算法描述:散列表是一种在时间和空间上做出权衡的查找算法。使用查找算法分为两步。第一步是通过散列函数将被查找的键转化未数组的一个索引。理想情况下,不同的键都能转为不同的索引值。当然,这只是理想情况,所以我们需要面对两个或多个键都被散列到相同索引值的情况。因此,散列查找的第二部就是处理碰撞冲突的过程。
一个比较令人满意的散列函数能够均匀并独立地将所有键散布于0到M-1之间。
一、基于拉链法的散列表
算法图示:
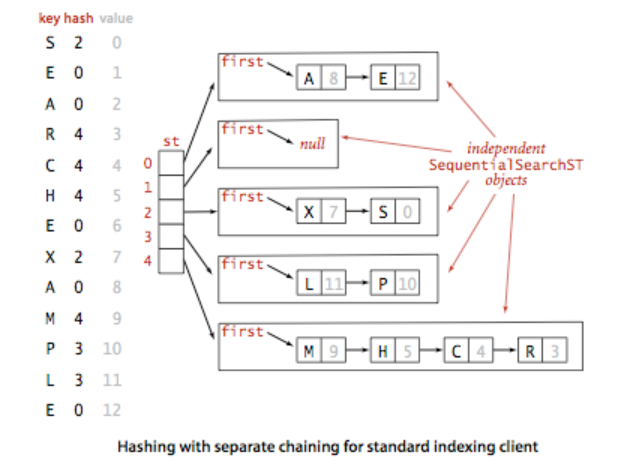
拉链散列表算法的本质是将哈希值相同的键保存在一个普通链表中,当我们需要调整数组长度的时候,需要将所有键在新的数组中重新散列。
代码示例:
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class SeparateChainingHashSymbolTable<Key, Value> { private int initCapacity; // 初始散列数组的长度 private int size; // 键值总数 private int len; // 散列数组的长度 private SequentialSearchSymbolTable<Key, Value>[] st; // 散列数组 public SeparateChainingHashSymbolTable(int len) { this.len = len; this.initCapacity = len; st = (SequentialSearchSymbolTable<Key, Value>[]) new SequentialSearchSymbolTable[len]; for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { st[i] = new SequentialSearchSymbolTable<>(); } } public Value get(Key key) { int h = hash(key); return st[h].get(key); } public boolean contains(Key key) { return get(key) != null; } public void put(Key key, Value val) { // 当包含元素的数量大于散列数组长度10倍时,扩展容量 if (size > 10 * len) { resize(2 * len); } int h = hash(key); if (!contains(key)) { size++; } st[h].put(key, val); } public void delete(Key key) { int h = hash(key); if (contains(key)) { st[h].delete(key); size--; } if (size > initCapacity && size <= 2 * len) { resize(len / 2); } } public Iterable<Key> keys() { List<Key> keys = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { for (Key key : st[i].keys()) { keys.add(key); } } return keys; } private void resize(int capacity) { SeparateChainingHashSymbolTable<Key, Value> nst = new SeparateChainingHashSymbolTable<>(capacity); // 遍历原先散列表中保存的元素,并重新散列进新的散列表 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { for (Key key : st[i].keys()) { nst.put(key, st[i].get(key)); } } this.size = nst.size; this.len = nst.len; this.st = nst.st; } /** * 散列算法 * * @param key * @return */ private int hash(Key key) { return (key.hashCode() & 0x7fffffff) % len; } }
二、基于探测法的散列表
这种算法在处理碰撞的时候并非将所有相同哈希键的对象保存在一条链表中而是沿数组向后查找并插入到一个空槽中。
算法图示:
