转自:https://blog.csdn.net/u012679707/article/details/80793916
【深度学习】AlexNet原理解析及实现
Alex提出的alexnet网络结构模型,在imagenet2012图像分类challenge上赢得了冠军。
要研究CNN类型DL网络模型在图像分类上的应用,就逃不开研究alexnet,这是CNN在图像分类上的经典模型。
一、Alexnet结构
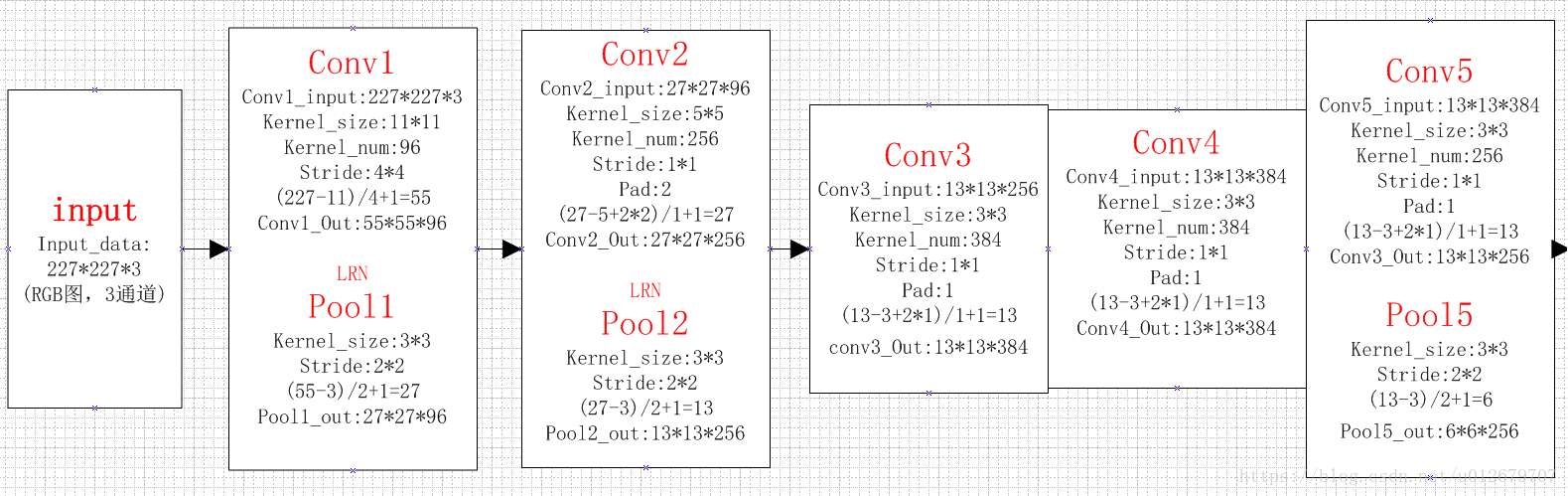
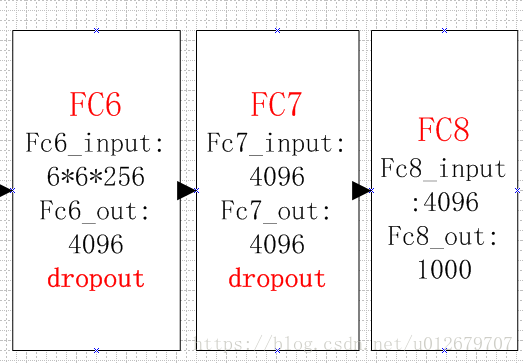
alexNet为8层深度网络,其中5层卷积层和3层全连接层,不计LRN层和池化层。如下图所示:
图 Alexnet结构
详解各层训练参数的计算:
前五层:卷积层
后三层:全连接层
整体计算图:
二、结构分析
AlexNet每层的超参数如下图所示,其中输入尺寸为227*227,第一个卷积使用较大的核尺寸11*11,步长为4,有96个卷积核;紧接着一层LRN层;然后是最大池化层,核为3*3,步长为2。这之后的卷积层的核尺寸都比较小,5*5或3*3,并且步长为1,即扫描全图所有像素;而最大池化层依然为3*3,步长为2.
