集合(collection)提供了一种结构化组织任意对象的方式,从广义的概念上讲,数组、枚举和结构等组合都是集合的一种表现,其内部的元素组织方式也都与集合的定义非常类似。但在C#中,集合这一专有名词特指System.Collections命名空间下的各种子类,数组、枚举和结构都不是System.Collections命名空间的成员。NET类库提供了丰富的集合数据类型,其种类之繁多甚至使许多人看得眼都花了,这些集合对象都具有各自的专用场合。不管怎么说,更多的选择也就意味着更高的灵活性,但同时也意味着更高的复杂性。因此,对集合各个类型的用途和使用条件具有适度的了解是完全必要的。
.NET集合定义
从.NET 的角度看,所谓的集合可以定义为一种对象,这种对象实现一个或者多个System.Collections.ICollection、 System.Collections.IDictionary和System.Collections.IList接口。这一定义把 System.Collections名称空间中的“内置”集合划分成了三种类别:
* 有序集合:仅仅实现ICollection接口的集合,在通常情况下,其数据项目的插入顺序控制着从集合中取出对象的的顺序。 System.Collections.Stack和 System.Collections.Queue类都是ICollection集合的典型例子。
* 索引集合:实现Ilist的集合,其内容能经由从零开始的数字检索取出,就象数组一样。System.Collections.ArrayList对象是索引集合的一个例子。
* 键式集合:实现 IDictionary 接口的集合,其中包含了能被某些类型的键值检索的项目。IDictionary集合的内容通常按键值方式存储,可以用枚举的方式排序检索。 System.Collections.HashTable类实现了IDictionary 接口。
正如你看到的那样,给定集合的功能在很大程度上受到特定接口或其实现接口的控制。如果你对面向对象编程缺乏了解,那么你可能对上面说的这些话感到难以理解。不过你至少应该知道,以接口这种方式构造对象的功能不但造就了具有整套类似方法的对象族,而且还能让这些对象在必要的情况下可以当作同类,以OOP (面向对象编程)的术语来说,这就是大名鼎鼎的多态性技术。
System.Collections概述:
System.Collections 名称空间包含了在你的应用程序中可以用到的6种内建通用集合。另一些更为专业化的集合则归属于 System.Collections.Specialized,在某些情况下你会发现这些专用集合也是非常有用的。加上一些异常(exception)类,这些专业化集合在功能上和内建集合是类似的。
System.Collections.Generic概述:
System.Collections.Generic 命名空间包含定义泛型集合的接口和类,泛型集合允许用户创建强类型集合,它能提供比非泛型强类型集合更好的类型安全性和性能。
System.Collections命名空间下常用的集合类有:
- ArrayList
- Queue
- Stack
- BitArray
- Hashtable
- SortedList
System.Collections.Generic命名空间下常用的集合类有:
- List<T>
- Queue<T>
- Stack<T>
- LinkedList<T>
- HashSet<T>
- Dictionary<TKey, TValue>
- SortedDictionary<TKey, TValue>
- SortedList<TKey, TValue>
- Lookup<TKey, TElement>
System.Collections命名空间中的接口
System.Collections命名空间中的几个接口提供了基本的集合功能
- IEnumerable:公开枚举数,该枚举数支持在非泛型集合上进行简单迭代。简单的说就是实现 IEnumerable接口后可以支持用Microsoft Visual Basic 的 foreach 语义来进行迭代集合中的项。它只有一个方法 GetEnumerator(),该方法可以返回一个IEnumerator枚举数,通过它可以遍历集合。基本上所有的集合类都实现了这个方法。
- ICollection:定义所有非泛型集合的大小、枚举数和同步方法。ICollection 接口是 System.Collections 命名空间中类的基接口,所有集合类都实现了这个接口。ICollection 接口继承于IEnumerable,扩展了IEnumerable。 IDictionary 和 IList 则是扩展 ICollection 的更为专用的接口。如果 IDictionary 接口和 IList 接口都不能满足所需集合的要求,则从 ICollection 接口派生新集合类以提高灵活性。
- IList:表示可排序并且可以按照索引访问对象的非泛型集合(列表)。IList 是 ICollection 接口的子代,并且是所有非泛型列表的基接口,IList 实现有三种类别:只读、固定大小和可变大小。无法修改只读 IList。固定大小的 IList 不允许添加或移除元素,但允许修改现有元素。可变大小的 IList 允许添加、移除和修改元素。
- IDictionary:IDictionary 可以称为字典、映射或者散列表,表示键/值对的非通用集合,即类似于IList但提供了可通过键值(而不是索引)访问的项列表。IDictionary是Icollection接口的子代,是键/值对的的集合的基接口,IDictionary 实现有三种类别:只读、固定大小、可变大小。无法修改只读 IDictionary 对象。固定大小的 IDictionary 对象不允许添加或移除元素,但允许修改现有元素。可变大小的 IDictionary 对象允许添加、移除和修改元素。C# 语言中的 foreach 语句需要集合中每个元素的类型。由于 IDictionary 对象的每个元素都是一个键/值对,因此元素类型既不是键的类型,也不是值的类型,而是 DictionaryEntry 类型。
System.Collections命名空间中常用集合类的使用
ArrayList
实现的接口:IList、ICollections、IEnumerable
使用大小可按需动态增加的数组实现 IList 接口(大小可变的数组列表),ArrayList 的默认初始容量为 0。随着元素添加到 ArrayList 中,容量会根据需要通过重新分配自动增加。ArrayList 接受 空引用作为有效值并且允许重复的元素。