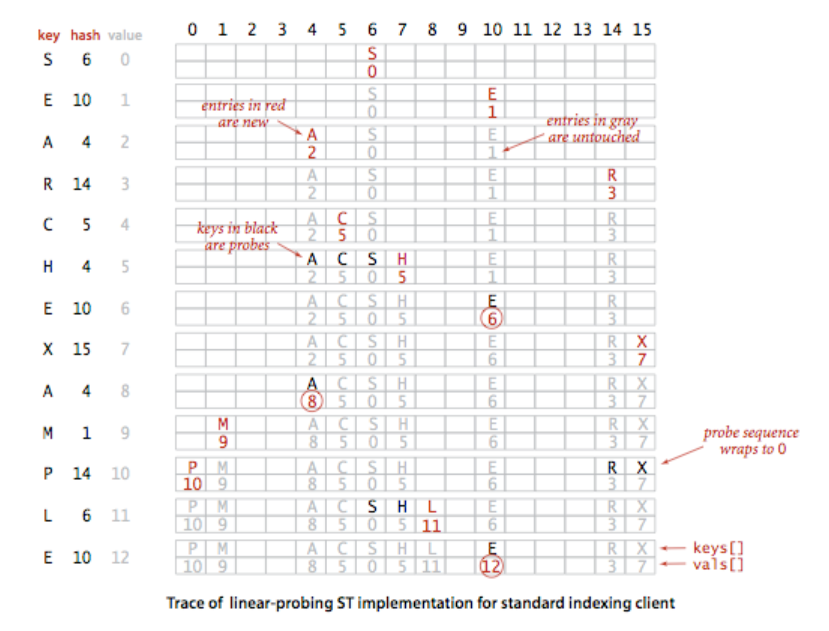
探测法哈希算法的一个比较重要的特征是:当我们需要删除一个键的时候,不能仅仅将数组中对应的位置设置未null,因为这会使得在此位置之后的元素无法被查找。因此,我们需要将簇中被删除的键的右侧的所有键重新散列计算并插入散列表。这个过程会比较复杂。
代码示例:
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class LinearProbingHashSymbolTable<Key, Value> { private int size; private int len; private Key[] keys; private Value[] vals; public LinearProbingHashSymbolTable(int capacity) { len = capacity; size = 0; keys = (Key[]) new Object[capacity]; vals = (Value[]) new Object[capacity]; } public void put(Key key, Value val) { // 始终保证元素数量只占数组长度的50% if (size > len / 2) { resize(2 * len); } // 线性碰撞检测 int h; for (h = hash(key); keys[h] != null; h = (h + 1) % len) { if (key.equals(keys[h])) { vals[h] = val; return; } } keys[h] = key; vals[h] = val; size++; } public Value get(Key key) { for (int h = hash(key); keys[h] != null; h = (h + 1) % len) { if (key.equals(keys[h])) { return vals[h]; } } return null; } public boolean contains(Key key) { return get(key) != null; } public void delete(Key key) { if (!contains(key)) { return; } int h = hash(key); while (!keys[h++].equals(key)) { h = h % len; } keys[h] = null; vals[h] = null; // 由于在删除了一个键之后可能造成查询的不连续,因此需要对一些键重新散列 h = (h + 1) % len; while (keys[h] != null) { // 在被删除的键后至空键前的所有键重新散列保存 Key nkey = keys[h]; Value nval = vals[h]; keys[h] = null; vals[h] = null; put(nkey, nval); h = (h + 1) % len; // 每次循环size--的目的时抵消put中的size++ size--; } size--; // 当包含的元素数量小于数组长度的12.5%时,按照1/2的比例收缩数组 if (size > 0 && size < len / 8) { resize(len / 2); } } public Iterable<Key> keys() { List<Key> keyList = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { if (keys[i] != null) { keyList.add(keys[i]); } } return keyList; } private int hash(Key key) { return (key.hashCode() & 0x7fffffff) % len; } private void resize(int capacity) { LinearProbingHashSymbolTable<Key, Value> nst = new LinearProbingHashSymbolTable<>(capacity); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { if (keys[i] != null) { nst.put(keys[i], vals[i]); } } this.size = nst.size; this.keys = nst.keys; this.vals = nst.vals; } }
相关链接: