At the children's day, the child came to Picks's house, and messed his house up. Picks was angry at him. A lot of important things were lost, in particular the favorite set of Picks.
Fortunately, Picks remembers something about his set S:
- its elements were distinct integers from 1 to limit;
- the value of
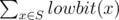 was
equal to sum; here lowbit(x) equals 2k where k is
the position of the first one in the binary representation of x. For example, lowbit(100102) = 102, lowbit(100012) = 12, lowbit(100002) = 100002 (binary
representation).
was
equal to sum; here lowbit(x) equals 2k where k is
the position of the first one in the binary representation of x. For example, lowbit(100102) = 102, lowbit(100012) = 12, lowbit(100002) = 100002 (binary
representation).
Can you help Picks and find any set S, that satisfies all the above conditions?
在儿童节这一天,我们的小朋友来到了Picks的家,把他家里弄得一团糟。Picks非常生气。非常多重要的东西都不见了,这当中包含了Picks最喜欢的集合。
幸运的是,Picks记得一些关于他的集合S的事情:1. 其元素是1至limit间的互异整数;
2. 全部lowbit(x)之和(x取遍S中的全部元素)等于sum,这里lowbit(x)等于2^k,k是x的二进制表示中第一个1的位置。比如(下面数字均为二进制表示),lowbit(10010)=10,lowbit(10001)=1,lowbit(10000)=10000。
你能帮助Picks找到一个符合上述条件的集合S吗?
Input
The first line contains two integers: sum, limit (1 ≤ sum, limit ≤ 105). 一行,两个整数,依次是sum和limit(1<=sum,limit<=10^5)。
Output
In the first line print an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105), denoting the size of S. Then print the elements of set S in any order. If there are multiple answers, print any of them.
If it's impossible to find a suitable set, print -1.
第一行输出n(1<=n<=10^5),为集合S的大小。然后在下一行以随意顺序输出S的全部元素。假设有多个符合要求的集合,输出随意一个就可以。
假设找不到这种集合,输出-1。
Sample test(s)
5 5
2 4 5
4 3
3 2 3 1
5 1
-1
In sample test 1: lowbit(4) = 4, lowbit(5) = 1, 4 + 1 = 5.
In sample test 2: lowbit(1) = 1, lowbit(2) = 2, lowbit(3) = 1, 1 + 2 + 1 = 4.
题解
lowbit就是x&(-x)。其余为模拟。
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int m,l,ans[100002];
struct shu {int w,b;} a[100002];
int lowbit(int x) {return x&(-x);}
bool kp(const shu &x,const shu &y)
{return x.b>y.b;}
void doit()
{
sort(a+1,a+l+1,kp);
for(int i=1;i<=l;i++)
{if(m>=a[i].b)
{m-=a[i].b;
ans[++ans[0]]=a[i].w;
}
}
if(m)printf("-1");
else
{
printf("%d
",ans[0]);
for(int i=1;i<=ans[0];i++)
printf("%d ",ans[i]);
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&m,&l);
for(int i=1;i<=l;i++)
{a[i].w=i; a[i].b=lowbit(i);}
doit();
return 0;
}