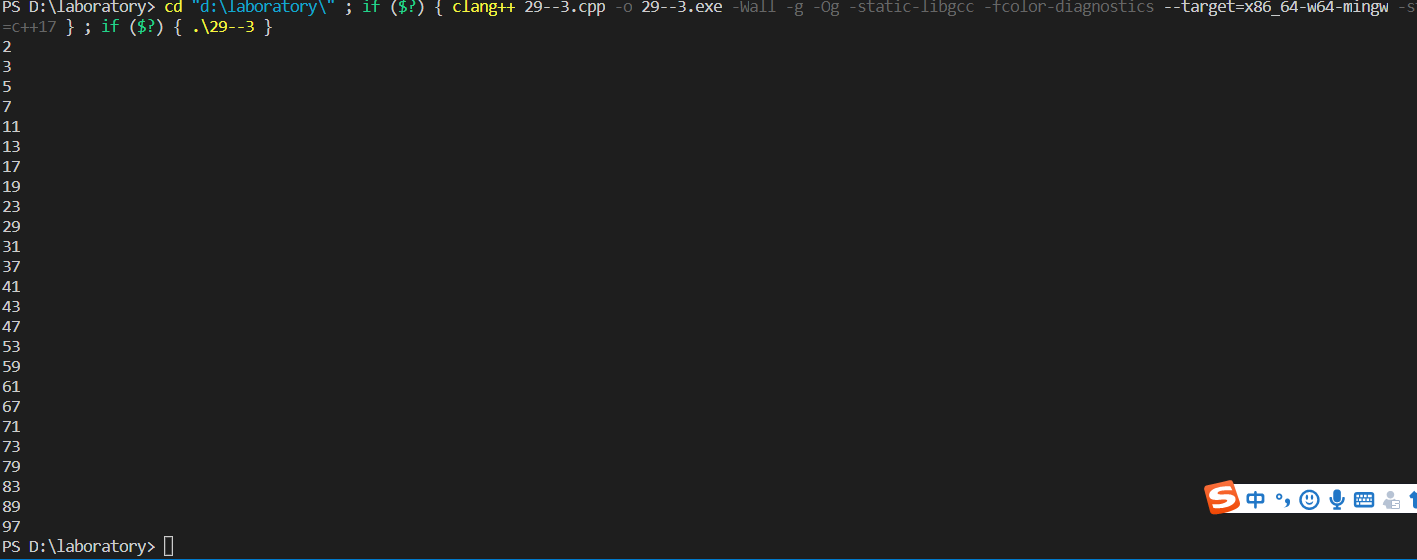
2-28 实现一个简单的菜单程序,运行时显示“Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Select one:” 提示用户输入。 A表示增加,D表示删除,S表示排序,Q表示退出。输入为A、D、S时分别提示“数据已经增加、删除、排序。”,输入为Q时程序结束
(1)if else
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char n;
cout<<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Select one:"<<endl;
while(true)
{
cin>>n;
if(n==65)
{
cout<<"Date has been added."<<endl;
continue;
}
else if(n==68)
{
cout<<"Date has been deleted."<<endl;
continue;
}
else if(n==83)
{
cout<<"Date has been sorted."<<endl;
continue;
}
else if(n==81)
{
cout<<"Over."<<endl;
break;
}
else
{cout<<"Please restart:"<<endl;
continue;
}
}
return 0;
}
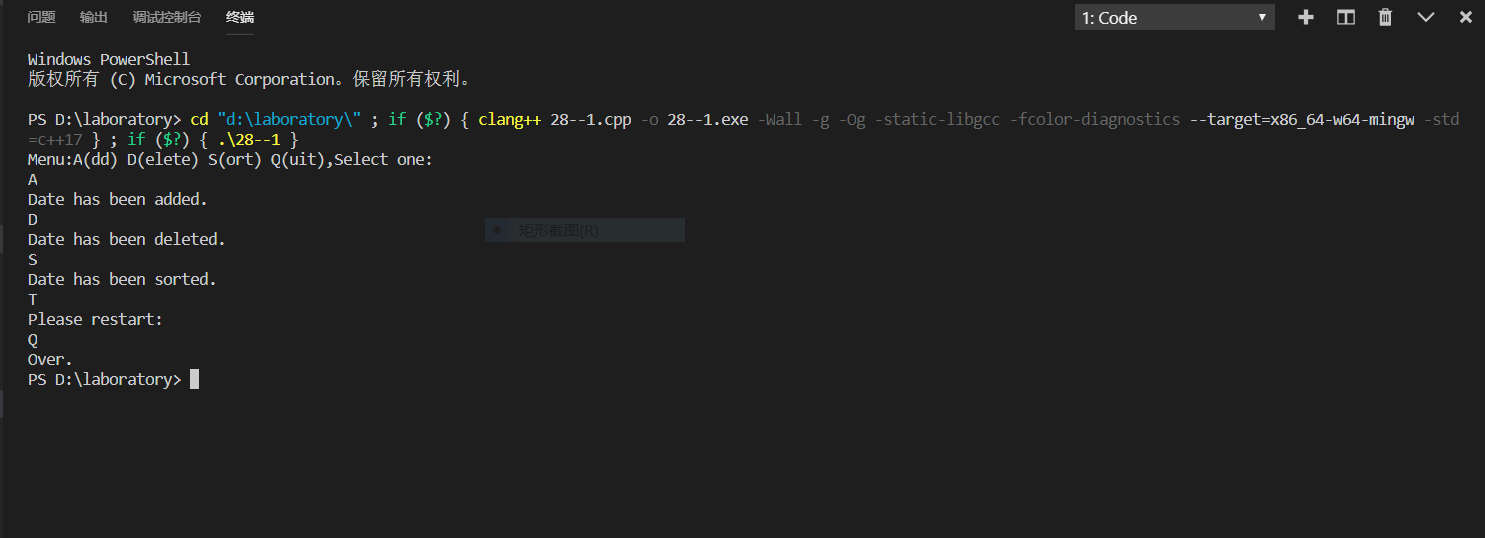
(2)switch语句
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char n;
cout<<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Select one:"<<endl;
while(true)
{
cin>>n;
switch(n)
{
case 'A':
cout<<"Date has been added."<<endl;
continue;
case 'D':
cout<<"Date has been deleted."<<endl;
continue;
case 'S':
cout<<"Date has been sorted."<<endl;
continue;
case 'Q':
cout<<"Over."<<endl;
break;
default:
cout<<"Please restart:"<<endl;
