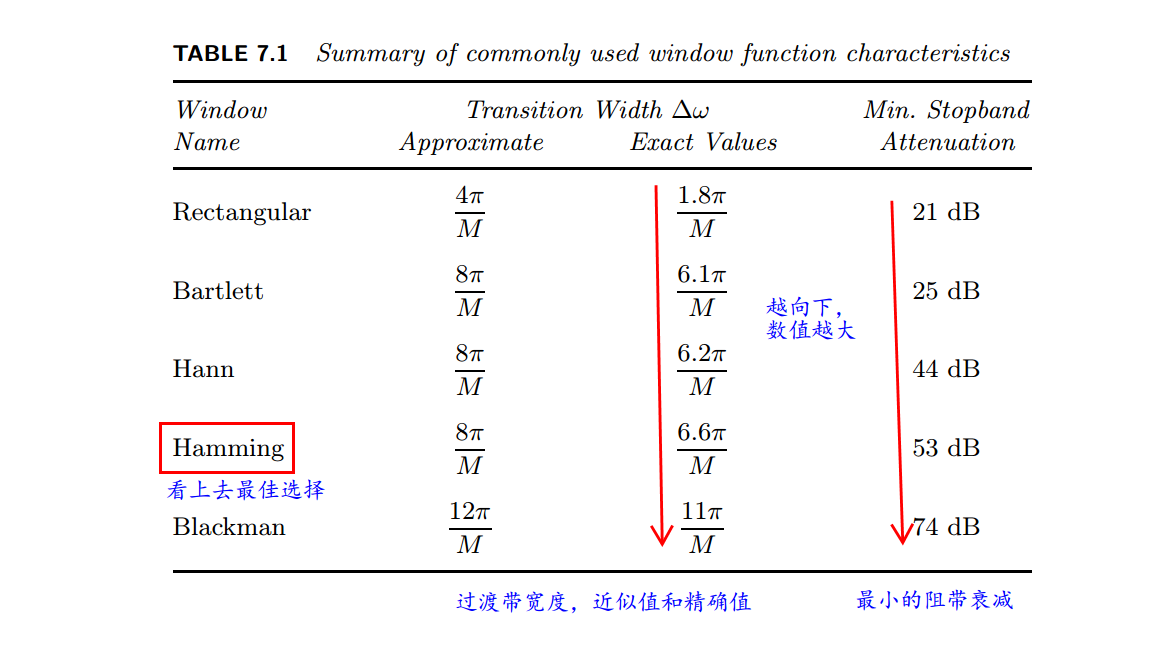
我们的目的:对于给定的要求,选择滤波器长度M和窗函数ω(n),该窗函数要有最窄的主瓣宽度和最小的旁瓣衰减。
前人为我们已经找好了许多窗函数,见下表:
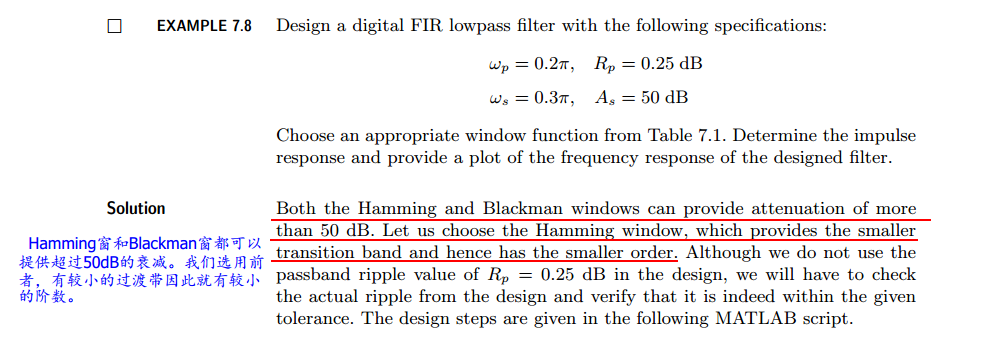
代码:
wp = 0.2*pi; ws = 0.3*pi; tr_width = ws - wp;
M = ceil(6.6*pi/tr_width) + 1
n = [0:1:M-1];
wc = (ws + wp)/2; % ideal LPF cutoff frequency
hd = ideal_lp(wc, M); w_ham = (hamming(M))'; h = hd .* w_ham;
[db, mag, pha, grd, w] = freqz_m(h, [1]); delta_w = 2*pi/1000;
Rp = -(min(db(1:1:wp/delta_w+1))) % Actual Passband Ripple
As = -round(max(db(ws/delta_w+1:1:501))) % Min Stopband attenuation
%Plot
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Exameple 7.8')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