using System; using System.Collections; public class SamplesArrayList { public static void Main() { // Creates and initializes a new ArrayList. ArrayList myAL = new ArrayList(); myAL.Add("Hello"); myAL.Add("World"); myAL.Add("!"); // Displays the properties and values of the ArrayList. Console.WriteLine( "myAL" ); Console.WriteLine( " Count: {0}", myAL.Count ); Console.WriteLine( " Capacity: {0}", myAL.Capacity ); Console.Write( " Values:" ); PrintValues( myAL ); } public static void PrintValues( IEnumerable myList ) { foreach ( Object obj in myList ) Console.Write( " {0}", obj ); Console.WriteLine(); } } /* This code produces output similar to the following: myAL Count: 3 Capacity: f Values: Hello World ! */
Queue
实现的接口:ICollection、IEnumerable
Queue是队列,先进先出的访问元素。可以调用Queque对象的GetEnumerator()方法,得到IEnumerator对象,来遍历队列中的各个元素。Queue 的默认初始容量为 32。向 Queue 添加元素时,将通过重新分配来根据需要自动增大容量。可通过调用 TrimToSize 来减少容量。Queue 接受 空引用(在 Visual Basic 中为 Nothing) 作为有效值并且允许重复的元素。
using System; using System.Collections; public class SamplesQueue { public static void Main() { // Creates and initializes a new Queue. Queue myQ = new Queue(); myQ.Enqueue("Hello"); myQ.Enqueue("World"); myQ.Enqueue("!"); // Displays the properties and values of the Queue. Console.WriteLine( "myQ" ); Console.WriteLine( " Count: {0}", myQ.Count ); Console.Write( " Values:" ); PrintValues( myQ ); } public static void PrintValues( IEnumerable myCollection ) { foreach ( Object obj in myCollection ) Console.Write( " {0}", obj ); Console.WriteLine(); } } /* This code produces the following output. T myQ Count: 3 Values: Hello World ! */
Stack
实现的接口:ICollection、IEnumerable
Stack是堆栈,先进后出的访问各个元素。
using System; using System.Collections; public class SamplesStack { public static void Main() { // Creates and initializes a new Stack. Stack myStack = new Stack(); myStack.Push("Hello"); myStack.Push("World"); myStack.Push("!"); // Displays the properties and values of the Stack. Console.WriteLine( "myStack" ); Console.WriteLine( " Count: {0}", myStack.Count ); Console.Write( " Values:" ); PrintValues( myStack ); } public static void PrintValues( IEnumerable myCollection ) { foreach ( Object obj in myCollection ) Console.Write( " {0}", obj ); Console.WriteLine(); } } /* This code produces the following output. myStack Count: 3 Values: ! World Hello */
HashTable
实现接口:IDictionary、ICollection、IEnumerable
表示键/值对的集合,这些键/值对根据键的哈希代码进行组织。可以想HasTable中自由添加和删除元素,有些像ArrayList,但没有那么大的性能开销。
每个元素都是一个存储在 DictionaryEntry 对象中的键/值对。键不能为 空引用(在 Visual Basic 中为 Nothing),但值可以。
当把某个元素添加到 Hashtable 时,将根据键的哈希代码将该元素放入存储桶中。该键的后续查找将使用键的哈希代码只在一个特定存储桶中搜索,这将大大减少为查找一个元素所需的键比较的次数。
using System; using System.Collections; class Example { public static void Main() { // Create a new hash table. // Hashtable openWith = new Hashtable(); // Add some elements to the hash table. There are no // duplicate keys, but some of the values are duplicates. openWith.Add("txt", "notepad.exe"); openWith.Add("bmp", "paint.exe"); openWith.Add("dib", "paint.exe"); openWith.Add("rtf", "wordpad.exe"); // The Add method throws an exception if the new key is // already in the hash table. try { openWith.Add("txt", "winword.exe"); } catch { Console.WriteLine("An element with Key = "txt" already exists."); } // The Item