continue;
}
return 0;
}
}
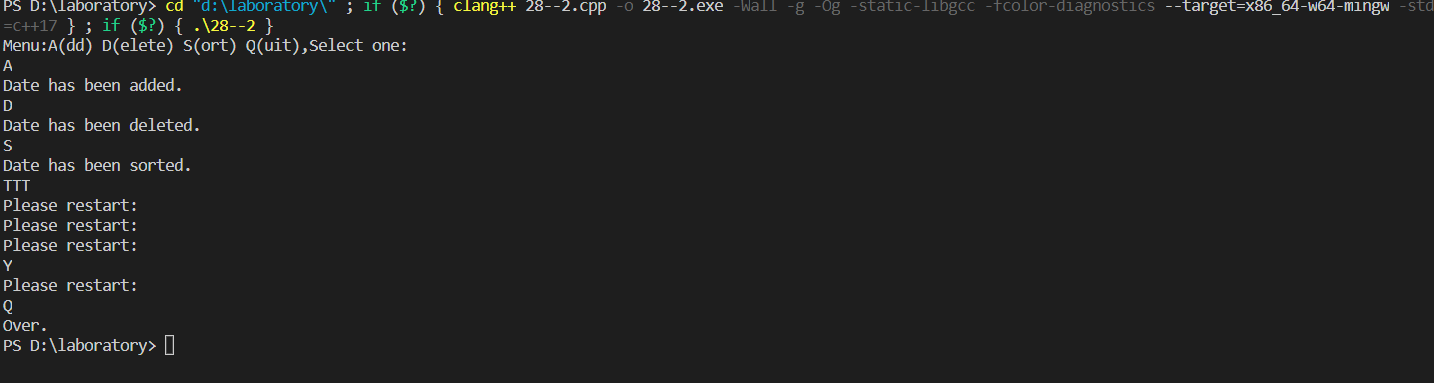
2-29 用穷举法找出1~100间的质数并显示出来。
(1)while
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i=2,j;
while(i<=100)
{
j=2;
while(i>j)
{
j++;
if(i%j==0)
{
break;
}
}
if(j==i)
{
cout<<i<<endl;
}
i++;
}
return 0;
}

(2)do while
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i=2,j;
do
{
j=1;
do
{
j++;
if(i%j==0)
{
break;
}
} while (i > j);
if(j==i)
{
cout<<i<<endl;
}
i++;
} while (i <= 100);
return 0;
}
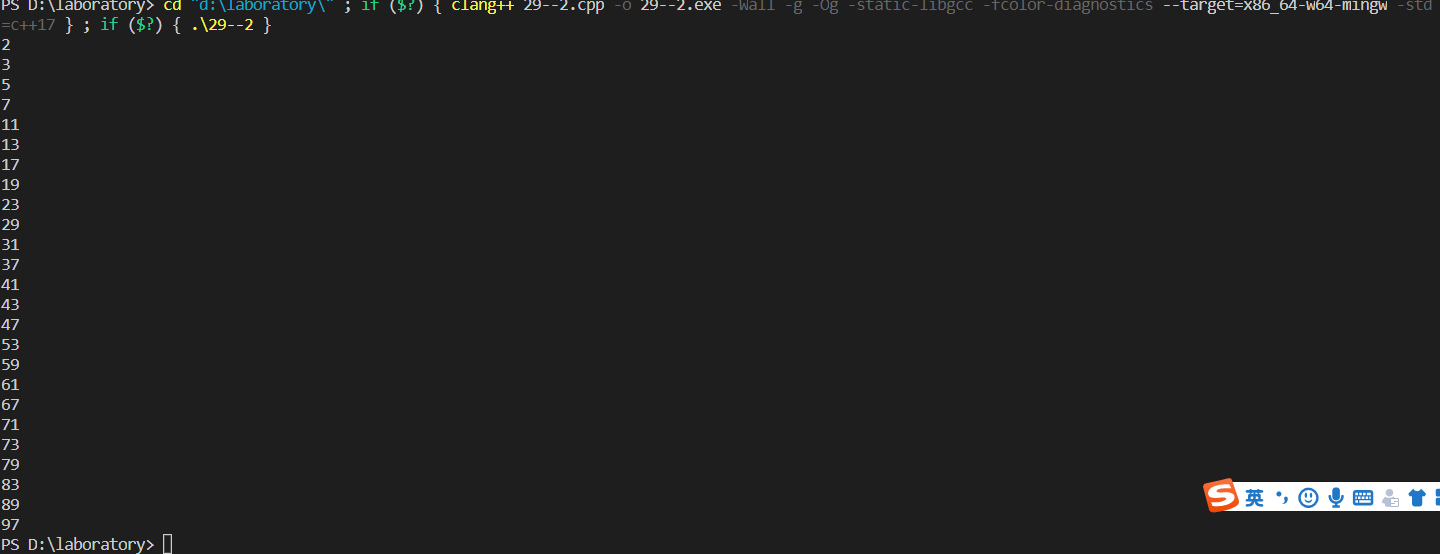
(3)for
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i, j;
for (i = 2; i <= 100;i++){
for (j = 2; j < i;j++)
{
if(i%j==0)
{
break;
}
}
if(i==j)
{
cout<<i<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
折半法
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int i,j,n,m;
i=2;
while(i<101)
{
m=1,n=i/2;j=2;
while(j<=n)
{
if(i%j==0)
{
m=0;
break;
}
j++;
}
if(m)
cout<<i<<" ";
i++;
}
}
开根法
public class TestPrintPrime {
public static void main(String args[]){
int count=0;
for (int i = 1; i <=100; i+=2) {
if (Prime(i)) {
System.out.println(i);
count++;
}
}
System.out.println("1-100的质数一共有"+count+"个");
}
public static boolean Prime(int n) {
if (n < 2) return false;
if (n == 2) return true;
for (int i = 2; i < (int) Math.sqrt(n); i++) {
if (0 == n % i) return false;
}
return true;
}
}
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/zs_dolphin/article/details/7018020
2-32 在程序中定义一个整形变量,赋予1~100的值。要求用户猜这个数,比较两个数的大小,把结果提示给用户,直到猜对为止。
(此处涉及rand和srand的用法,分别是设置伪随机数和真随机数,关键在于是否设置种子)
(1)while
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
srand(int(time(0)));
int i, j;
i = rand() % 100+1;
while(true)
{
cout << "Please input you guess number." << endl;
cin >> j;
if(j<i)
{
cout <<"Bigger than that." << endl;
continue;
}
else if(j>i)
{
cout << "Smaller than that." << endl;
continue;
}
else
{
cout << "Bingo EXP+1" << endl;
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
(2)do while
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
srand(int(time(0)));
int i, j;
i = rand() % 100+1;
do
{
cout << "Please input you guess number." << endl;
cin >> j;
if(j<i)
{
cout <<"Bigger than that." << endl;
continue;
}
else if(j>i)
{
cout << "Smaller than that." << endl;
continue;
}
else
{
cout << "Bingo EXP+1" << endl;
break;
}
} while (true);
return 0;
}
2-34 口袋中有红、黄、蓝、白、黑 5 种颜色的球若干个。每次从口袋中取出3个不同颜色的球,问有多少种取法?
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void output(int x);
enum balls
{
Red,
Yellow,
Blue,
White,
Black
};
int main()
{
int n=0;
int third;
for (int first = Red; first <= Black; first++)
{
for (int second = first + 1; second <= Black; second++)
{
for (third = second + 1; third <= Black; third++)
{
output(first);
output(second);
output(third);
cout << endl;
n++;
}
}
}
cout << "The all kinds are " << n << endl;
return 0;
}
void output(int x)
{
switch(x)
{
case 0:
cout << "Red ";break;
case 1:
cout << "Yellow ";break;
case 2:
cout << "Blue ";break;
case 3:
cout << "White ";break;
case 4:
cout << "Black ";break;
}
}
注意for循环的嵌套,以及利用switch来把枚举类型里的数字转化为字符。
总结:1.随机数问题--rand和scrand
包含在头文件<cstdlib>中
伪随机数
rand()函数的使用通式(取余法):
取得[0,x)的随机整数:rand()%x;
取得(a,b)的随机整数:rand()%(b-a-1)+a+1;
取得[a,b)的随机整数:rand()%(b-a)+a;
取得[a,b]的随机整数:rand()%(b-a+1)+a;
取得(a,b]的随机整数:rand()%(b-a)+a+1;
取得0-1之间的浮点数:rand()/double(RAND_MAX)
真随机数()
原理:time()函数(头文件在<ctime>中)
time(0)可以输出一个与时间有关的数
在结合srand()函数即可产生真正的随机数
如:srand(int(time(0)))
(2)do while用起来还是比较麻烦,目前没有感觉先运行一次有多方便,我屈服于for循环。
----X.Raven