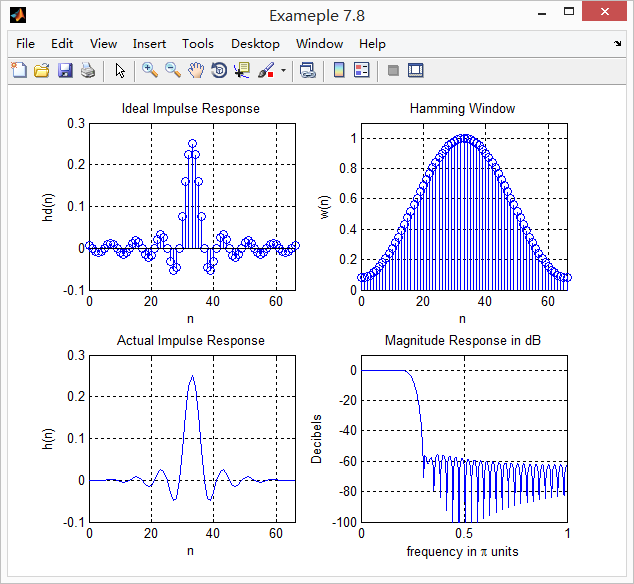
subplot(2,2,1); stem(n, hd); axis([0 M-1 -0.1 0.3]); grid on;
xlabel('n'); ylabel('hd(n)'); title('Ideal Impulse Response');
subplot(2,2,2); stem(n, w_ham); axis([0 M-1 0 1.1]); grid on;
xlabel('n'); ylabel('w(n)'); title('Hamming Window');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(n, h); axis([0 M-1 -0.1 0.3]); grid on;
xlabel('n'); ylabel('h(n)'); title('Actual Impulse Response');
subplot(2,2,4); plot(w/pi, db); axis([0 1 -100 10]); grid on;
xlabel('frequency in pi units'); ylabel('Decibels'); title('Magnitude Response in dB');
运行结果:
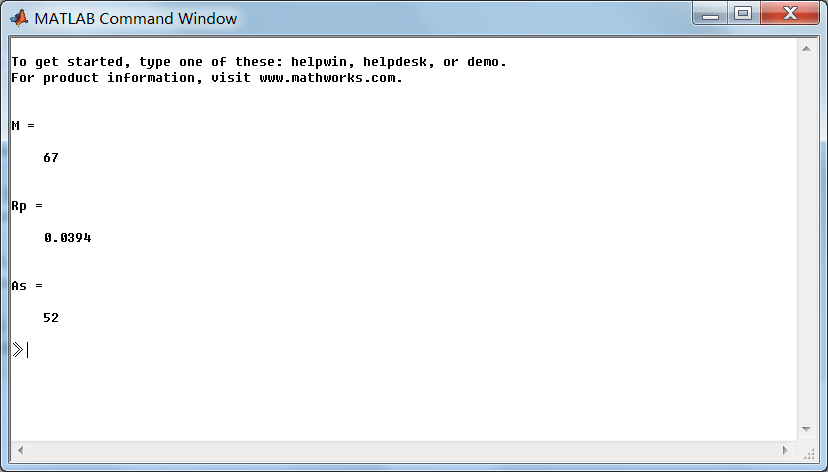
我们注意到滤波器长度M=67,通带震荡0.0394dB,阻带衰减52dB。满足设计要求。
代码中求Rp和As的方法强烈推荐,后文经常用到。