property is the default property, so you // can omit its name when accessing elements. Console.WriteLine("For key = "rtf", value = {0}.", openWith["rtf"]); // The default Item property can be used to change the value // associated with a key. openWith["rtf"] = "winword.exe"; Console.WriteLine("For key = "rtf", value = {0}.", openWith["rtf"]); // If a key does not exist, setting the default Item property // for that key adds a new key/value pair. openWith["doc"] = "winword.exe"; // The default Item property throws an exception if the requested // key is not in the hash table. try { Console.WriteLine("For key = "tif", value = {0}.", openWith["tif"]); } catch { Console.WriteLine("Key = "tif" is not found."); } // ContainsKey can be used to test keys before inserting // them. if (!openWith.ContainsKey("ht")) { openWith.Add("ht", "hypertrm.exe"); Console.WriteLine("Value added for key = "ht": {0}", openWith["ht"]); } // When you use foreach to enumerate hash table elements, // the elements are retrieved as KeyValuePair objects. Console.WriteLine(); foreach( DictionaryEntry de in openWith ) { Console.WriteLine("Key = {0}, Value = {1}", de.Key, de.Value); } // To get the values alone, use the Values property. ICollection valueColl = openWith.Values; // The elements of the ValueCollection are strongly typed // with the type that was specified for hash table values. Console.WriteLine(); foreach( string s in valueColl ) { Console.WriteLine("Value = {0}", s); } // To get the keys alone, use the Keys property. ICollection keyColl = openWith.Keys; // The elements of the KeyCollection are strongly typed // with the type that was specified for hash table keys. Console.WriteLine(); foreach( string s in keyColl ) { Console.WriteLine("Key = {0}", s); } // Use the Remove method to remove a key/value pair. Console.WriteLine(" Remove("doc")"); openWith.Remove("doc"); if (!openWith.ContainsKey("doc")) { Console.WriteLine("Key "doc" is not found."); } } } /* This code example produces the following output: An element with Key = "txt" already exists. For key = "rtf", value = wordpad.exe. For key = "rtf", value = winword.exe. For key = "tif", value = . Value added for key = "ht": hypertrm.exe Key = dib, Value = paint.exe Key = txt, Value = notepad.exe Key = ht, Value = hypertrm.exe Key = bmp, Value = paint.exe Key = rtf, Value = winword.exe Key = doc, Value = winword.exe Value = paint.exe Value = notepad.exe Value = hypertrm.exe Value = paint.exe Value = winword.exe Value = winword.exe Key = dib Key = txt Key = ht Key = bmp Key = rtf Key = doc Remove("doc") Key "doc" is not found. */
ArrayList list = new ArrayList(); list.Add(new Class1()); ((Class1)list[0]).function();
list[0]无法直接调用Class1的方法function,因为在ArrayList中的各项都是System.Object类型的,但是可以通过数据类型转换实现(多态性)。
我们如何避免数据类型的转换呢?解决办法是使用强类型的集合类。

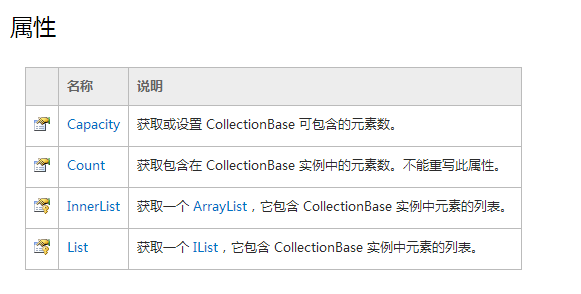
CollectionBase还提供了两个受保护的属性List、InnerList,《c#入门经典》中的描述是:我们可以使用List和InnerList,其中通过List属性可以调用IList接口访问项目,InnerList则是用于存储项目的ArrayList对象。
示例:
有三个类Animal、Cow、Chicken,其中Cow、Chicken是抽象类Animal的派生类,我们要创建一个Animal类的集合类Animals来存储Animal对象。
