在Android中一共提供了5种数据存储方式,分别为:
(1)Files:通过FileInputStream和FileOutputStream对文件进行操作。
(2)Shared Preferences:常用来存储键值对形式的数据,对系统配置信息进行保存。
(3)Content Providers:数据共享,用于应用程序之间数据的访问。
(4)SQLite:Android自带的轻量级关系型数据库,支持SQL语言,用来存储大量的数据,并且能够对数据进行使用、更新、维护等操作。
(5)Network:通过网络来存储和获取数据。
本文主要介绍第一种方式,通过文件存储数据。
在Android中,所创建的用于保存数据的文件可以位于两个位置:设备本身的存储空间中,或是外接的存储设备中(SD卡)。无论存储在哪个位置,在默认的情况下,该文件都是不能够供不同的应用程序共享的。
下面分别介绍如何将文件存储在设备本身的存储空间中以及外接的存储设备中。
1.将文件存储在设备本身的存储空间中
在Android中,可以使用Context类提供的以下两个方法来实现文件存储。
(1)public abstract FileInputStream openFileInput(String name);//打开文件输入流
(2)public abstract FileOutStream openFileOutput(String name, int mode);//打开文件输出流
其中,openFileInput()方法表示打开文件输入流,用于从文件中读取数据;openFileOutput()方法表示打开文件输出流,用于向文件中写入内容。
此外,openFileOutput()方法中的第二个参数mode用于指定文件的操作模式,其可选值有以下4种:
(1)Context.MODE_APPEND;//内容追加模式。在该模式下,系统会检查文件是否存在,如果存在,则将内容追加到文件的末尾,如果文件不存在,则创建该文件并写入内容。
(2)Context.MODE_PRIVATE;//默认操作模式。在该模式下,文件作为私有数据,只能被该应用程序本身访问。并且,在该模式下,写入的内容会覆盖原文件的内容。
(3)Context.MODE_WORLD_READABLE;//可读模式。在该模式下,别的应用程序可以读取该文件内容。
(4)Context.MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE;//可写模式。在该模式下,别的应用程序可以将内容写入该文件。
存储和读写文件
package com.leaf.android; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import android.R.bool; import android.R.integer; import android.content.Context; import android.os.Environment; public class FileService { private Context context; public FileService(Context context) { this.context = context; } public FileService() { } public String getFileFromSdcard(String filename) { FileInputStream inputStream = null; // 缓存的流,与磁盘无关,不需要关闭 ByteArrayOutputStream outputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); File file = new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory(), filename); if (Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED.equals(Environment .getExternalStorageState())) { try { inputStream = new FileInputStream(file); int len = 0; byte[] data = new byte[1024]; try { while ((len = inputStream.read(data)) != -1) { outputStream.write(data, 0, len); } } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (inputStream != null) { try { inputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } } return new String(outputStream.toByteArray()); } /** * * @param filename 文件的名称 * @param content 文件的内容 * @return */ public boolean saveContentToSdcard(String filename, String content) { boolean flag = false; FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null; // 获得sdcard所在的路径 File file = new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory(), filename); // 判断sdcard是否可用 if (Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED.equals(Environment .getExternalStorageState())) { try { fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file); fileOutputStream.write(content.getBytes()); flag = true; } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (fileOutputStream != null) { try { fileOutputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } } return flag; } }
单元测试类:
package com.leaf.android; import android.content.Context; import android.test.AndroidTestCase; import android.util.Log; public class MyTest extends AndroidTestCase { private final String TAG = "MyTest"; public MyTest() { // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public void saveFile() { Context context = getContext(); FileService fileService = new FileService(context); boolean flag = fileService.saveContentToSdcard("hello.txt", "你好"); Log.i(TAG, "-->>" + flag); } public void readFile() { Context context = getContext(); FileService fileService = new FileService(context); String msgString = fileService.getFileFromSdcard("hello.txt"); Log.i(TAG, "-->>" + msgString); } }
2.将文件存储在外接存储设备中(SD卡)
通常,手机的内存是极其有限的,更普遍的做法是将文件存储到SD卡中。
将文件存储在外接存储设备中的方法和将文件存储在设备本身的存储空间中的方法类似,唯一的区别是每次向SD卡中存储以及从SD卡中读取文件时,都需要检测SD卡的状态。
2.1检测SD卡的状态
在Android中,检测SD卡的状态需要使用到Environment类。通过使用该类的getExternalStorageState()方法可以获得外接存储设备(SD卡)的状态。其中,外接存储设备的状态有九种,具体如图2所示。
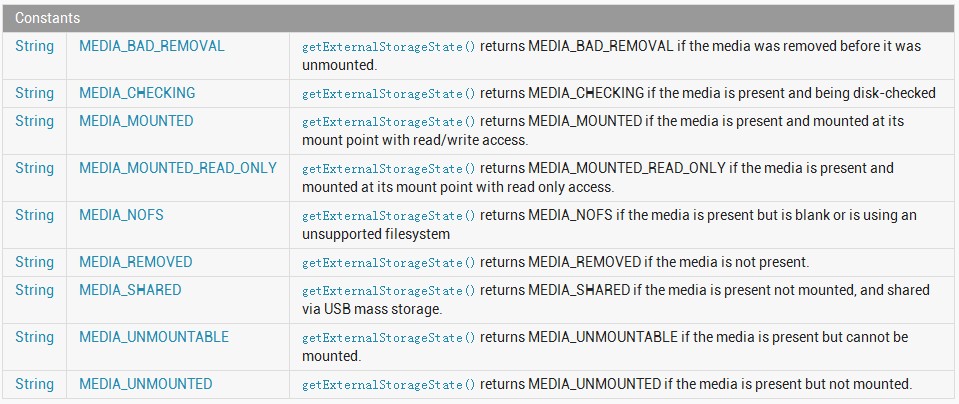
图2 外接存储设备状态
其中,MEDIA_MOUNTED表示外接存储设备可读可写。
参考文献:http://www.cnblogs.com/menlsh/archive/2013/04/02/2997084.html