参考:线程之线程同步
多个线程同时使用共享对象会造成很多问题,同步这些线程使得对共享对象的操作能够以正确的顺序执行是非常重要的。如果无需共享对象,就无需进行线程同步。大多数时候可以通过重新设计程序来移除共享状态,从而去掉复杂的同步构造。要尽可能避免在多个线程间使用单一对象。

原子操作
所谓原子操作是指不会被线程调度机制打断的操作;这种操作一旦开始,就一直运行到结束,中间不会有任何 context switch (切 [1] 换到另一个线程)。

1 using System; 2 using System.Threading; 3 4 namespace Chapter2.Recipe1 5 { 6 internal class Program 7 { 8 private static void Main(string[] args) 9 { 10 Console.WriteLine("Incorrect counter"); 11 12 var c = new Counter(); 13 14 var t1 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c));//3个线程共享同一对象c 15 var t2 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c)); 16 var t3 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c)); 17 t1.Start(); 18 t2.Start(); 19 t3.Start(); 20 t1.Join(); 21 t2.Join(); 22 t3.Join(); 23 24 Console.WriteLine("Total count: {0}", c.Count); //计算结果是不确定的 25 Console.WriteLine("--------------------------"); 26 27 Console.WriteLine("Correct counter"); 28 29 var c1 = new CounterNoLock(); 30 31 t1 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c1)); 32 t2 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c1)); 33 t3 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c1)); 34 t1.Start(); 35 t2.Start(); 36 t3.Start(); 37 t1.Join(); 38 t2.Join(); 39 t3.Join(); 40 41 Console.WriteLine("Total count: {0}", c1.Count); 42 Console.ReadKey(); 43 } 44 45 static void TestCounter(CounterBase c) 46 { 47 for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) 48 { 49 c.Increment(); 50 c.Decrement(); 51 } 52 } 53 54 class Counter : CounterBase 55 { 56 private int _count; 57 58 public int Count { get { return _count; } } 59 60 public override void Increment() 61 { 62 _count++; 63 } 64 65 public override void Decrement() 66 { 67 _count--; 68 } 69 } 70 71 class CounterNoLock : CounterBase 72 { 73 private int _count; 74 75 public int Count { get { return _count; } } 76 77 public override void Increment() 78 { 79 //Interlocked类提供了基本数学操作的原子方法 80 Interlocked.Increment(ref _count); 81 } 82 83 public override void Decrement() 84 { 85 Interlocked.Decrement(ref _count); 86 } 87 } 88 89 abstract class CounterBase 90 { 91 public abstract void Increment(); 92 93 public abstract void Decrement(); 94 } 95 } 96 }
使用Mutex类

1 using System; 2 using System.Threading; 3 4 namespace Chapter2.Recipe2 5 { 6 class Example 7 { 8 // Create a new Mutex. The creating thread does not own the mutex. 9 private static Mutex mut = new Mutex(); 10 private const int numIterations = 1; 11 private const int numThreads = 3; 12 13 static void Main() 14 { 15 // Create the threads that will use the protected resource. 16 for (int i = 0; i < numThreads; i++) 17 { 18 Thread newThread = new Thread(new ThreadStart(ThreadProc)); 19 newThread.Name = String.Format("Thread{0}", i + 1); 20 newThread.Start(); 21 } 22 23 // The main thread exits, but the application continues to 24 // run until all foreground threads have exited. 25 } 26 27 private static void ThreadProc() 28 { 29 for (int i = 0; i < numIterations; i++) 30 { 31 UseResource(); 32 } 33 } 34 35 // This method represents a resource that must be synchronized 36 // so that only one thread at a time can enter. 37 private static void UseResource() 38 { 39 // Wait until it is safe to enter. 40 Console.WriteLine("{0} is requesting the mutex", 41 Thread.CurrentThread.Name); 42 mut.WaitOne(); 43 44 Console.WriteLine("{0} has entered the protected area", 45 Thread.CurrentThread.Name); 46 47 // Place code to access non-reentrant resources here. 48 49 // Simulate some work. 50 Thread.Sleep(500); 51 52 Console.WriteLine("{0} is leaving the protected area", 53 Thread.CurrentThread.Name); 54 55 // Release the Mutex. 56 mut.ReleaseMutex(); 57 Console.WriteLine("{0} has released the mutex", 58 Thread.CurrentThread.Name); 59 } 60 } 61 }