我们可以发现,前几个卷积层的计算量很大,但参数量很小,只占Alexnet总参数的很小一部分。这就是卷积层的优点!通过较小的参数量来提取有效的特征。
要注意,论文中指出,如果去掉任何一个卷积层,都会使网络的分类性能大幅下降。
三、AlexNet的新技术点
AlexNet的新技术点(即大牛论文的contribution),如下:
(1)ReLU作为激活函数。
ReLU为非饱和函数,论文中验证其效果在较深的网络超过了SIgmoid,成功解决了SIgmoid在网络较深时的梯度弥散问题。
(2)Dropout避免模型过拟合
在训练时使用Dropout随机忽略一部分神经元,以避免模型过拟合。在alexnet的最后几个全连接层中使用了Dropout。
(3)重叠的最大池化
之前的CNN中普遍使用平均池化,而Alexnet全部使用最大池化,避免平均池化的模糊化效果。并且,池化的步长小于核尺寸,这样使得池化层的输出之间会有重叠和覆盖,提升了特征的丰富性。
(4)提出LRN层
提出LRN层,对局部神经元的活动创建竞争机制,使得响应较大的值变得相对更大,并抑制其他反馈较小的神经元,增强了模型的泛化能力。
(5)GPU加速
(6)数据增强
随机从256*256的原始图像中截取224*224大小的区域(以及水平翻转的镜像),相当于增强了(256-224)*(256-224)*2=2048倍的数据量。使用了数据增强后,减轻过拟合,提升泛化能力。避免因为原始数据量的大小使得参数众多的CNN陷入过拟合中。
四、AlexNet的搭建
利用tensorflow实现ALexNet,环境为:win10+anaconda+python3+CPU(本人仅利用CPU,未使用GPU加速,所以最终模型训练速度较慢)。
利用tensorboard可视化ALexNet结构为:
(1)首先看一下卷积层的搭建:带有LRN和池化层的卷积层
- with tf.name_scope('conv1') as scope:
- """
- images:227*227*3
- kernel: 11*11 *64
- stride:4*4
- padding:name
-
- #通过with tf.name_scope('conv1') as scope可以将scope内生成的Variable自动命名为conv1/xxx
- 便于区分不同卷积层的组建
-
- input: images[227*227*3]
- middle: conv1[55*55*96]
- output: pool1 [27*27*96]
-
- """
- kernel=tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([11,11,3,96],
- dtype=tf.float32,stddev=0.1),name="weights")
- conv=tf.nn.conv2d(images,kernel,[1,4,4,1],padding='SAME')
- biases=tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[96], dtype=tf.float32),
- trainable=True,name="biases")
- bias=tf.nn.bias_add(conv,biases) # w*x+b
- conv1=tf.nn.relu(bias,name=scope) # reLu
- print_architecture(conv1)
- parameters +=[kernel,biases]
-
- #添加LRN层和max_pool层
- """
- LRN会让前馈、反馈的速度大大降低(下降1/3),但最终效果不明显,所以只有ALEXNET用LRN,其他模型都放弃了
- """
- lrn1=tf.nn.lrn(conv1,depth_radius=4,bias=1,alpha=0.001/9,beta=0.75,name="lrn1")
- pool1=tf.nn.max_pool(lrn1,ksize=[1,3,3,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],
- padding="VALID",name="pool1")
- print_architecture(pool1)
- with tf.name_scope('conv3') as scope:
- """
- input: pool2[13*13*256]
- output: conv3 [13*13*384]
-
- """
- kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 256, 384],
- dtype=tf.float32, stddev=0.1), name="weights")
- conv = tf.nn.conv2d(pool2, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
- biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[384], dtype=tf.float32),
- trainable=True, name="biases")
- bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases) # w*x+b
- conv3 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope) # reLu
- parameters += [kernel, biases]
- print_architecture(conv3)
(3)全连接层的搭建
- #全连接层6
- with tf.name_scope('fc6') as scope:
- """
- input:pool5 [6*6*256]
- output:fc6 [4096]
- """
- kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([6*6*256,4096],
- dtype=tf.float32, stddev=0.1), name="weights")
- biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[4096], dtype=tf.float32),
- trainable=True, name="biases")
- # 输入数据变换
- flat = tf.reshape(pool5, [-1, 6*6*256] ) # 整形成m*n,列n为7*7*64
- # 进行全连接操作
- fc = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(flat, kernel) + biases,name='fc6')
- # 防止过拟合 nn.dropout
- fc6 = tf.nn.dropout(fc, keep_prob)
- parameters += [kernel, biases]
- print_architecture(fc6)
(4)训练测试:
因未下载ImageNet数据集(太大),只是简单的测试了一下alexnet的性能。使用的是随机生成的图片来作为训练数据。
