mini batch 在优化算法中的作用:
深度学习的优化算法,说白了就是梯度下降。每次的参数更新有两种方式。
第一种,遍历全部数据集算一次损失函数,然后算函数对各个参数的梯度,更新梯度。
这种方法每更新一次参数都要把数据集里的所有样本都看一遍,计算量开销大,计算速度慢,不支持在线学习,这称为批梯度下降, Batch gradient descent。
另一种,每看一个数据就算一下损失函数,然后求梯度更新参数,这个称为随机梯度下降,stochastic gradient descent。这个方法速度比较快,但是收敛性能不太好,可能在最优点附近晃来晃去,hit不到最优点。两次参数的更新也有可能互相抵消掉,造成目标函数震荡的比较剧烈。
为了克服两种方法的缺点,现在一般采用的是一种 折中手段,mini-batch gradient decent,小批的梯度下降,这种方法把数据分为若干个批,按批来更新参数,这样,一个批中的一组数据共同决定了本次梯度的方向,下降起来就不容易跑偏,减少了随机性。另一方面因为批的样本数与整个数据集相比小了很多,计算量也不是很大。
epochs vs iteration vs batch size
-
一个
epoch是 整个数据集(所有训练样本) 只通过神经网络向前和向后传递一次。 -
batch size是单个批次中出现的训练示例的总数。Note: Batch size (batch大小 — 一个batch有多少样例) and number of batches (batch数量 — 有几个batch) are two different things.
-
iteration是完成一个历元所需的批数。Note: The number of batches is equal to number of iterations for one epoch.
有几个 batch 就需要几次 iteration 来完成一次 epoch
Why we use more than one Epoch?
I know it doesn’t make sense in the starting that — passing the entire dataset through a neural network is not enough. And we need to pass the full dataset multiple times to the same neural network. But keep in mind that we are using a limited dataset and to optimise the learning and the graph we are using Gradient Descent which is an iterative process. So, updating the weights with single pass or one epoch is not enough.
One epoch leads to underfitting of the curve in the graph (below).
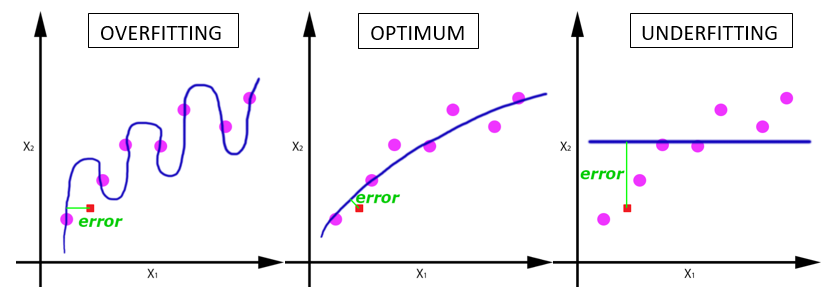
As the number of epochs increases, more number of times the weight are changed in the neural network and the curve goes from underfitting to optimal to overfitting curve.