Spring框架概述
Spring大约包含了20个模块,这些模块组成了核心容器(Core Container)、数据访问/集成(Data Access/Integration)、Web、AOP(面向切面编程,Aspect Oriented Programming)、Instrumentation、消息处理(Messaging)和测试(Test),如下图:
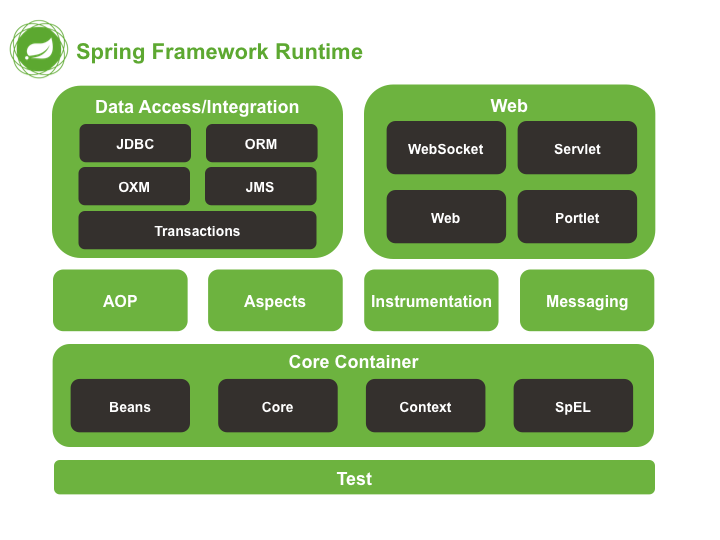
spring-test模块通过JUnit和TestNG组件支持单元测试和集成测试。它提供了一致性地加载和缓存Spring上下文,也提供了用于单独测试代码的模拟对象(mock object)。
spring 是是一个开源框架,是为了解决企业应用程序开发,功能如下
- 目的:解决企业应用开发的复杂性
- 功能:使用基本的JavaBean代替EJB,并提供了更多的企业应用功能
- 范围:任何Java应用
简单来说,Spring是一个轻量级的控制反转(IoC)和面向切面(AOP)的容器框架。
Spring的两大核心AOP与IOC,可以单独用于任何应用,包括与Struts等MVC框架与Hibernate等ORM框架的集成,目前很多公司所谓的轻量级开发就是用 Spring + Struts(2)+Hibernate。spring mvc类似于struts的一个MVC开框架,其实都是属于spring,spring mvc需要有spring的架包作为支撑才能跑起来
测试Spring项目
开发环境:
- jdk1.8
- IDEA 2017
- maven 3.5
项目结构如下:
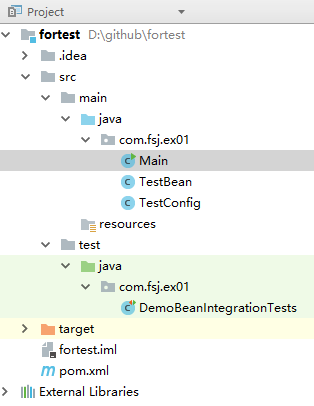
首先创建Maven项目,添加Spring Test支持:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>4.1.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
</dependency>
TestBean
package com.fsj.ex01;
public class TestBean {
private String content;
public TestBean(String content) {
super();
this.content = content;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
}
TestConfig
package com.fsj.ex01;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile;
@Configuration
public class TestConfig {
@Bean // 声明当前方法的返回值是一个bean
@Profile("dev")
public TestBean devTestBean() {
return new TestBean("from development profile");
}
@Bean
@Profile("prod")
public TestBean prodTestBean() {
return new TestBean("from production profile");
}
}
Main
package com.fsj.ex01;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext实例化Spring容器
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles("dev"); //激活profile
context.register(TestConfig.class);// 注册bean配置类。
context.refresh(); //刷新容器
TestBean demoBean = context.getBean(TestBean.class);
System.out.println(demoBean.getContent());
context.close();
}
}
DemoBeanIntegrationTest
package com.fsj.ex01;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ActiveProfiles;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) //表示该测试用例是运用junit4进行测试,也可以换成其他测试框架
@ContextConfiguration(classes = {TestConfig.class}) //此注解用来加载配置ApplicationContext
@ActiveProfiles("prod") //声明活动的profile
public class DemoBeanIntegrationTests {
@Autowired //注入bean
private TestBean testBean;
@Test //@Test标注在方法前,表示其是一个测试的方法 无需在其配置文件中额外设置属性.