Animal
public abstract class Animal { protected string name; public string Name { get { return name; } set { name = value; } } public Animal() { name = "The animal with no name"; } public Animal(string newName) { name = newName; } public void Feed() { Console.WriteLine("{0} has been fed.", name); } }
Cow
public class Cow : Animal { public void Milk() { Console.WriteLine("{0} has been milked.", name); } public Cow(string newName) : base(newName) { } }
Chicken
public class Chicken : Animal { public void LayEgg() { Console.WriteLine("{0} has laid an egg.", name); } public Chicken(string newName) : base(newName) { } }
存储Animal对象的集合类可以定义如下:
public class Animals : CollectionBase { public void Add(Animal newAnimal) { List.Add(newAnimal); } public void Remove(Animal newAnimal) { List.Remove(newAnimal); } }
前面说过CollectionBase实现的接口只提供了IList的Clear()及RemoveAt()方法和ICollection的Count属性,想要实现向集合中添加及删除对象就需要自己来实现。我们实现了Add方法及Remove方法。
我们通过CollectionBase的List属性使用了IList接口中用于访问项的标准Add方法,并且限制了只能处理Animal类或派生于Animal的类,而前面介绍的ArrayList的实现代码可以处理任何对象不是强类型的。
这样我们就可以向Animals集合类中添加对象
Animals animalCollection = new Animals(); animalCollection.Add(new Cow("Jack")); animalCollection.Add(new Chicken("Vera"));
但是我们不能使用下面的代码
animalCollection[0].Feed();
要通过索引的方式来访问项,就需要使用索引符。
索引符(索引器)
索引符是一个特殊类型的属性,可以把它添加到一个类中,以提供类似于数组的访问。
定义索引器的方式与定义属性有些类似,其一般形式如下:
[修饰符] 数据类型 this[索引类型 index] { get{//获得属性的代码} set{ //设置属性的代码} }
数据类型是将要存取的集合元素的类型。索引类型表示该索引器使用哪一种类型的索引来存取集合元素,可以是整数,可以是字符串。this表示操作本对象deep集合成员,可以简单理解成索引器的名字,因此索引器不能具有用户定义的名称。
示例:
class Z { //可容纳100个整数的整数集 private long[] arr = new long[100]; //声明索引器 public long this[int index] { get { //检查索引范围 if (index < 0 || index >= 100) { return 0; } else { return arr[index]; } } set { if (!(index < 0 || index >= 100)) { arr[index] = value; } } }
这样我们就可以像访问数组一样访问类型Z中的arr数组
Z z=new z(); z[0]=100; z[1]=101; Console.WriteLine(z[0]);
C#中并不将索引器的类型限制为整数。例如,可以对索引器使用字符串。通过搜索集合内的字符串并返回相应的值,可以实现此类的索引器。由于访问器可以被重载,字符串和整数版本可以共存。
class DayCollection { string[] days={"Sun","Mon","Tues","Wed","Thurs","Fri","Sat"}; private int GetDay(string testDay) { int i=0; foreach(string day in days) { if(day==testDay) return i; i++; } return -1; } public int this[string day] { get{return (GetDay(day))} } } static void Main(string[] args) { DayCollection week=new DayCollection(); Console.WriteLine("Fri:{0}",week["Fri"]); Console.WriteLine("ABC:{0}",week["ABC"]); }
结果:Fri:5
ABC:-1
接口中的索引器
在接口中也可以声明索引器,接口索引器与类索引器的区别有两个:一是接口索引器不使用修饰符;二是接口索引器只包含访问器get或set,没有实现语句。访问器的用途是指示索引器是可读写、只读还是只写的,如果是可读写的,访问器get或set均不能省略;如果只读的,省略set访问器;如果是只写的,省略get访问器。
public interface IAddress { string this[int index]{get;set;} string Address{get;set;} string Answer(); }
通过索引访问自定义集合类
我们修改Animals类如下
public class Animals : CollectionBase { public void Add(Animal newAnimal) { List.Add(newAnimal); } public void Remove(Animal newAnimal) { List.Remove(newAnimal); } public Animal this[int animalIndex] { get { return (Animal)List[animalIndex]; } set { List[animalIndex] = value; } } }
这样 Animais animaiCollection=new Animails(); 就可以通过animaiCollection[0]这种方式来访问了。