目录
@
定义与使用
-
Go中struct与C中的struct非常相似,并且Go没有class,没有构造函数
-
使用
type <name> strct{}结构定义,名称遵循可见性规则(大写开头表示public,非大写开头为private) -
指向指向自身的指针类型成员,(类似this??)
-
可以使用字面值对结构进行初始化
-
允许直接通过指针来读写结构成员(用'.')
type person struct{
Name string
Age int
}
func main(){
//go语言习惯上定义的时候用取地址符,这样作为指针使用会很方便,而且是不是指针都可以直接用'.'来取值
a := &person{}
a.Name = "joe"
a.Age = 19
/*字面值对结构进行初始化
a := &person{
Name: "joe",
Age: 19,
}
*/
a.Name = "ok"
fmt.Println(a)
A(a)
fmt.Println(a)
B(a)
fmt.Println(a)
}
func A(per person){
//值拷贝
per.Age = 13
fmt.Println("A",per)
}
func B(per *person){
//引用拷贝
per.Age = 13
fmt.Println("A",per)
}
/*
> Output:
{joe 19}
A {joe 13}
{joe 19}
A &{joe 13}
{joe 13}
*/
匿名结构
- 支持匿名结构,可用作成员或者定义成员变量
- 匿名结构也可以用于map的值
func main(){
//匿名结构
a := &struct {
Name string
Age int
}{
Name : "joe",
Age : 19,
}
fmt.Println(a)
}
type person struct {
Name string
Age int
Contact struct{
Phone, City string
}
}
func main(){
a := person{Name:"joe", Age: 19}
a.Contact.Phone = "1234565875"
a.Contact.City = "beijing"
fmt.Println(a)
}
匿名字段
- 支持匿名字段,本质上是定义了以某个类型名为名称的字段
- 嵌入结构作为匿名字段看起来像继承,但是不是继承
- 可以使用匿名字段指针
type person struct {
string
int
}
func main(){
//字段顺序一定要一致
a := person{"joe", 19}
b := a
fmt.Println(a)
fmt.Println(b)
}
结构之间的赋值与比较
- 相同类型成员可以进行直接拷贝赋值
- 支持==和!=比较运算符,只能在相同类型之间比较,但不支持>或<
type person struct {
Name string
Age int
}
type person1 struct {
Name string
Age int
}
func main(){
a := person{Name:"joe", Age:19}
b := person1{Name:"joe", Age:19}
fmt.Println(a)
fmt.Println(b)
fmt.Println( b == a)
}
/*
> Output:
command-line-arguments
# command-line-arguments
.hello2.go:18:15: invalid operation: b == a (**mismatched types person1 and person)**
*/
嵌入结构
- Go语言里面没有class和继承
- 嵌入的结构名称就当做类型名称
type human struct{
Sex int
}
type teacher struct {
human
Name string
Age int
}
type student struct{
human
Name string
Age int
}
func main(){
a := teacher{Name:"joe", Age:19,human: human{Sex:0}}
b := student{Name:"joe", Age:19,human: human{Sex:1}}
a.Name ="joe2"
a.Age = 13
a.Sex =100
fmt.Println(a, b)
}
/*
> Output:
command-line-arguments
{{100} joe2 13} {{1} joe 19}
*/
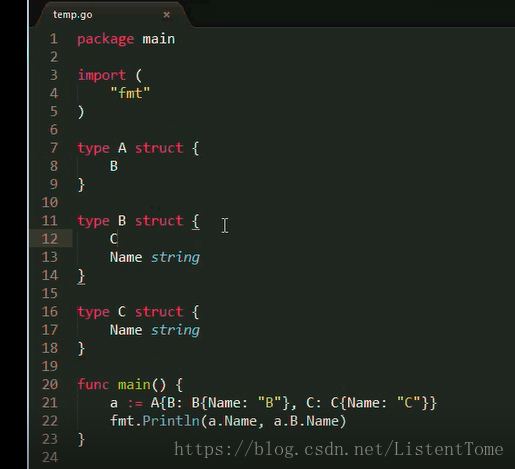
当使用匿名字段或者嵌入字段的时候,如果内层和外层结构具有相同的字段名称,该怎么办呢?
type A struct {
B
C
Name string
}
type B struct {
Name string
}
type C struct {
Name string
}
func main(){
a := A{Name:"A",B: B{Name:"B"},C: C{Name:"C"}}
fmt.Println(a.Name, a.B.Name,a.C.Name)
}
/*
> Output:
command-line-arguments
A B C
*/
在当前层次结构中找不到的话,就更深层次的结构找
图片中,C如果放在结构A里面,那么a.Name就会产生歧义