public void prodBeanShouldInject(){
String expected = "from production profile";
String actual = testBean.getContent();
Assert.assertEquals(expected, actual);
}
@Before
public void beforeMethod(){
System.out.println("before all tests");
}
@After
public void afterMethod(){
System.out.println("after all tests.");
}
}
其中,RunWith注解表示JUnit将不会跑其内置的测试,而是运行所引用的类中的所有测试
http://junit.sourceforge.net/javadoc/org/junit/runner/RunWith.html
@Retention(value=RUNTIME)
@Target(value=TYPE)
@Inherited
public @interface RunWithWhen a class is annotated with @RunWith or extends a class annotated with @RunWith, JUnit will invoke the class it references to run the tests in that class instead of the runner built into JUnit.
启动Main运行项目。
启动DemoBeanIntegrationTests测试本项目。
测试Spring MVC项目
和Spring项目类似,项目完成后,在src/test/java下编写对应的测试用例。
不同的是,为了测试web项目,需要一些Servlet相关的模拟对象,比如:MockMVC / MockHttpServletRequest / MockHttpServletResponse / MockHttpSession等等。
TestControllerIntegration
package com.fsj.ex02;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.get;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.content;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.forwardedUrl;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.model;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.view;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.mock.web.MockHttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.mock.web.MockHttpSession;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import org.springframework.test.context.web.WebAppConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.setup.MockMvcBuilders;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import com.fsj.ex02.MyMvcConfig;
import com.fsj.ex02.service.DemoService;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = {MyMvcConfig.class})
@WebAppConfiguration("src/main/resources") //1 此注解指定web资源的位置,默认为src/main/webapp
public class TestControllerIntegrationTests {
private MockMvc mockMvc; //2 模拟MVC对象
@Autowired
private DemoService demoService;//3 在测试用例注入spring的bean
@Autowired
