Dijkstra算法分析
题目分析参照《数据结构》(严蔚敏)7-6节
最短路径问题描述
参照日常生活中的公交查询系统。我们有选项:
少换乘/最少站数
价格最少/时间最短....
(ps:下边这个图是网页查询的,略有出入)
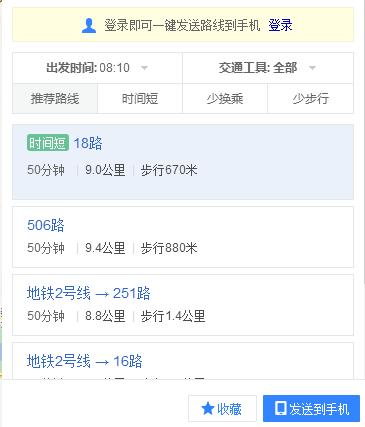
根据这样的分类。我们可以将最短路径分为:结点最少(经过的站数最少),权值最小(这个就是个心里期望了,看你是相花费时间最少,金钱最少....)
结点最少
(参照途中描述)
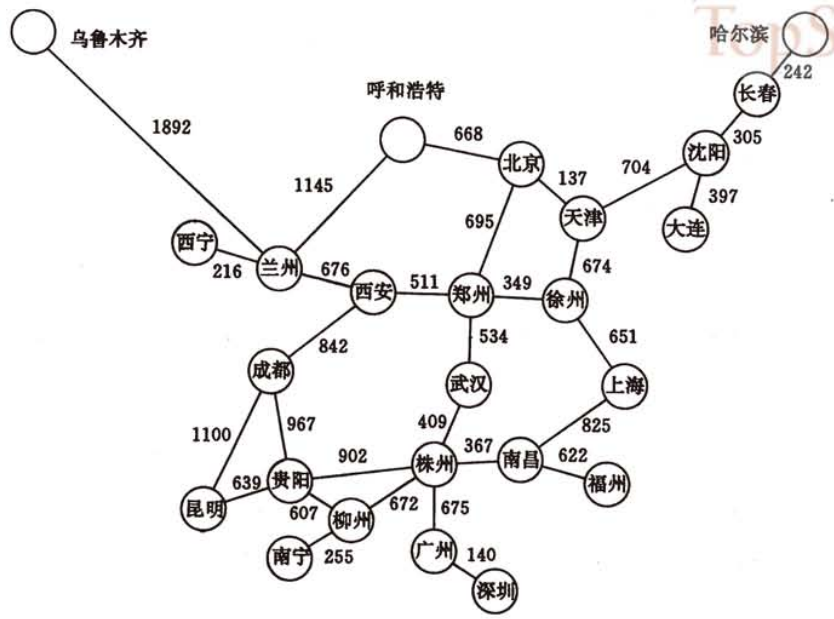

由此可以看出,对于经过站点最少,换乘最少这种问题,我们只需要对图进行广度遍历,即可获取相关结果。
我们重点分析下面的情况
权值最小(花费最少)
理论:从A到B,他们之间的路径要么是A->B,要么经过中间节点 A->..->B其最短路径也就是两条路径中最短的一条。
于是有:对于最短路径问题,我们只需要利用动态规划,在遍历中更新,逐步获取最短路径。
具体分析图如下
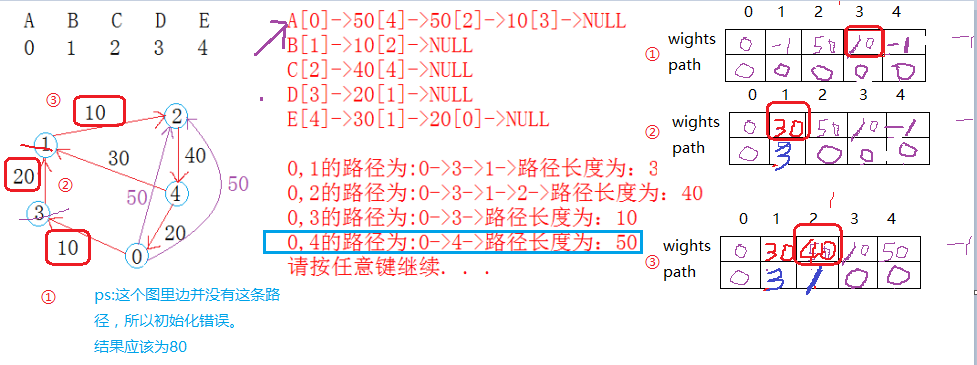
如上为寻找下标0-2结点过程的分析。对应代码
bool Dijkstra(const V&src,const V&dst,int &ret) { //如果只有顶点,那么返回true,ret =0; if (_size <= 1) { ret = 0; return true; } int cur = FindIndexV(src); int end = FindIndexV(dst); int beg = cur; size_t wights[6] = {}; int paths[6] = {}; for (size_t i = 0; i < _size; ++i) { wights[i] = -1; paths[i] = src; } wights[cur] = 0; paths[cur] = 0; Edge* pcur = _eList[cur]; //首次更新 while (pcur) { wights[pcur->_dst] = pcur->_wight; pcur = pcur->_next; } pcur = _eList[cur]; int visitedCount = 0; while (cur!=end)//未走到目的 { if (cur == beg) visitedCount++; //如果起点没有路径且目标不可达//或者回到起点了 if (pcur == NULL&&wights[dst] == -1||cur == beg&&visitedCount==2) { return false; } //获取最短边 Edge* minCur = _eList[cur]; Edge* pcur = _eList[cur]; while (pcur) { if (minCur->_wight > pcur->_wight) minCur = pcur; pcur = pcur->_next; } cur = minCur->_src; //根据局部最短更新路径 if (wights[cur] + minCur->_wight < wights[minCur->_dst]) { wights[minCur->_dst] = wights[cur] + minCur->_wight; paths[minCur->_dst] = minCur->_src; } cur = minCur->_dst; if (minCur->_dst == FindIndexV(dst)) { ret = wights[minCur->_dst]; return true; } } }
以下是整个图项目文件以及对应于最短路径的测试用例

#pragma once //邻接表实现图 #include<queue> #include<stack> #include"UnionFindset.h" #include<map> template<class V, class E> struct Edge { Edge(size_t dst,size_t src, const E&e) :_wight(e) ,_dst(dst) ,_src(src) , _next(NULL) {} E _wight; //权值,边比重 size_t _dst; //目的顶点下标 size_t _src; //源顶点下标 struct Edge<V, E>* _next; bool operator<(const Edge* &ed) { return _wight < ed->_wight; } }; template<class V,class E> class GraphList { typedef Edge<V, E> Edge; protected: V* _vArr; //顶点存储数组 size_t _size; Edge** _eList; //边存储指针数组 public: GraphList(const V* vArray, const size_t size) :_size(size) , _vArr(new V[size]) { //初始化顶点保存 for (size_t i = 0; i < size; ++i) { _vArr[i] = vArray[i]; } //初始化边结构 _eList = new Edge*[size]; memset(_eList, 0, sizeof(Edge*)*size); } int FindIndexV(const V& v) const { for (size_t i = 0; i < _size; ++i) { if (_vArr[i] == v) return i; } return -1; } //添加v1->v2的边 void AddEdge2(const V& v1, const V&v2, const E& e, bool IsDir = true) { int ind1 = FindIndexV(v1); int ind2 = FindIndexV(v2); Edge* cur = new Edge(ind2, ind1, e); cur->_next = _eList[ind1]; _eList[ind1] = cur; if (!IsDir) { Edge* cur = new Edge(ind1, ind2, e); cur->_next = _eList[ind2]; _eList[ind2] = cur; } } void Display()const { cout << "顶点集合" << endl; for (size_t i = 0; i < _size; ++i) { cout << _vArr[i] << " "; } cout << endl << "边表示" << endl; for (size_t i = 0; i < _size; ++i) { cout << "边["<<i << "]>>"; Edge* cur = _eList[i]; while (cur) { //cout << "[" << cur->_dst << "]" << cur->_wight << " "; //printf("[%d]:", cur->_dst, cur->_wight); cout << "[" << cur->_dst << "]" << cur->_wight << "--> "; cur = cur->_next; } cout <<"NULL"<< endl; } cout << endl; } //广度优先 void BSP(const V& root) { cout << "广度优先遍历:" << endl; bool *visited = new bool[_size](); queue<int> q; int index = FindIndexV(root); q.push(index); while (!q.empty()) { index = q.front(); if (visited[index] == false) { cout << _vArr[index]<<"-->"; } visited[index] = true; q.pop(); Edge* cur = _eList[index]; while (cur) { if (visited[cur->_dst] == false)//未访问过那么压入 { q.push(cur->_dst); } cur = cur->_next; } } cout << endl << endl; } //深度优先 void DSP(const V& root) { // cout << "深度优先遍历:" << endl; _DSP(root); cout << endl << endl; } void _DSP(const V& root) { static bool *visited = new bool[_size](); int index = FindIndexV(root); if (visited[index] == false) { cout << _vArr[index] << "-->"; visited[index] = true; } Edge* cur = _eList[index]; while (cur) { if (visited[cur->_dst] == false) _DSP(_vArr[cur->_dst]); cur = cur->_next; } if (cur == NULL) return; } //在所有边中获取最小权值的边 int FindMinEdgeIndex(vector<Edge*>&v) { int min = 0; for (size_t i = 1; i < v.size(); ++i) { if (v[i]->_wight < v[min]->_wight) min = i; } return min; } bool Kruskal(GraphList<V,E>& minTree) { vector<Edge*> ve; for (size_t i = 0; i < _size; ++i) { Edge* cur = _eList[i]; while (cur) { //只插入有效边 ve.push_back(cur); cur = cur->_next; } } UnionFindSet us(_size); while (!ve.empty()) { //找到最小权值边 