- def time_compute(session,target,info_string):
- num_step_burn_in=10 #预热轮数,头几轮迭代有显存加载、cache命中等问题可以因此跳过
- total_duration=0.0 #总时间
- total_duration_squared=0.0
- for i in range(num_batch+num_step_burn_in):
- start_time=time.time()
- _ = session.run(target)
- duration= time.time() -start_time
- if i>= num_step_burn_in:
- if i%10==0: #每迭代10次显示一次duration
- print("%s: step %d,duration=%.5f "% (datetime.now(),i-num_step_burn_in,duration))
- total_duration += duration
- total_duration_squared += duration *duration
- time_mean=total_duration /num_batch
- time_variance=total_duration_squared / num_batch - time_mean*time_mean
- time_stddev=math.sqrt(time_variance)
- #迭代完成,输出
- print("%s: %s across %d steps,%.3f +/- %.3f sec per batch "%
- (datetime.now(),info_string,num_batch,time_mean,time_stddev))
-
- def main():
- with tf.Graph().as_default():
- """仅使用随机图片数据 测试前馈和反馈计算的耗时"""
- image_size =224
- images=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([batch_size,image_size,image_size,3],
- dtype=tf.float32,stddev=0.1 ) )
- fc8,parameters=inference(images)
-
- init=tf.global_variables_initializer()
- sess=tf.Session()
- sess.run(init)
-
- """
- AlexNet forward 计算的测评
- 传入的target:fc8(即最后一层的输出)
- 优化目标:loss
- 使用tf.gradients求相对于loss的所有模型参数的梯度
-
-
- AlexNet Backward 计算的测评
- target:grad
-
- """
- time_compute(sess,target=fc8,info_string="Forward")
-
- obj=tf.nn.l2_loss(fc8)
- grad=tf.gradients(obj,parameters)
- time_compute(sess,grad,"Forward-backward")
(5)测试结果:
结构输出 (注意,32是我设置的batch_size,即训练的图片数量为32)
前向预测用时:
后向训练(学习)用时:
可以看出后向训练用时比前向推理用时长很多,大概是5倍。
【附录】完整代码
- # -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
- """
- @author:Lisa
- @file:alexNet.py
- @function:实现Alexnet深度模型
- @note:learn from《tensorflow实战》
- @time:2018/6/24 0024下午 5:26
- """
-
- import tensorflow as tf
- import time
- import math
- from datetime import datetime
-
- batch_size=32
- num_batch=100
- keep_prob=0.5
-
-
- def print_architecture(t):
- """print the architecture information of the network,include name and size"""
- print(t.op.name," ",t.get_shape().as_list())
-
-
- def inference(images):
- """ 构建网络 :5个conv+3个FC"""
- parameters=[] #储存参数
-
- with tf.name_scope('conv1') as scope:
- """
- images:227*227*3
- kernel: 11*11 *64
- stride:4*4
- padding:name
-
- #通过with tf.name_scope('conv1') as scope可以将scope内生成的Variable自动命名为conv1/xxx
- 便于区分不同卷积层的组建
-
- input: images[227*227*3]
- middle: conv1[55*55*96]
- output: pool1 [27*27*96]
-
- """
- kernel=tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([11,11,3,96],
- dtype=tf.float32,stddev=0.1),name="weights")
- conv=tf.nn.conv2d(images,kernel,[1,4,4,1],padding='SAME')
- biases=tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[96], dtype=tf.float32),
- trainable=True,name="biases")
- bias=tf.nn.bias_add(conv,biases) # w*x+b
- conv1=tf.nn.relu(bias,name=scope) # reLu
- print_architecture(conv1)
- parameters +=[kernel,biases]
-
- #添加LRN层和max_pool层
- """
- LRN会让前馈、反馈的速度大大降低(下降1/3),但最终效果不明显,所以只有ALEXNET用LRN,其他模型都放弃了
- """
- lrn1=tf.nn.lrn(conv1,depth_radius=4,bias=1,alpha=0.001/9,beta=0.75,name="lrn1")
- pool1=tf.nn.max_pool(lrn1,ksize=[1,3,3,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],