WebApplicationContext wac; //4 注入WebApplicationContext
@Autowired
MockHttpSession session; //5 注入模拟的http session
@Autowired
MockHttpServletRequest request; // 模拟request
@Before //7 测试开始前的初始化工作
public void setup() {
mockMvc =
MockMvcBuilders.webAppContextSetup(this.wac).build(); //2
}
@Test
public void testNormalController() throws Exception{
String exp_str = demoService.saySomething(); // expect str
mockMvc.perform(get("/normal")) //8 模拟GET /normal
.andExpect(status().isOk())//9 预期返回状态为200
.andExpect(view().name("page"))//10 预期view的名称
.andExpect(forwardedUrl("/WEB-INF/classes/views/page.jsp"))//11 预期页面转向的真正路径
.andExpect(model().attribute("msg", exp_str));//12 预期model里的值
}
@Test
public void testRestController() throws Exception{
mockMvc.perform(get("/testRest")) //13 GET
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().contentType("text/plain;charset=UTF-8"))//14
.andExpect(content().string(demoService.saySomething()));//15
}
}
完整项目在: https://github.com/shenjiefeng/spring-fortest
运行结果:
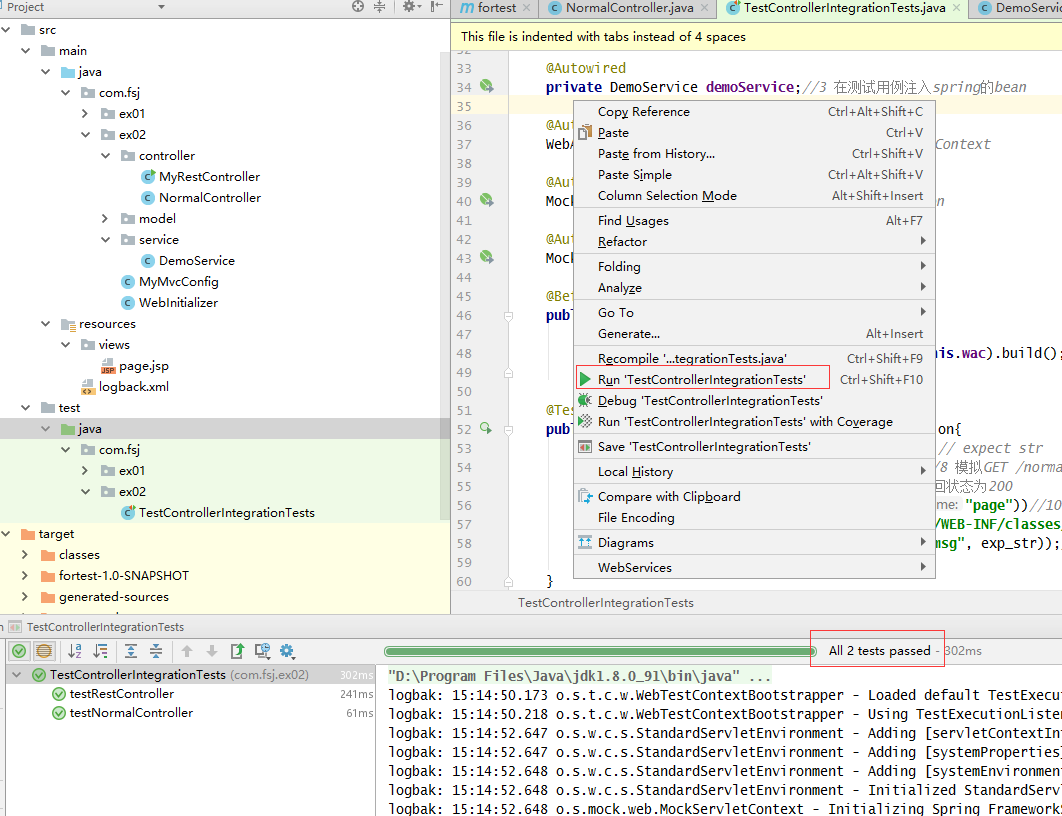
拾遗
使用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext实例化Spring容器
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext是在Spring 3.0中新增的。这个多功能的ApplicationContext实现即可接收@Configuration类作为输入,也可接收普通的@Component类,及使用JSR-330元数据注解的类。
当将@Configuration类作为输入时,@Configuration类本身被注册为一个bean定义,并且该类中所有声明的@Bean方法也被注册为bean定义。
当将@Component和JSR-330类作为输入时,它们被注册为bean定义,并且在需要的地方使用DI元数据,比如@Autowired或@Inject。
构造器实例化跟实例化一个ClassPathXmlApplicationContext时将Spring XML文件用作输入类似,在实例化一个AnnotationConfigApplicationContext时可以使用@Configuration类作为输入。这就允许Spring容器完全零XML配置:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
MyService myService = ctx.getBean(MyService.class);
myService.doStuff();
}
如上所述,AnnotationConfigApplicationContext不局限于仅仅使用@Configuration类。不论什么@Component或JSR-330注解的类都能够作为AnnotationConfigApplicationContext构造器的输入。比如:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MyServiceImpl.class, Dependency1.class, Dependency2.class);
MyService myService = ctx.getBean(MyService.class);
myService.doStuff();
}