int i = FindMinEdgeIndex(ve); //并查集插入相关结点 bool sure = us.Combine(ve[i]->_src, ve[i]->_dst); if (sure) //如果不是连通的,那么加入该边 { minTree.AddEdge2(_vArr[ve[i]->_src], _vArr[ve[i]->_dst], ve[i]->_wight); } ve.erase(ve.begin()+i); } return us.IsOnlyOneRoot(); } //在相关边中获取最小权值的边 int FindMinEdgeIndexByInGraph(vector<Edge*>&v,vector<int>& nodes) { if (nodes.size() == 0) return FindMinEdgeIndex(v); int min = -1; for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i) //遍历所有结点 { //如果 if (v[i]->_wight < v[min]->_wight) { bool inNodes = false; for (size_t j = 0; j < nodes.size(); ++i) { if (v[i]->_dst == nodes[j] || v[i]->_src == nodes[j]) { inNodes = true; break; } } if(inNodes) min = i; } } return min; } bool Prim(GraphList<V, E>& minTree) { vector<Edge*> ve; vector<int> inGraph; for (size_t i = 0; i < _size; ++i) { Edge* cur = _eList[i]; while (cur) { //只插入有效边 ve.push_back(cur); cur = cur->_next; } } UnionFindSet us(_size); while (!ve.empty()) { //找到最小权值边 int i = FindMinEdgeIndexByInGraph(ve,inGraph); if (us.IsOnlyOneRoot()) return true; else if (i == -1 && !us.IsOnlyOneRoot()) return false; //并查集插入相关结点 bool sure = us.Combine(ve[i]->_src, ve[i]->_dst); if (sure) //如果不是连通的,那么加入该边 { minTree.AddEdge2(_vArr[ve[i]->_src], _vArr[ve[i]->_dst], ve[i]->_wight); } ve.erase(ve.begin() + i); } return us.IsOnlyOneRoot(); } //size_t wights[6] = {}; //int paths[6] = {}; bool Dijkstra(const V&src,const V&dst,int &ret) { //如果只有顶点,那么返回true,ret =0; if (_size <= 1) { ret = 0; return true; } int cur = FindIndexV(src); int end = FindIndexV(dst); int beg = cur; size_t wights[6] = {}; int paths[6] = {}; for (size_t i = 0; i < _size; ++i) { wights[i] = -1; paths[i] = src; } wights[cur] = 0; paths[cur] = 0; Edge* pcur = _eList[cur]; //首次更新 while (pcur) { wights[pcur->_dst] = pcur->_wight; pcur = pcur->_next; } pcur = _eList[cur]; int visitedCount = 0; while (cur!=end)//未走到目的 { if (cur == beg) visitedCount++; //如果起点没有路径且目标不可达//或者回到起点了 if (pcur == NULL&&wights[dst] == -1||cur == beg&&visitedCount==2) { return false; } //获取最短边 Edge* minCur = _eList[cur]; Edge* pcur = _eList[cur]; while (pcur) { if (minCur->_wight > pcur->_wight) minCur = pcur; pcur = pcur->_next; } cur = minCur->_src; //根据局部最短更新路径 if (wights[cur] + minCur->_wight < wights[minCur->_dst]) { wights[minCur->_dst] = wights[cur] + minCur->_wight; paths[minCur->_dst] = minCur->_src; } cur = minCur->_dst; if (minCur->_dst == FindIndexV(dst)) { ret = wights[minCur->_dst]; return true; } } } ~GraphList() { if (_vArr) { delete[]_vArr; _vArr = NULL; } if (_eList) { for (size_t i = 0; i < _size;++i) { while (_eList[i] != NULL) { Edge* del = _eList[i]; _eList[i] = del->_next; delete del; del = NULL; } } } } }; void testD() { //int vArr1[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 }; //GraphList<int, int> gh1(vArr1, sizeof(vArr1) / sizeof(vArr1[0])); //gh1.AddEdge2(1, 2, 11); //gh1.AddEdge2(1, 3, 33); //gh1.AddEdge2(1, 5, 33); //gh1.AddEdge2(2, 3, 33); //gh1.AddEdge2(2, 6, 99); //gh1.AddEdge2(5, 3, 33); //gh1.AddEdge2(3, 4, 44); //gh1.AddEdge2(4, 5, 55); //gh1.AddEdge2(4, 7, 32); //gh1.AddEdge2(7, 8, 65); //gh1.AddEdge2(1, 9, 12); //gh1.AddEdge2(9, 7, 22); int vArr1[] = { 0,1,2,3,4,5}; GraphList<int, int> gh1(vArr1, sizeof(vArr1) / sizeof(vArr1[0])); gh1.AddEdge2(0, 3, 10); gh1.AddEdge2(0, 2, 50); gh1.AddEdge2(3, 1, 20); gh1.AddEdge2(1, 2, 10); gh1.AddEdge2(2, 4, 40); gh1.AddEdge2(4, 0, 20); gh1.AddEdge2(4, 1, 30); gh1.AddEdge2(5, 1, 10); gh1.Display(); gh1.BSP(1); gh1.DSP(1); GraphList<int, int> gMin(vArr1, sizeof(vArr1) / sizeof(vArr1[0])); GraphList<int, int> gMin1(vArr1, sizeof(vArr1) / sizeof(vArr1[0])); if (gh1.Kruskal(gMin)) { cout << "kruskal最小生成树:" << endl; gMin.Display(); } if (gh1.Prim(gMin1)) { cout << "prim最小生成树:" << endl; gMin1.Display(); } int ret = 0; if (gh1.Dijkstra(0, 1, ret)) { cout <<"gh1.Dijkstra(0, 1, ret)"<< ret << endl; } if (gh1.Dijkstra(0, 2, ret)) { cout << "gh1.Dijkstra(0, 2, ret)" << ret << endl; } if (gh1.Dijkstra(0, 3, ret)) { cout << "gh1.Dijkstra(0, 3, ret)" << ret << endl; } if (gh1.Dijkstra(0, 4, ret)) { cout << "gh1.Dijkstra(0, 4, ret)" << ret << endl; } if (gh1.Dijkstra(0, 5, ret)) { cout << "gh1.Dijkstra(0, 5, ret)" << ret << endl; } //char vArr2[] = { 'A','B','C','D','E','F' }; //GraphList<char, int> gh(vArr2, sizeof(vArr2) / sizeof(vArr2[0])); //gh.AddEdge2('A', 'B', 11); //gh.AddEdge2('B', 'C', 33); //gh.AddEdge2('C', 'D', 44); //gh.AddEdge2('D', 'E', 55); //gh.AddEdge2('E','F', 66); //gh.Display(); // gh.BSP('A'); }
参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/hxsyl/archive/2013/08/20/3270401.html