- padding="VALID",name="pool1")
- print_architecture(pool1)
-
- with tf.name_scope('conv2') as scope:
- """
- input: pool1[27*27*96]
- middle: conv2[27*27*256]
- output: pool2 [13*13*256]
-
- """
- kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, 96, 256],
- dtype=tf.float32, stddev=0.1), name="weights")
- conv = tf.nn.conv2d(pool1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
- biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[256], dtype=tf.float32),
- trainable=True, name="biases")
- bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases) # w*x+b
- conv2 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope) # reLu
- parameters += [kernel, biases]
- # 添加LRN层和max_pool层
- """
- LRN会让前馈、反馈的速度大大降低(下降1/3),但最终效果不明显,所以只有ALEXNET用LRN,其他模型都放弃了
- """
- lrn2 = tf.nn.lrn(conv2, depth_radius=4, bias=1, alpha=0.001 / 9, beta=0.75, name="lrn1")
- pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(lrn2, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
- padding="VALID", name="pool2")
- print_architecture(pool2)
-
- with tf.name_scope('conv3') as scope:
- """
- input: pool2[13*13*256]
- output: conv3 [13*13*384]
-
- """
- kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 256, 384],
- dtype=tf.float32, stddev=0.1), name="weights")
- conv = tf.nn.conv2d(pool2, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
- biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[384], dtype=tf.float32),
- trainable=True, name="biases")
- bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases) # w*x+b
- conv3 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope) # reLu
- parameters += [kernel, biases]
- print_architecture(conv3)
-
- with tf.name_scope('conv4') as scope:
- """
- input: conv3[13*13*384]
- output: conv4 [13*13*384]
-
- """
- kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 384, 384],
- dtype=tf.float32, stddev=0.1), name="weights")
- conv = tf.nn.conv2d(conv3, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
- biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[384], dtype=tf.float32),
- trainable=True, name="biases")
- bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases) # w*x+b
- conv4 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope) # reLu
- parameters += [kernel, biases]
- print_architecture(conv4)
-
- with tf.name_scope('conv5') as scope:
- """
- input: conv4[13*13*384]
- output: conv5 [6*6*256]
-
- """
- kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 384, 256],
- dtype=tf.float32, stddev=0.1), name="weights")
- conv = tf.nn.conv2d(conv4, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
- biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[256], dtype=tf.float32),
- trainable=True, name="biases")
- bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases) # w*x+b
- conv5 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope) # reLu
- pool5 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv5, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
- padding="VALID", name="pool5")
- parameters += [kernel, biases]
- print_architecture(pool5)
-
- #全连接层6
- with tf.name_scope('fc6') as scope:
- """
- input:pool5 [6*6*256]
- output:fc6 [4096]
- """
- kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([6*6*256,4096],
- dtype=tf.float32, stddev=0.1), name="weights")
- biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[4096], dtype=tf.float32),
- trainable=True, name="biases")
- # 输入数据变换
- flat = tf.reshape(pool5, [-1, 6*6*256] ) # 整形成m*n,列n为7*7*64
- # 进行全连接操作
- fc = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(flat, kernel) + biases,name='fc6')
- # 防止过拟合 nn.dropout
- fc6 = tf.nn.dropout(fc, keep_prob)
- parameters += [kernel, biases]
- print_architecture(fc6)
-
- # 全连接层7
- with tf.name_scope('fc7') as scope:
- """
- input:fc6 [4096]
- output:fc7 [4096]
- """
- kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([4096, 4096],
- dtype=tf.float32, stddev=0.1), name="weights")
- biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[4096], dtype=tf.float32),
- trainable=True, name="biases")
- # 进行全连接操作
- fc = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(fc6, kernel) + biases, name='fc7')
- # 防止过拟合 nn.dropout
- fc7 = tf.nn.dropout(fc, keep_prob)
- parameters += [kernel, biases]
- print_architecture(fc7)
-
- # 全连接层8
- with tf.name_scope('fc8') as scope:
- """
- input:fc7 [4096]
- output:fc8 [1000]
- """
- kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([4096, 1000],
- dtype=tf.float32, stddev=0.1), name="weights")
- biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[1000], dtype=tf.float32),
- trainable=True, name="biases")
- # 进行全连接操作
- fc8 = tf.nn.xw_plus_b(fc7, kernel, biases, name='fc8')
- parameters += [kernel, biases]
- print_architecture(fc8)
-
- return fc8,parameters
-
- def time_compute(session,target,info_string):
- num_step_burn_in=10 #预热轮数,头几轮迭代有显存加载、cache命中等问题可以因此跳过
- total_duration=0.0 #总时间
- total_duration_squared=0.0
- for i in range(num_batch+num_step_burn_in):
- start_time=time.time()
- _ = session.run(target)
- duration= time.time() -start_time
- if i>= num_step_burn_in:
- if i%10==0: #每迭代10次显示一次duration
- print("%s: step %d,duration=%.5f "% (datetime.now(),i-num_step_burn_in,duration))
- total_duration += duration
- total_duration_squared += duration *duration
- time_mean=total_duration /num_batch
- time_variance=total_duration_squared / num_batch - time_mean*time_mean
- time_stddev=math.sqrt(time_variance)
- #迭代完成,输出
- print("%s: %s across %d steps,%.3f +/- %.3f sec per batch "%
- (datetime.now(),info_string,num_batch,time_mean,time_stddev))
-
- def main():
- with tf.Graph().as_default():
- """仅使用随机图片数据 测试前馈和反馈计算的耗时"""
- image_size =224
- images=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([batch_size,image_size,image_size,3],
- dtype=tf.float32,stddev=0.1 ) )
- fc8,parameters=inference(images)
-
- init=tf.global_variables_initializer()
- sess=tf.Session()
- sess.run(init)
-
- """
- AlexNet forward 计算的测评
- 传入的target:fc8(即最后一层的输出)
- 优化目标:loss
- 使用tf.gradients求相对于loss的所有模型参数的梯度
-
-
- AlexNet Backward 计算的测评
- target:grad
-
- """
- time_compute(sess,target=fc8,info_string="Forward")
-
- obj=tf.nn.l2_loss(fc8)
- grad=tf.gradients(obj,parameters)
- time_compute(sess,grad,"Forward-backward")
-
-
- if __name__=="__main__":
- main()
-
参考:
《tensorflow实战》黄文坚(本文内容及代码大多源于此书,感谢!)
大牛论文《ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks 》Alex Krizhevsky 等