1 using System; 2 using System.Threading; 3 4 namespace Chapter2.Recipe2 5 { 6 class Example 7 { 8 // Create a new Mutex. The creating thread does not own the mutex. 9 private static Mutex mut = new Mutex(); 10 private const int numIterations = 1; 11 private const int numThreads = 3; 12 13 static void Main() 14 { 15 Example ex = new Example(); 16 ex.StartThreads(); 17 } 18 19 private void StartThreads() 20 { 21 // Create the threads that will use the protected resource. 22 for (int i = 0; i < numThreads; i++) 23 { 24 Thread newThread = new Thread(new ThreadStart(ThreadProc)); 25 newThread.Name = String.Format("Thread{0}", i + 1); 26 newThread.Start(); 27 } 28 29 // The main thread returns to Main and exits, but the application continues to 30 // run until all foreground threads have exited. 31 } 32 33 private static void ThreadProc() 34 { 35 for (int i = 0; i < numIterations; i++) 36 { 37 UseResource(); 38 } 39 } 40 41 // This method represents a resource that must be synchronized 42 // so that only one thread at a time can enter. 43 private static void UseResource() 44 { 45 // Wait until it is safe to enter, and do not enter if the request times out. 46 Console.WriteLine("{0} is requesting the mutex", Thread.CurrentThread.Name); 47 //调用WaitOne()来获取互斥体,如果超时,WaitOne()返回false,线程没有获取到互斥体,没有访问资源的权限。 48 if (mut.WaitOne(1000)) //设置超时时间1s 49 { 50 Console.WriteLine("{0} has entered the protected area", 51 Thread.CurrentThread.Name); 52 53 // Place code to access non-reentrant resources here. 54 55 // Simulate some work. 56 Thread.Sleep(5000); 57 58 Console.WriteLine("{0} is leaving the protected area", 59 Thread.CurrentThread.Name); 60 61 // Release the Mutex. 62 mut.ReleaseMutex(); 63 Console.WriteLine("{0} has released the mutex", 64 Thread.CurrentThread.Name); 65 } 66 else 67 { 68 Console.WriteLine("{0} will not acquire the mutex", 69 Thread.CurrentThread.Name); 70 } 71 } 72 73 ~Example() 74 { 75 mut.Dispose(); 76 } 77 } 78 }
使用SemaphoreSlim类
SemaphoreSlim类是Semaphore类的轻量级版本,该类限制了同时访问同一个资源的线程数量。

1 using System; 2 using System.Threading; 3 4 namespace Chapter2.Recipe3 5 { 6 class Program 7 { 8 static void Main(string[] args) 9 { 10 for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) 11 { 12 string threadName = "Thread " + i; 13 int secondsToWait = 2 + 2 * i; 14 var t = new Thread(() => AccessDatabase(threadName, secondsToWait)); 15 t.Start(); 16 } 17 } 18 //指定并发线程数量为4 19 static SemaphoreSlim _semaphore = new SemaphoreSlim(4); 20 21 static void AccessDatabase(string name, int seconds) 22 { 23 Console.WriteLine("{0} waits to access a database", name); 24 _semaphore.Wait(); 25 Console.WriteLine("{0} was granted an access to a database", name); 26 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(seconds)); 27 Console.WriteLine("{0} is completed", name); 28 _semaphore.Release(); 29 30 } 31 } 32 }
使用AutoResetEvent类
AutoResetEvent类可以通知等待的线程有某事件发生。此类不能被继承。
- AutoResetEvent(bool initialState):构造函数,用一个指示是否将初始状态设置为终止的布尔值初始化该类的新实例。
- Reset ():将事件状态设置为非终止状态,导致线程阻止;如果该操作成功,则返回true;否则,返回false。
- Set ():将事件状态设置为有信号,从而允许一个或者多个等待线程继续执行;如果该操作成功,则返回true;否则,返回false。
- WaitOne(): 阻止当前线程,直到收到信号。如果收到信号,则返回true,如果当前实例永不发出信号,则WaitOne()永不返回。
- WaitOne(Int32) :阻止当前线程,直到收到信号,同时指定超时时间间隔。线程被阻止直到收到信号或者超时发生。如果收到信号则返回true,否则返回false。
- WaitOne(TimeSpan, Boolean) :阻止当前线程,直到当前实例收到信号,使用 TimeSpan 度量时间间隔并指定是否在等待之前退出同步域。
- WaitAll():等待全部信号。
AutoResetEvent.WaitOne()每次只允许一个线程进入,当某个线程得到信号后,AutoResetEvent会自动又将信号置为不发送状态,则其他调用WaitOne的线程只有继续等待,也就是说AutoResetEvent一次只唤醒一个线程;

1 using System; 2 using System.Threading; 3 4 namespace Chapter2.Recipe4 5 { 6 class WaitOne 7 { 8 static AutoResetEvent autoEvent = new AutoResetEvent(false); 9 10 static void Main() 11 { 12 Console.WriteLine("Main starting."); 13 14 ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem( 15 new WaitCallback(WorkMethod), autoEvent); 16 17 // Wait for work method to signal. 18 if (autoEvent.WaitOne(1000)) 19 { 20 Console.WriteLine("Work method signaled."); 21 } 22 else 23 { 24 Console.WriteLine("Timed out waiting for work " + 25 "method to signal."); 26 } 27 Console.WriteLine("Main ending."); 28 } 29 30 static void WorkMethod(object stateInfo) 31 { 32 Console.WriteLine("Work starting."); 33 34 // Simulate time spent working. 35 Thread.Sleep(new Random().Next(100, 2000)); 36 37 // Signal that work is finished. 38 Console.WriteLine("Work ending."); 39 ((AutoResetEvent)stateInfo).Set(); 40 } 41 } 42 }
使用ManualResetEventSlim类
AutoResetEvent类似一个旋转门,一次只允许一人通过。而ManualResetEventSlim类似人群通过大门,会一直保持大门打开直到手动调用Reset方法。
除非手工调用了ManualResetEvent.Reset()方法,则ManualResetEvent将一直保持有信号状态,ManualResetEvent也就可以同时唤醒多个线程继续执行。
使用CountDownEvent类
表示在计数变为零时处于有信号状态的同步基元。

