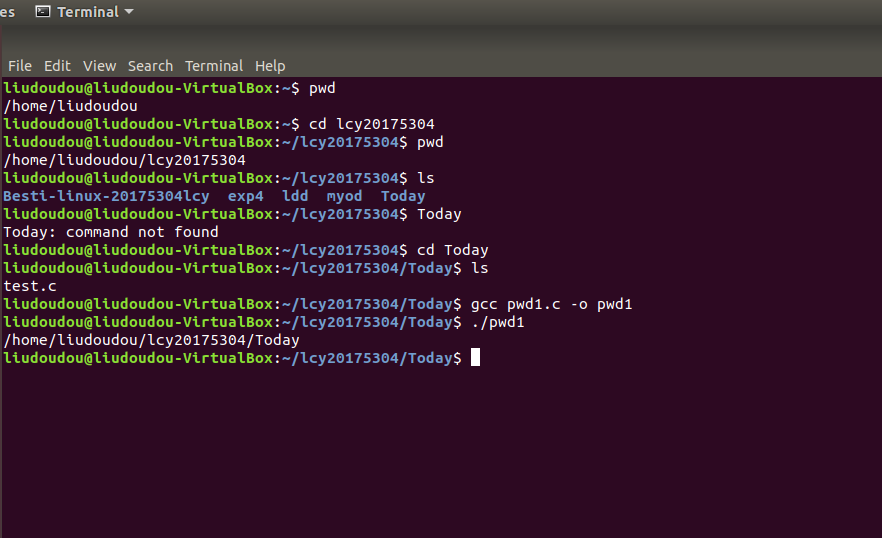
1.答:pwd是Print Working Directory的缩写,其功能是显示当前所在工作目录的全路径。主要用在当不确定当前所在位置时,通过pwd来查看当前目录的绝对路径。
pwd [选项]
参数:
-L:--logical,显示当前的路径,有连接文件时,直接显示连接文件的路径,(不加参数时默认此方式),
-p:--physical,显示当前的路径,有连接文件时,不使用连接路径,直接显示连接文件所指向的文件。当包含多层连接文件时,显示连接文件最终指向的文件。
--help:显示帮助信息。
--version:显示版本信息。
示例:
2.答:使用man -k dir | grep 2命令查看有哪些跟pwd相关的系统调用。发现有两个可能用到的函数 getcwd()和readdir
伪代码如下:
定义数组buf[MAXPATH];
调用getcwd(buf, MAXPATH);
输出返回值;
while(1)
{
读取"."和".."的信息
if("."的inode==".."的inode)
{
退出;
}
else
{
chdir("..");
while(dirent->inode!=前面"."的inode)
{
dirent=readdir();
}
dirent->name入栈;
}
}
for 栈顶->栈底
print 栈顶信息
3.答:
实验代码:
//pwd1.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define MAXPATH 50
int main()
{
char path[MAXPATH];
puts(getcwd(path, MAXPATH));
return 0;
}
//pwd2.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
DIR *dirptr=NULL;
struct dirent *current_dirent=NULL, *parent_dirent=NULL, *tmp_dirent=NULL;
int count=0;
ino_t current_inode;
char path[256][256];
while(1)
{
dirptr=opendir(".");
do
{
current_dirent=readdir(dirptr);
}while(strcmp(current_dirent->d_name, ".")!=0);
current_inode=current_dirent->d_ino;
closedir(dirptr);
dirptr=opendir(".");
do
{
parent_dirent=readdir(dirptr);
}while(strcmp(parent_dirent->d_name, "..")!=0);
closedir(dirptr);
if(((long)parent_dirent->d_ino)==((long)current_dirent->d_ino))
{
break;
}
else
{
chdir("..");
dirptr=opendir(".");
do
{
tmp_dirent=readdir(dirptr);
}while(tmp_dirent->d_ino!=current_inode);
closedir(dirptr);
count++;
strcpy(path[count], tmp_dirent->d_name);
}
}
int i;
for(i=count;i>0;i--)
{
printf("/%s", path[i]);
}
printf("
");
return 0;
}
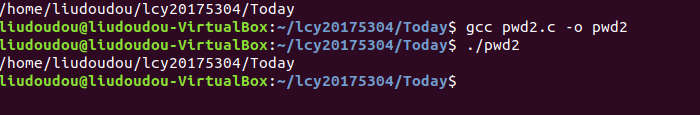
4.测试