1 using System; 2 using System.Threading; 3 4 namespace Chapter2.Recipe6 5 { 6 class Program 7 { 8 static void Main(string[] args) 9 { 10 Console.WriteLine("Starting two operations"); 11 var t1 = new Thread(() => PerformOperation("Operation 1 is completed", 4)); 12 var t2 = new Thread(() => PerformOperation("Operation 2 is completed", 8)); 13 t1.Start(); 14 t2.Start(); 15 _countdown.Wait(); 16 Console.WriteLine("Both operations have been completed."); 17 _countdown.Dispose(); 18 } 19 20 static CountdownEvent _countdown = new CountdownEvent(2); 21 22 static void PerformOperation(string message, int seconds) 23 { 24 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(seconds)); 25 Console.WriteLine(message); 26 // 向 System.Threading.CountdownEvent 注册信号,同时减小 System.Threading.CountdownEvent.CurrentCount 27 // 的值。 28 _countdown.Signal(); 29 } 30 } 31 }
使用Barrier类
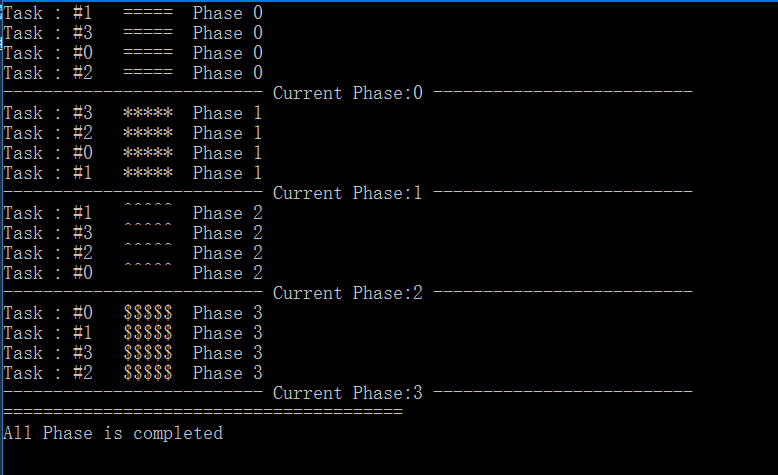
Barrier类用于组织多个线性及时在某一时刻碰面,其提供了一个回调函数,每次线程调用了SignalAndWait方法后,该回调函数会被执行。它像一个屏障,把所有任务的阶段隔离开来,当前阶段不完成,不会开始下一个阶段。

1 using System; 2 using System.Threading; 3 using System.Threading.Tasks; 4 5 namespace Sample5_1_barrier 6 { 7 class Program 8 { 9 private static void Phase0Doing(int TaskID) 10 { 11 Console.WriteLine("Task : #{0} ===== Phase 0", TaskID); 12 } 13 14 private static void Phase1Doing(int TaskID) 15 { 16 Console.WriteLine("Task : #{0} ***** Phase 1", TaskID); 17 } 18 19 private static void Phase2Doing(int TaskID) 20 { 21 Console.WriteLine("Task : #{0} ^^^^^ Phase 2", TaskID); 22 } 23 24 private static void Phase3Doing(int TaskID) 25 { 26 Console.WriteLine("Task : #{0} $$$$$ Phase 3", TaskID); 27 } 28 29 private static int _TaskNum = 4; 30 private static Task[] _Tasks; 31 private static Barrier _Barrier; 32 33 34 static void Main(string[] args) 35 { 36 _Tasks = new Task[_TaskNum]; 37 _Barrier = new Barrier(_TaskNum, (barrier) => 38 { 39 Console.WriteLine("-------------------------- Current Phase:{0} --------------------------", 40 _Barrier.CurrentPhaseNumber); 41 }); 42 43 for (int i = 0; i < _TaskNum; i++) 44 { 45 _Tasks[i] = Task.Factory.StartNew((num) => 46 { 47 var taskid = (int)num; 48 49 Phase0Doing(taskid); 50 _Barrier.SignalAndWait(); // 发出参与者已达到屏障并等待所有其他参与者也达到屏障 51 52 Phase1Doing(taskid); 53 _Barrier.SignalAndWait(); 54 55 Phase2Doing(taskid); 56 _Barrier.SignalAndWait(); 57 58 Phase3Doing(taskid); 59 _Barrier.SignalAndWait(); 60 61 }, i); 62 } 63 64 var finalTask = Task.Factory.ContinueWhenAll(_Tasks, (tasks) => 65 { 66 Task.WaitAll(_Tasks); 67 Console.WriteLine("========================================"); 68 Console.WriteLine("All Phase is completed"); 69 70 _Barrier.Dispose(); 71 }); 72 73 finalTask.Wait(); 74 75 Console.ReadLine(); 76 } 77 } 78 }
使用ReaderWriterLockSlim类
ReaderWriterLockSlim代表了一个管理资源访问的锁,允许多个线程同时读取,以及独占写。
